The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Clinical Neuroscience - 2022;75(05-06)
Content
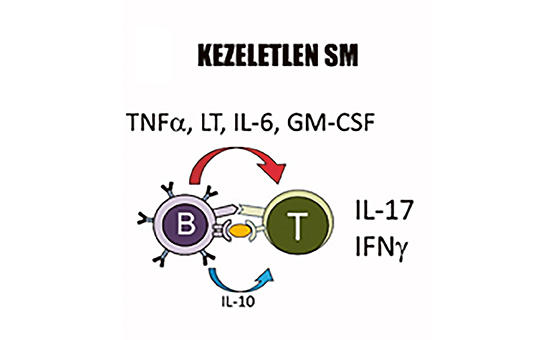
[B-cell depletion in the therapy of multiple sclerosis: ofatumumab is a new player]
[Research results in recent years have demonstrated that B-lymphocytes play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis (MS). The increased understanding of the disease process has resulted in the development of B cell-targeting antibodies as potential drugs for both relapsing and progressive forms of MS. Therefore, B-cell depletion therapies are becoming more prominent and determining in reducing disease progression. The first B-cell depleting anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody was rituximab, which has also been studied in MS and, following favourable results, new drugs have been developed with a similar point of attack. In 2017, the FDA and in 2018, the EMA approved ocrelizumab, another anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of relapsing-remitting (RRMS) and primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS). This was a particularly significant advance in the treatment of PPMS, as it was the first medication with a proven effect of reducing progression in PPMS. Ofatumumab, a fully human anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has emerged recently as a new player in B-cell depletion therapy. The drug has also recently been approved by the EMA in March 2021 for use in relapsing forms of MS. In this review, we detail the mechanism of action and efficacy of anti-CD20 therapies currently used in MS. ]
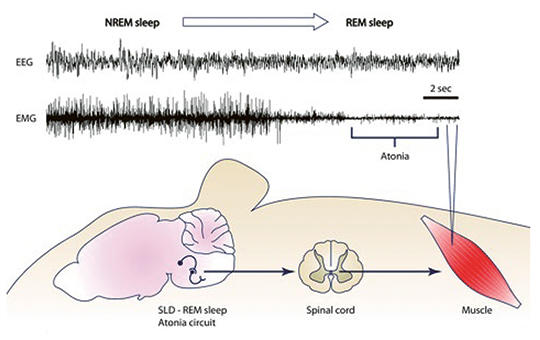
REM sleep, REM parasomnias, REM sleep behaviour disorder
We review the literature on REM parasomnias, and their the underlying mechanisms. Several REM parasomnias are consistent with sleep dissociations, where certain elements of the REM sleep pattern emerge in an inadequate time (sleep paralysis, hypnagogic hallucinations and cataplexy) or are absent/partial in their normal REM sleep time (REM sleep without atonia, underlying REM sleep behavior disorder). The rest of REM parasomnias (sleep related painful erection, catathrenia) may have other still unclear mechanisms. REM parasomnias deserve attention, because in addition to disturbing sleep and causing injuries, they may shed light on REM sleep functions as well as the heterogeneous etiologies of parasomnias. One of them, REM sleep behavior disorder has special importance as a warning sign of evolving neurodegenerative conditions mainly synucleinopathies (some cases synucleinopathies themselves) and it is a model parasomnia revealing that parasomnias may have by autoimmune, iatrogenic and even psychosomatic etiologies.
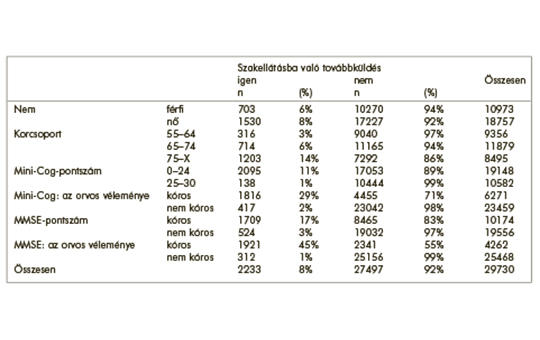
[Investigating cognitive impairment in communities of practice – lessons learned]
[In the “Three Generations for Health” programme, general practitioners were responsible for screening for dementia in their practices using mini-COG and Mini Mental State Examination. The aim was to present the screening results of those included, their assessment by the doctor and the further fate of the patients. After mini-COG test, MMSE test was performed in case of suspected dementia. The examiner categorized the result as abnormal or no abnormal, recorded the referral, and recorded the data in an online interface. Our study is a cross-sectional study; the evolution and distribution of the parameters described in the objectives are described with raw case numbers and proportions. Patients aged 55 years and over were recruited consecutively. Only those cases (29 730) where mini-COG and MMSE test results were available, their assessment by the physician, and referral data to specialist care were analyzed. The Mini-COG test revealed that 64% of the subjects were suspected of cognitive decline. Misclassification occurred in 13 015 cases, with 21% of the Mini-Cog test scores matching cognitive decline and 21% of lesions considered abnormal by GPs. The MMSE test raised the suspicion of dementia in 34% of the sample (10 174 people), with 4 262 (42%) of the participating GPs considering the result abnormal. 11% (2095 people) of people with abnormal Mini-Cog test scores and 17% (1709 people) of people with suspected dementia based on MMSE test scores were referred to specialist care. Our study assessed the practice of detecting cognitive decline in primary health care. The tools adopted for screening for dementia were used by practices, but the assessment of results and referral of suspected cases of dementia to specialist care were below the expected level. There is a need to improve primary care providers’ knowledge of dementia detection and treatment and to strengthen links with specialist care.]
