The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Clinical Neuroscience - 2024;77(7-8)
Content
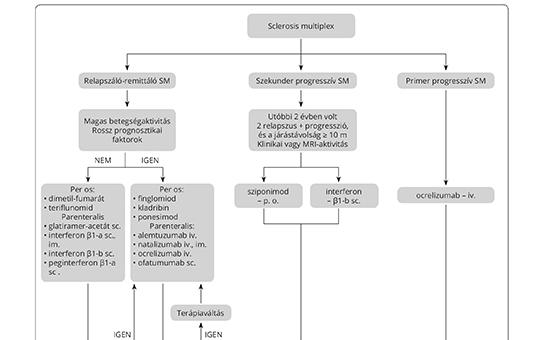
[Theoretical approach and prognostic significance of high disease activity in multiple sclerosis]
[Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune inflammatory disease of the central nervous system with demyelination and neurodegeneration. In addition to the inflammatory immune processes that characterise the onset of the disease with relapses, chronic inflammation is also present from the onset of the disease. The catabolic processes induced by chronic inflammation are responsible for the axonal degeneration that causes the progression of the disease. The activity of the disease is well defined, an important prognostic factor, and a determining factor in the indication of disease-modifying therapies. It is important to establish disease activity at the time of diagnosis and to monitor it continuously during patient care, both clinically and radiologically, as it is the basis for deciding on the current treatment. If detected on the basis of the professional guideline, it is necessary to start or switch to a highly effective therapy. ]
An update on approved and emerging drugs for the treatment of postpartum depression
Depression, anxiety and psychotic disorders are common perinatal mental health disorders in the postpartum period. Depressive symptoms that occur postpartum are also present in the prenatal period in 50% of patients. Risk factors for the development of postpartum depression include poor relationship with the partner, lack of social support, mother’s low socioeconomic status and multiparity.
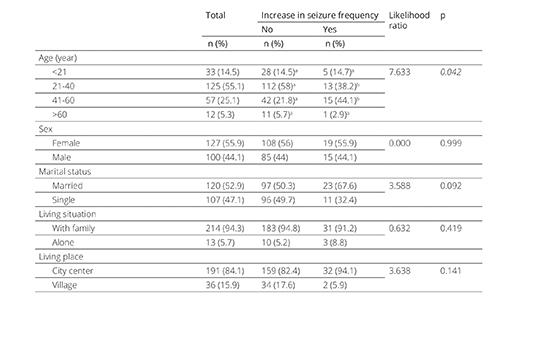
Effect of COVID-19 on seizures and patient behavior in people with epilepsy
To evaluate the long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on seizure frequency and levels of mental distress in individuals with epilepsy and identify potential risk factors associated with increased seizure frequency. This is a cross-sectional study conducted in Türkiye in May 2021 by phone. Information on epilepsy syndromes, antiseizure medications, average seizure frequency, and drug resistance was obtained from medical records.
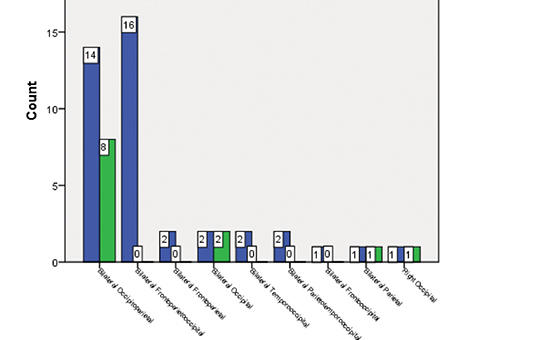
Risk factors of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with preeclampsia or eclampsia: A retrospective review
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is characterized by vasogenic edema, usually reversible, with the prominent involvement of the parietal and occipital lobes. The exact etiopathogenesis leading to PRES is unknown. Because signs of eclampsia and preeclampsia in neuroimaging often overlap and manifest as PRES, we aimed to evaluate whether demographic, clinical, and laboratory parameters predict PRES in patients with preeclampsia or eclampsia.
