The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Clinical Neuroscience - 2022;75(03-04)
Content
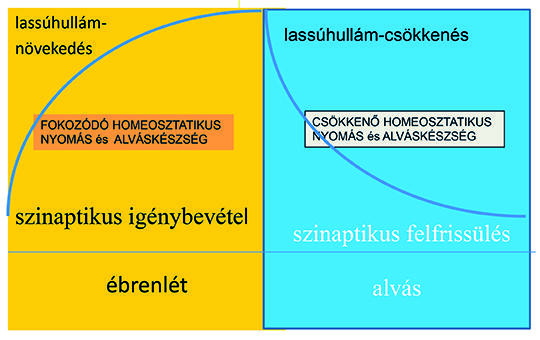
[How our view of epileptogenesis and mechanism of epilepsy changes? The system epilepsies’ concept]
[To examine the ways of epileptogenesis closely linked to the system epilepsies’ concept. We follow the ways of epileptic transformation in the declarative memory-system, in the sleep/arousal twin-systems, in the perisylvian neuronal network and in postinjury epilepsy, which we consider a general model of the epileptic transformation. In the presented systems, epileptogenesis shares a similar mechanism in the form of augmentation and derailment of plasticity and sleep-related synaptic homeostasis. This highlights the central role of NREM sleep in those epilepsies. We try to characterize the concept of system epilepsies and suggest a shared mechanism of epileptogenesis. ]
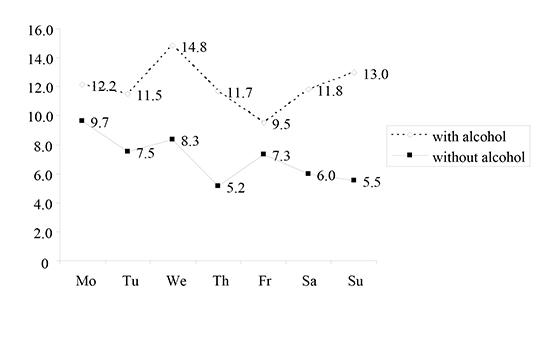
Weekly patterns of suicide and the influence of alcohol consumption in an urban sample
The weekly fluctuation in suicide rates is influenced by several factors including sex, psychiatric illness and alcohol dependence. The purpose of this study is to explore the impact of current alcohol use on suicid Data on sex, date of death, results of blood and/or urine alcohol tests and history of alcohol dependence in suicide victims over the 1997-2002 period were retrieved from a forensic database in two cities in Chuvash Republic. Over the six-year study period, 1,379 suicides were committed, 59% of them under the influence of alcohol. The peak incidence for men and women regardless of previous alcohol consumption was on Wednesdays and Mondays, respectively. The overall suicide rate was highest on Mondays and lowest on Thursdays. Both sexes were less likely to commit suicide during holidays than on weekends or workdays while intoxicated with alcohol. In this urban sample, the distribution of suicide across weekdays only partly followed the international pattern. The peak incidence of suicide showed sex difference, with the highest incidence for women on Mondays and for men on Wednesdays. The higher suicide rate on workdays might be accounted for by work-related stress, while the lower rate on weekends could be explained that people usually drink alcohol in the comforting company of family or friends, which reduces psychological tension and suicidal ideation. The majority of men consumed alcohol before committing suicide, regardless of the day of the week, while this observation was true for women only on Fridays and Sundays. Alcohol consumption greatly contributes to suicidal behavior in Chuvash Republic.
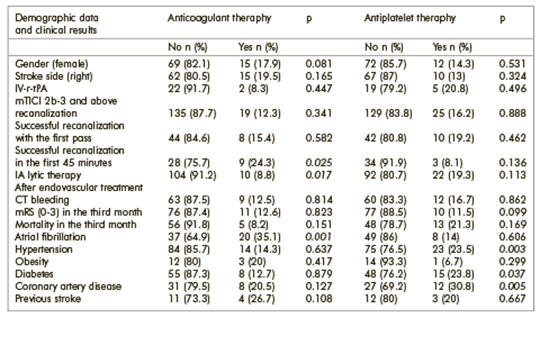
How does the use of antiplatelet and anticoagulants affect the success of mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke cases?