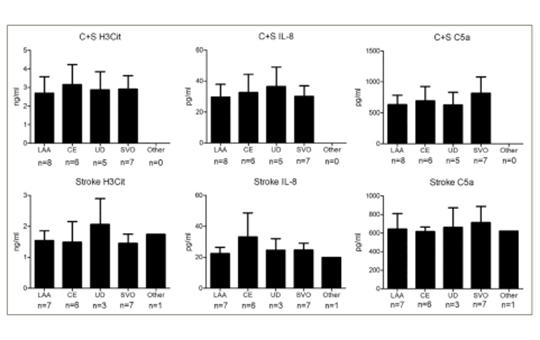
Increased serum citrullinated histone H3 levels in COVID-19 patients with acute ischemic stroke
Prevalence of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is increased in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). A proposed hypothesis is increased virus-induced propensity to hypercoagulation resulting in arterial thrombosis. Our aim was to provide evidence regarding the involvement of neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation (NETosis) in COVID-19 related AIS. Twenty-six consecutively enrolled COVID-19+ pneumonia patients with AIS, 32 COVID-19+ pneumonia patients without AIS and 24 AIS patients without COVID-19 infection were included to the study. Clinical characteristics of recruited patients were collected. Serum levels of citrullinated histone H3 (H3Cit; a factor of NETosis), IL-8 and C5a (mediators associated with NETosis) were measured by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). H3Cit levels were significantly higher in COVID-19+ AIS patients, whereas all study groups showed comparable IL-8 and C5a levels. There were no significant differences among etiological subgroups of AIS patients with or without COVID-19. AIS patients with COVID-19 showed relatively increased white blood cell, lymphocyte, neutrophil, D-dimer, C-reactive protein and procalcitonin levels than control groups. H3Cit levels did not correlate with clinical/prognostic features and inflammation parameters. H3Cit and IL-8 levels were correlated in COVID-19 patients without stroke but not in COVID-19 positive or negative AIS patients. Increased levels of inflammation parameters and H3Cit in COVID-19 related AIS suggest that NETosis may cause susceptibility to arterial thrombosis. However, H3Cit levels do not correlate with clinical severity measures and inflammation parameters diminishing the prognostic biomarker value of NETosis factors. Moreover, the link between IL-8 and NETosis appears to be abolished in AIS.
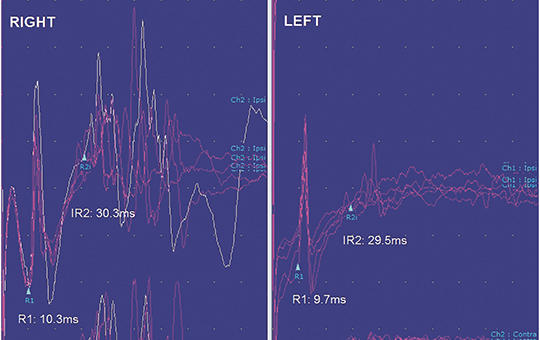
COVID-19 can cause blink reflex abnormalities
Neurological symptoms and complications associated with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) are well known. It was aimed to evaluate the brainstem and trigeminal/facial nerves and the pathways between these structures in COVID-19 using the blink reflex test. Thirty patients with post COVID-19 (16 males, 14 females) and 30 healthy individuals (17 males, 13 females) were included in this prospective study. Individuals who previously had a positive nose swap polymerase chain reaction test for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and whose previously clinical features were compatible with COVID-19 were included in the post COVID-19 patient group. Neurological examination of the participants should be normal. Blink reflex test was performed on all participants. R1, ipsilateral R2 (IR2), and contralateral R2 (CR2) waves obtained from the test were analyzed. The mean ages of healthy individuals and post COVID-19 patients were 34.0±6.4 and 38.4±10.6 years, respectively. Both age and gender were matched between the groups. R1, IR2, and CR2 latencies/amplitudes were not different between the two groups. The side-to-side R1 latency difference was 0.5±0.3 and 1.0±0.8 ms in healthy individuals and post COVID-19 patients, respectively (p=0.011). One healthy individual and 12 patients with post COVID-19 had at least one abnormal blink reflex parameter (p=0.001). This study showed that COVID-19 may cause subclinical abnormalities in the blink reflex, which includes the trigeminal nerve, the seventh nerve, the brainstem, and pathways between these structures.
COVID-19 and post-poliomyelitis syndrome: coincidence?
Although severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel virus, many central and peripheral nervous system manifestations associated with coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) infection have been reported. Beyond the neurologic manifestations, we may still have much to learn about the neuropathologic mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here we report a case of post-poliomyelitis syndrome (PPS) related to COVID-19 and attempt to predict the possible pathophysiologic mechanism behind this association.
TikTok and tics: the possible role of social media in the exacerbation of tics during the COVID lockdown
Over the past year, many cases with newly onset or significantly exacerbated tic disorders were observed worldwide, where some aspects of the clinical presentation or the symptomatology were atypical for established tic diagnoses. Our purpose was to describe the atypical cases and raise relevant diagnostic issues. Consecutive cases with atypical tic presentations were documented. Five atypical tic cases are described. These cases shared some common characteristics, most notably the fact that all of them had been exposed to online presentation of ticking behaviour on social media platforms prior to the de novo development or exacerbation of their tics. Even though the order of events suggests causality and therefore the diagnosis of a functional tic disorder, unambiguous criteria for classifying atypical tics as functional symptoms are lacking. Differentiating neurodevelopmental and functional tics in childhood is currently problematic. Based on the currently unresolved issues in differential diagnosis, the importance of watchful waiting and behavioural interventions is highlighted to avoid unwarranted pharmacotherapy.
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
2.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]3.
4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]