The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2012;22(12)
Content
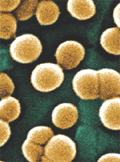
[The altered role of coagulase-negative staphylococci]
[Coagulase-negative staphylococci are differentiated from the more virulent Staphylococcus aureus by their inability to produce coagulase enzyme. Currently, more than 40 recognized species of coagulasenegative staphylococci are known. The great majority of these bacteria are normal inhabitants of the human skin and mucous membranes. Therefore, it is very difficult to distinguish isolates that are of clinical significance. Recently, coagulase-negative staphylococci have been increasingly detected to cause clinically significant infections. This is due in most cases to the increasing use of medical devices inserted or implanted in the human body. This overview discusses the various infections caused by these microbes, as well as their pathogenesis, epidemiology, and management.]
[The importance of balneotherapy in osteology]
[The authors overview the role of hydroand balneotherapy in osteology. As Hungary is very rich in thermal-mineral water, this kind of therapy has a great importance in the rehabilitation of locomotor diseases. In the past years, an increasing number of data have been published about the immunomodulatory, metabolic and analgesic role of hydro- and balneotherapy. Although balneotherapy’s mechanism of action has not been clarified yet, a number of reviews and metaanalyses have found that hydro- and balneotherapy have a beneficial effect on locomotor diseases. The majority of these articles - many of them written by Hungarian authors - discusses the treatment of arthrosis. Furthermore, an increasing amount of data is available on calcium supplementation with mineral water. In this paper, we discuss the role of hydro- and balneotherapy in the therapy of osteological diseases, on the basis of the available evidence.]
[Substitution of drugs with narrow therapeutic window in transplant immunology]
[Because of the economic crisis affecting the health care system, the Hungarian government have envisaged a number of measures. In Hungary, the system of reference support or fixing is an excellent cost-saving tool in the financing of drugs that have a similar mechanism of effect or contain the same molecule. However, in case of certain patient groups and of “critical drugs”, it is to be feared that an inadequate agent might actually bring loss rather than benefit. In this paper, we would like to draw attention to the fact that switching the original microemulsion cyclosporin to generic, no-microemulsion preparations might pose a direct risk for the safety of the transplanted organ and the transplanted patient.]
[Cost minimization analysis of basal insulin analogues in the treatment of type 2 diabetes]
[INTRODUCTION - Basal insulin analogues are essential drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Basal insulin analogues have been shown to reduce the frequency of hypoglycaemia versus NPH insulin, and thus may be beneficial in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Here we present a cost-minimisation analysis of basal insulin analogues, comparing insulin glargine and insulin detemir available in Hungary. METHODS - A literature review was conducted to identify randomized, controlled clinical trials with a duration of 12 weeks or more in which a direct comparison of insulin glargine and insulin detemir was made in patients with type 2 diabetes. In a meta-analysis of the eligible trials, the following endpoints were investigated: metabolic status, body weight, frequency of hypoglycaemia, insulin doses administered and the number of insulin injections required. If a high heterogeneity (I2>75%) was found, meta-regression was performed to identify the underlying reasons. The funder’s perspective was applied in the cost-minimization analysis by taking into account the cost of the drug and of medical devices necessary for its administration, based on the daily number of insulin injections. RESULTS - No further studies were found in addition to those included in a metaanalysis published by The Cochrane Library. On the basis of three eligible studies, insulin detemir was injected more frequently compared with glargine (weighted mean difference: 0.42 95% CI 0.14-0.69 injections/day). High heterogeneity was present in case of two endpoints: the incidence of overall hypoglycaemia per patient-year (I2=83%), and daily basal insulin dose in units per body weight (I2=94%). The reason for the high heterogeneity in hypoglycaemia rates was not identified by meta-regression; however, the difference in insulin doses per body weight was negatively associated with body weight (-0.027 IU/kg per 1 kg, 95%CI: -0.051; -0.004). On the basis of the present meta-analysis and meta-regression, our calculations suggest that treating an average weight (90 kg) patient with type 2 diabetes with insulin glargine would result in an annual cost reduction of 93 452 HUF compared with insulin detemir by employing gross public drug prices. CONCLUSION - On the basis of the available clinical evidence, insulin glargine might be a cost-saving alternative of insulin detemir in an average-weight patient with type 2 diabetes. In an era of scarce resources, the role of therapeutic alternatives offering cost savings with the same efficacy become more important. The generalisability of our conclusions might be influenced by potential differences in the manufacturers’ claw-back rate of detemir vs glargine insulin.]
[E-physicians and e-patients in Hungary - Qualitative survey about physicians’ internet use and attitudes toward their patients’ internet use]
[BACKGROUND - Physicians and patiensinternet use has been challenged the med-ical and the social studies as well. InHungary, approximately 100% of physi-cians use the internet, and about 80% ofpatients search for medical informationonline.METHODS - A qualitative, pilot study(N=83) was performed among practisingphysicians in Hungary. The structuredinterview was focused on medical internetuse, and the attitudes of doctors regardingtheir patients’ internet use.RESULTS - The interviewed physicians usethe internet for the daily work. However76% of them do not support their patients’intenet use: firstly because of professionalcauses, secondly because of the changes ofthe doctor-patient relationship. 24% of theresponders agreed with the use of internetof patients for medical reasons.CONCLUSIONS - Our study is a pilot forquantitative research. Our findings suggestthat Hungarian physicians start to open tothe new communication technologies.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]