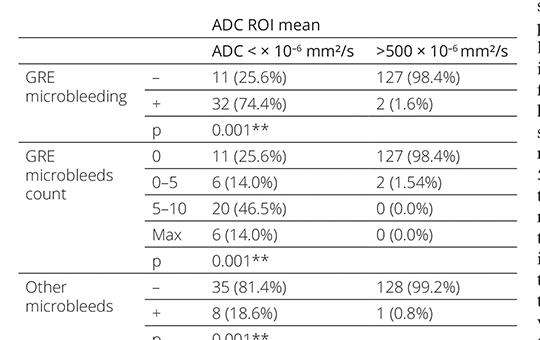
Determination of hemorrhagic transformation risk in acute ischemic cerebrovascular disease: The relationship between ADC values and GRE hemo sequence microhemorrhage
To determine the risk of hemorrhagic transformation in patients with acute ischemic cerebrovascular disease, we investigated the relationship between Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Magnetic Resonance Imaging values measured within the infarct area and microbleeds observed on Gradient Echo Sequence Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
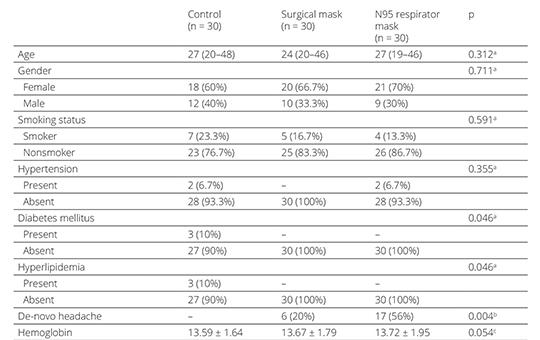
Effect of surgical mask and N95 respirator mask use on cerebrovascular reactivity
Face masks are crucial parts of personal protective equipment (PPE) to reduce the risk of respiratory infections. The COVID-19 outbreak has increased healthcare workers’ use of face masks. This study aimed to evaluate changes in cerebrovascular response among healthcare workers using surgical and N95 respirator masks. 90 healthcare workers: 30 wearing surgical masks, 30 wearing N95 respirators, and 30 without masks were included.
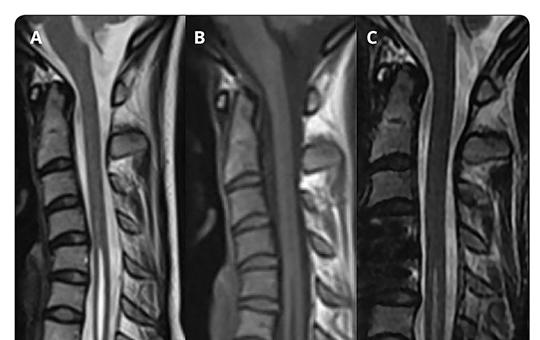
Cervical syringomyelia associated with cervical disc disease
Syringomyelia is a neurological condition in which a longitudinal fluid-filled cavity is formed within the spinal cord. It usually occurs in the cervical region and is associated with Chiari malformation, infections, trauma, and tumors of the spinal cord. However, syringomyelia associated with cervical disc disease (SCD) is very rare and only a few cases have been reported so far.
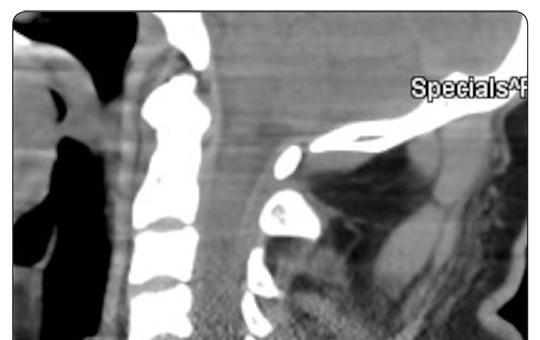
[Vertebral artery dissection during traumatic injury of the cervical spine, two case reports ]
[If severe cervical spinal cord injury or severe cervical vertebral fracture, subluxation or luxation is confirmed, 20-40% of the cases have vertebral artery dissection or occlusion. These can be asymptomatic, but can cause additional neurological damage in addition to cervical myelon and cervical nerve root symptoms. Vertebral artery dissection can be caused by direct injuries, stab wounds or gunshot wounds. Indirect vertebral artery dissection can occur at the same time as subluxation, luxation, or complex fractures of the cervical vertebra. CTA is the examination procedure of choice. In many cases, digital subtaction angiography examination and, if necessary, neurointerventional treatment must precede open neurosurgery. In our report, in the first patient, complete luxation of the C.VI vertebra caused unilateral vertebral artery 2-segment dissection-occlusion, while in our second patient, a stab injury caused direct vertebral artery compression and dissection. The occlusion of the vertebral artery did not cause neurological symptoms in any of the cases. In both of our cases, parent vessel occlusion was performed at the level of the vertebral artery injury before the neurosurgical operation.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
2.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]3.
4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]