The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2013;23(01)
Content
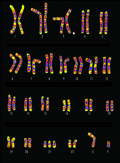
[Fifty years of the Hungarian congenital abnormality registry and some important results]
[The Hungarian Congenital Abnormality Registry (HCAR) was established in 1962 after the greatest tragedy of human teratology, the thalidomide-Contergan catastrophe. As far as we know HCAR was the first national-based registry in the world based on the mandatory notification of patients with different structural birth defects, i.e. congenital abnormalities (CAs) by medical doctors. The main task of the HCAR has been to determine as reliably as possible the baseline occurrence of different CAs. In addition three other secondary missions of the HCAR were defined: 1) to detect temporal and/or spatial increases (“clusters”) of CA and to evaluate the permanent changing trends of CAs; 2) to help plan medical and social services for cases with different CA; and 3) to estimate the public health importance of different CAs so that resources can be properly allocated. Here some important results of HCAR between 1962 and 2011, i.e. during 50 years are reported.]
[Rituximab therapy in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies]
[Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies are systemic autoimmune diseases characterized by symmetrical weakness of proximal limb muscles. In the everyday practice it is not easy to treat idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. First-line therapy is based on corticosteroids. If there is no improvement in the symptoms and complaints in two months, a new immunosuppressant therapy has to be initiated. The aim of this summary is to present the biological agent rituximab in the therapy of this condition.]
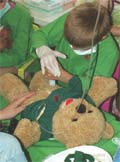
[Fear of medical care: epidemiology and prevention among 5-6 years old children]
[INTRODUCTION - At least 5-10% of the adult population is afraid of medical care. These fears may begin in preschool years. Therefore, the aim of our study was to assess the rates of medical fears among 5-6 year old children, and to prove that medical fears can be reduced by a health promotion program for children called “Teddy Bear Hospital” POPULATION AND METHODS - 248 children participated in the study (average age: 5.5 years, 45% girl, 55% boy). The “Teddy group” (129 children) took part in the Teddy Bear hospital program (Teddy group). The control group (119 children) did not take part in this program (control group). Questionnaires, including a Visual Analog Scale, a picture test, and drawing analyses were completed on two separate occasions three weeks apart difference. RESULTS - Fear of needles was the most frequent fear (59%) among the participating children, followed by the fear of medical environment (33%), the fear because of the lack of information (27%), the fear of doctors (20%), and the fear of pain (15%). On the basis of the picture test the fear of doctors significantly decreased in the Teddy group (from 18% to 7%) compared with the control group (from 10% to 11%, p<0.05). Drawing analyses also showed that children in the Teddy group had significantly lower levels of medical anxiety (29% and from 19.3 point to 17.6 point) than the control group (19% p<0.05 and from 18.8 point to 18,33 point p<0.05). On the drawings of the Teddy group we found significantly more new medical information (38%) compared with the control group (21%, p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS - Medical fears are frequently present among 5-6 year old children, therefore, their prevention is greatly needed. A potential way of the prevention is the “Teddy Bear Hospital” program, which efficiently reduces children's medical fears and anxiety.]
[A popular error of histochemistry seems to be change]
[In medical practice there are a number of “truths etched in stone” that are passed on from textbook to textbook and learned by generations before they become obsolete. This short study aims to eliminate a misbelief from the diagnosis of gout that is related to the histological detectability of urate deposits. According to the generally accepted thesis, urate crystals obtained from patients with gout are dissolved in formalin solution, therefore, tissue samples should be fixated in alcohol. The authors have found that urate crystals can be detected on conventionally mounted, native (unstained) sections, despite formalin fixation, whereas the great majority of urate crystals are dissolved during haematoxylin-eosin staining. Therefore, for the detection of urate crystals the tissue samples should be examined on native, unstained sections.]
[Lifestyle and self-perceived health status differences of Hungarian and foreign medical students]
[INTRODUCTION - Physicians, while concerning also the whole personality, advice their patients in life-style problems too and these types of advices may contribute even decisively to the patients’ recovery. The physicians’ personal health behaviour and self-assessed health status are interrelated with counselling the patients. Undergraduate years play a significant role in the later established behavioural patterns therefore it is important to study the medical students’ health status and lifestyle. MATERIAL AND METHODS - Self-administered questionnaires were used to assess the lifestyle and self-perceived health status differences of domestic (Hungarian) and foreign (English course) medical and dental school students in the 4th year of the Semmelweis University (response rate: 96% and 55.6%). Dichotomous variables were analysed by Pearson chi-square probe and multivariable logistic regression models at significance level of p<0.05 and odds ratios were calculated with 95% confidence interval. RESULTS - The rate of healthy diet was 41.0% (n=55) among Hungarian students and 57.7% (n=67) among the foreign students. Foreign students exercise more often vigorously 41.5% (n=51) than the Hungarians 20.0% (n=29). Foreign students ranked their self-perceived health status higher in all but one categories, than Hungarians. CONCLUSIONS - The results of our study indicate that comparing health behaviour of students of different cultural-geographical background, dietary habits and the selfperceived health status are more favourable among those out of foreign countries.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]