In this study, we wanted to investigate the effect of antiplatelet and anticoagulant use on the success of mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke cases. 174 patients who were brought to the Stroke Center of Gaziantep University Şahinbey Research and Practice Hospital between January 2018 and February 2019 due to acute ischemic stroke and who underwent mechanical thrombectomy were retrospectively analyzed. The demographic characteristics, antiplatelet/anticoagulant use before the stroke and mTICI (modified-Thrombolysis-In-Cerebral-Infarction) scores used for reperfusion in mechanical thrombectomy were evaluated. The findings were analyzed statistically (p<0.05). The mean age was 63.3 ± 13.5 in 174 patients who underwent mechanical thrombectomy. 23/174 (13.2%) patients were using anticoagulant therapy (warfarin-OAC or new generation oral anticoagulant-NOAC) and 28/174 (16.1%) were using antiplatelet therapy. A history of atrial fibrillation (AF) was significantly higher in patients receiving anticoagulant therapy before acute ischemic stroke (p=0.001). Patients with a history of hyper tension (HT), diabetes mellitus (DM) and coronary artery disease (CAD) before acute ischemic stroke were receiving antiplatelet therapy in higher rates (respectively; p=0.003, p=0.037, p=0.005). Successful recanalization (mTICI ≥ 2b) was higher in patients with a history of anticoagulant use and who underwent mechanical thrombectomy (p=0.025). Our study showed that the use of antiplatelet or anticoagulants before mechanical thrombectomy may have an indirect positive effect on the success of the procedure.
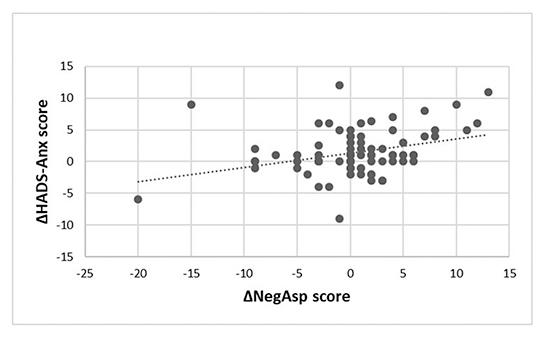
Can we influence the negative drug attitude? Interpretation of the rejection of COVID-19 vaccine in the light of results of a pilot study
Vaccination refusal is a serious obstacle to minimizing the spread of COVID-19. Nevertheless, the rejection of vaccine can be considered the result of a negative attitude towards medical treatment, and according to our previously published data, it can be influenced by the underlying affective state. Increased incidence of affective disorders and anxiety could be observed globally during the pandemic, which may have a significant impact on vaccination acceptance. The aim of our pilot study was to determine the association between clinical improvement of affective and neurocognitive symptoms and change of drug attitude and health control beliefs in a sample of psychiatric patients.
A data set of 85 patients with psychiatric disorder has been analysed with the use of Patient’s Health Belief Questionnaire on Psychiatric Treatment (PHBQPT) with 5 subscales (Negative Aspect of Medication – NA; Positive Aspect of Medication – PA; Doctor health locus of control- Doctor HLOC; Internal HLOC; Psychological Reactance – PR); Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale (HADS-Anx; HADS-Dep) and neurocognitive tests, such as the Stroop test and the Trail Making Tests. All the tests were performed before and after a 14 days treatment. Paired t-tests and generalized linear models were performed to assess the associations between the variables.
The baseline scores of NA and HADS-Anx correlated significantly (p=0.001) and after two weeks of treatment NA decreased (p=0.001), while Doctor HLOC and Internal HLOC increased (p=0.001 and p=0.006). The patients performance of the neurocognitive tests improved (all p<0.05). The reduction of HADS-Anx (p=0.002) and HADS-Dep (p=0.006) scores showed significant associations with the decrease of NA. Increase of the PA score was associated with reduction of HADS-Dep (p=0.028). Improvement of neurocognitive functions had no effect on PHBQPT scores.
