The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Specialities
Diabetology
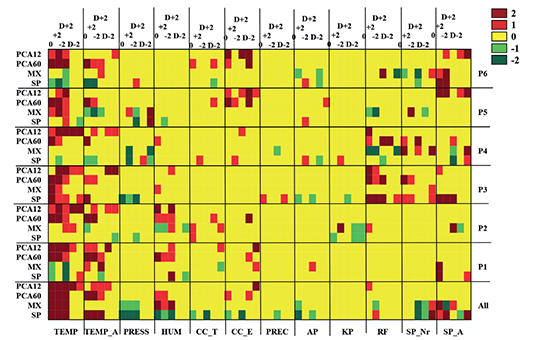
Personalized analysis of pain–weather associations: a pilot study
It is a wellknown belief that weather can influence human health, including pain sensation. However, the current data are controversial, which might be due to the wide range of interindividual differences. The present study aimed to characterize the individual pain–weather associations during chronic pain by utilizing several data analytical methods.
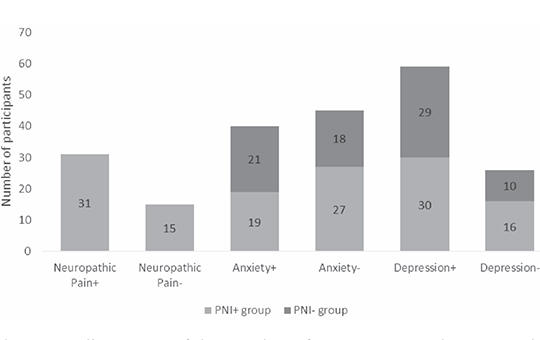
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, frequently result in mood disorders among affected individuals. It is established that neuropathic pain arising from traumatic neuropathies is also linked to mood disorders. This study investigates the influence of neuropathic pain on the development of mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries, following the earthquake centered in Kahramanmaraş on February 6, 2023.
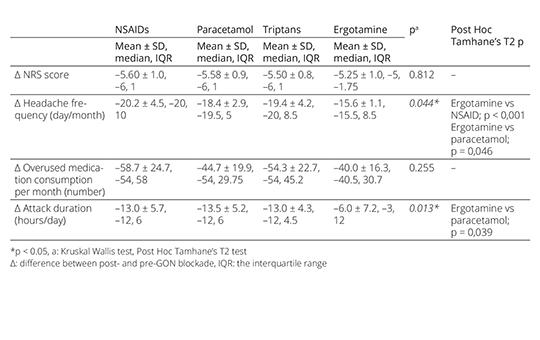
The effect of anesthetic blockade of greater occipital nerve during the withdrawal period of the medication overuse headache treatment
Discontinuation of medication still remains a key element in the treatment of medication overuse headache (MOH), but there is no consensus on the withdrawal procedure. We aimed to share the promising results of anesthetic blockade of greater occipital nerve (GON), which can be an alternative to existing treatments during the early withdrawal period of MOH treatment.
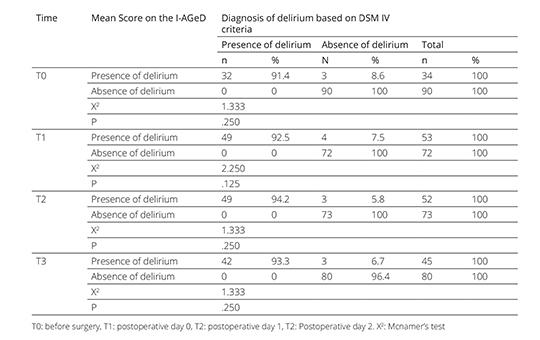
Validity and reliability of the Turkish version of the Informant Assessment of Geriatric Delirium Scale
Delirium is a common complication developing in elderly patients. Therefore, it is important to diagnose delirium earlier. Family caregivers play an active role in early diagnosis of delirium and build a bridge between health professionals and patients. The purpose of this research was to achieve the validity and reliability of the Turkish version of the Informant Assessment of Geriatric Delirium Scale (IAGeD).
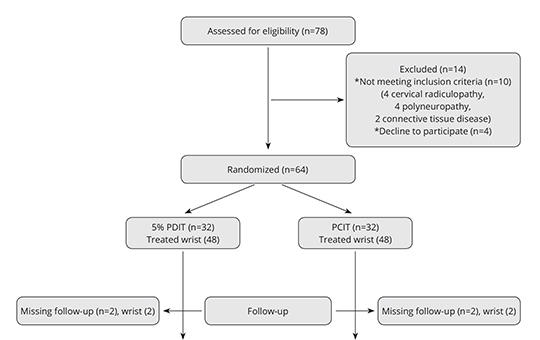
Perineural 5% dextrose versus corticosteroid injection in non-surgical carpal tunnel syndrom treatment
We aimed to investigate the difference of clinical and electrophysiological improvement between perineural corticosteroid injection therapy and perineural 5% dextrose injection therapy in carpal tunnel syndrome. Total of 92 wrists that were diagnosed as mild-to-moderate idiopathic CTS and completed their follow-up were included in our study. The severity of pain, symptom severity and functional status were assessed by visual analog scale.
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.