Important conclusions can be drawn regarding the rejection of the COVID-19 vaccine based on the associations found between the intensity of affective and anxiety symptoms and the attitude towards treatment. Our findings suggest that affective symptoms have a negative influence on the attitude towards treatment and that the improvement of these symptoms can facilitate the acceptance of the therapy, regardless of diagnosis. The modest effect of the improvement of neurocognitive functioning on the attitude towards drugs and the significant role of affective-emotional factors suggest that the acceptance of vaccination probably cannot be facilitated solely with the aid of educational programs. Considering the increasing incidence of affective disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic, the screening of affective and anxiety symptoms and treatment of these disorders could be an important step towards the acceptance of the vaccine. Although psychiatry is not considered as a frontline care unit of the COVID cases, more attention is needed to pay on the availability of mental health services because refuse of vaccine can develop due to affective disorders too.
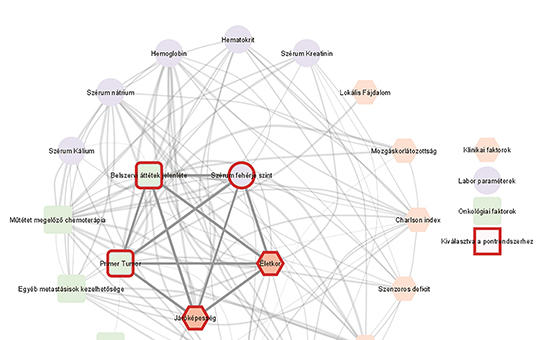
[New, innovative prognosis calculator for patients with metastatic spinal tumors]
[The aim of our research was to create a scoring system that predicts prognosis and recommends therapeutic options for patients with metastatic spine tumor. Increasing oncological treatment opportunities and prolonged survival have led to a growing need to address clinical symptoms caused by metastases of the primary tumor. Spinal metastases can cause a significant reduction in quality of life due to the caused neurological deficits. A scoring system that predicts prognosis with sufficient accuracy could help us to achieve personalised treatment options. Methods – We performed a retrospective clinical research of data from patients over 18 years of age who underwent surgery due to symptomatic spinal metastasis at the National Institute of Mental Disorders, Neurology and Neurosurgery between 2008 and 2018. Data from 454 patients were analysed. Survival analysis (Kaplan-Meier, log-rank, Cox model) was performed, network science-based correlation analysis was used to select the proper prognostic factors of our scoring system, such that its C value (predictive ability index) was maximized. Multivariate Cox analysis resulted in the identification of 5 independent prognostic factors (primary tumour type, age, ambulatory status, internal organ metastases, serum protein level). Our system predicted with an average accuracy of 70.6% over the 10-year study period. Our large case series of surgical dataset of patients with symptomatic spinal metastasis was used to create a risk calculator system that can help in the choice of therapy. Our risk calculator is also available online at https://emk.semmelweis.hu/gerincmet.]
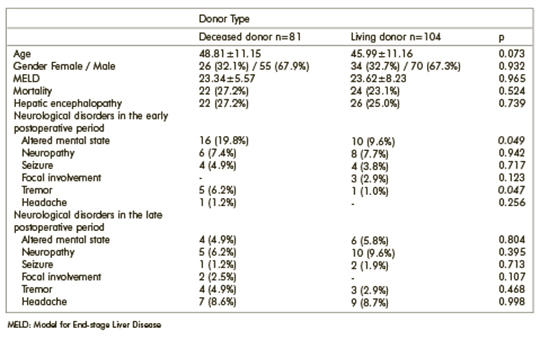
Neurological disorders in liver transplantation
Liver transplantation is the only curative treatment in patients with end-stage liver failure. It has been associated with neurological disorders more frequently than other solid organ transplantations. We aimed to detect neurological disorders in liver transplantation patients and determine those that affect mortality. One hundred eighty-five patients, 105 with and 80 without neurological disorders, were included in this study. The follow-up was categorized into three periods: preoperative, early postoperative and late postoperative. We analyzed all medical records, including demographic, laboratory, radiological, and clinical data. Neurological disorders were observed in 52 (28.1%) patients in the preoperative period, in 45 (24.3%) in the early postoperative, and in 42 (22.7%) in the late postoperative period. Hepatic encephalopathy in the preoperative and altered mental state in the postoperative period were the most common neurological disorders. Both hepatic encephalopathy (37.5%) and altered mental state (57.7%) caused high mortality (p=0.019 and 0.001) and were determined as independent risk factors for mortality. Living donor transplantation caused less frequent mental deterioration (p=0.049). The mortality rate (53.8%) was high in patients with seizures (p=0.019). While mortality was 28.6% in Wilson’s disease patients with neurological disorders, no death was observed in patients without neurological disorders. We identified a wide variety of neurological disorders in liver transplantation patients. We also demonstrated that serious neurological disorders, including hepatic encephalopathy and seizures, are associated with high morbidity and mortality. Therefore, in order to avoid poor outcomes, hepatic encephalopathy should be considered as a prioritization criterion for liver transplantation.
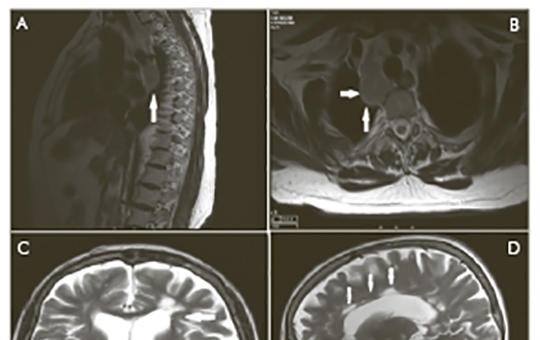
Lymphopenia and tuberculous lymphadenitis under immunomodulatory agents in a multiple sclerosis patient: Follow-up of a challenging case
Interferon-beta (IFN-β) 1a and glatiramer acetate (GA) are first-line therapies for multiple sclerosis (MS) with immunomodulatory effects. We present a patient who developed lymphopenia and tuberculous lymphadenitis under treatment with these agents. The female patient who at present 65 year old is followed at our MS outpatient clinics had received GA (20 mg/day, subcutaneous injection) and later IFN-β 1a (44 µg, thrice weekly, subcutaneous injection). During the course of her treatment, she developed mild to severe lymphopenia. A follow up thoracic spinal MRI (when lymphocyte count was 800/µl) showed multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the posterior mediastinum incidentally. Further investigation revealed tuberculous lymphadenitis. She received anti-tuberculosis (TB) treatment for nine months and her condition resolved. Although immunomodulatory treatments are considered safe with regard to opportunistic infections, and lymphopenia under these treatments are generally accepted as mild and asymptomatic, our experience was different with this patient. Further studies on the management of patients with lymphopenia and assessment of the risk of TB under immunomodulatory agents are needed.
How to manage MuSK antibody-positive myasthenic crisis during pregnancy?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease that is characterised by the formation of antibodies against acetylcholine receptors in the postsynaptic membrane of the neuromuscular junction. The course of the disease cannot be predicted during pregnancy. A subtype of MG with positive muscle-specific receptor tyrosine kinase (anti-MuSK) antibodies exhibits more localised clinical characteristics and a poor response to treatment compared with the disease subtype that involves positivity for acetylcholine receptor antibodies. Myasthenic crisis is more frequently observed in anti-MuSK-positive myasthenia patients. Anti-MuSK-positive myasthenic crisis management is very difficult and a risky situation during pregnancy. The reported case was 30 years old, female, 9 weeks pregnant and musk antibody positive. She stopped her treatment without asking her doctor because she was planning pregnancy in the 6-month period before her hospitalization. She was intubated for a long time in the intensive care unit due to myasthenic crisis and was very resistant to treatment. During this period, her pregnancy was terminated due to fetal anomaly. Plasmapheresis, IVIg and immunosuppressive treatments were applied. Our patient was discharged after a period of about 10 weeks. We share our treatment management.
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.