The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2006;16(01)
Content
[MODERN PRINCIPLES OF EARLY DETECTION, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT IN LUNG CANCER]
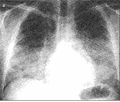
[New clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer contain important advancements. It is necessary therefore that these novelties are widely known by health care professionals. With an existing X-ray screening network in Hungary, we have a unique chance to discover lung malignancies in an early stage in the population. Annual screening is recommended in risk groups over 40 years of age using a nation wide established digital screening network technology. In the therapy of small cell lung cancer there has been no major advance in the past ten years. However, by today, the number of small cell lung cancer patients represent only about 15% of all lung cancer cases. There have been advancements in other fields of the therapy of non small cell lung cancer. Third generation cytotoxic agents used in a platinum based chemotherapy protocol improved quality of life, response rate and survival time. Radiochemotherapy used in locally advanced stages also represented a step forward. In early stage of non small cell lung cancer it has been revealed that significantly improved survival time can be reached with adjuvant combined cytotoxic chemotherapy. Based on these results adjuvant chemotherapy became part of the therapeutic protocol. The use of molecular targeted chemotherapy in the clinical practice of non small cell lung cancer treatment is also a novelty. New therapeutic approaches are epidermal growth factor inhibitors, angiogenesis inhibitors, antivascular, signal transduction modifiers, apoptosis inducing, eicosanoid signal transduction modifiers and immunotherapeutic drugs. Placebo controlled trials have proved the effectiveness of the epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib in the second and third line therapy of non small cell lung cancer and can be administered in the European Union in this indication. The improvement in the complex care of lung cancer patients in Hungary is characterized by the gradual increase in the prevalence data, meaning the gradual increase of the number of lung cancer patients still alive.]
[THE RESULTS OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF MYELOMA MULTIPLEX]
[Among heamatological diseases, myeloma multiplex is the disease demanding the greatest attention. This statement could refer to the difficulties in diagnosis through the success or failure of a medical treatment and to the unavoidable deterioration of condition caused by complications. The illness, as it is known, is incurable but can be treated for a long period of time. The results of molecular biology offer new possibilities to secure the collection of instruments facilitating future recovery. These new modalities are targeted radiotherapy, the abundance of new drugs attacking the subcellular organellums of affected cells (thalidomid, Neovastat, oblimersen, bortezomib, etc.) and immunotherapy against myeloma cells. The introduction of new therapies, however, is to be permitted only with the greatest caution because the crossing of roads cannot be calculated and this could bring about deterioration too. The delay in theoretical considerations and experience however, allows the possibility to do a critical analysis. The application would become reality after collecting numerous experiences.]
[AUTOIMMUNE PATHOGENESIS IN THE BACKGROUND OF PULMONARY ALVEOLAR PROTEINOSIS]
[Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare form of interstitial lung disease. The etiology and pathogenesis of PAP has remained uncertain. It is characterized by the accumulation of surfactant in alveolar space, which leads to impaired oxygen diffusion and lung restriction. Patients develop chronic respiratory failure. Traditional treatment of the disease has been whole-lung lavage. In recent years the role of alveolar macrophages in the removal of surfactant has been discovered with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) triggering this function of macrophages. In the most frequent “idiopathic” subtype of this disease autoantibodies against GM-CSF have been shown to be present in blood. These autoantibodies block GM-CSF-induced surfactant removal by the alveolar macrophages. Clinical studies indicated that longterm, high dose therapy with GM-CSF can be effective in the cleaning the alveolar space and treating respiratory failure. This new treatment modality makes high-risk whole-lung lavage avoidable.]
[THE POSSIBILITIES OF USING PROBIOTICS IN DIGESTIVE DISEASES]
[The mammalian intestinal tract contains a complex, dynamic and diverse society of microorganisms. The beneficial effects of developing a normal bacterial flora are: colonic resistance against pathogens, immunmodulation and intact intestinal barrier. Probiotics are live microbial supplements which beneficially affect the host by improving its intestinal microbial balance after oral administration. The health benefits of probiotics have been the subject of increased research interests. This paper gives a review of the literature that study the roles of probiotics in the prevention and treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea, traveller's diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, Helicobacter pylori infection and hepatic encephalopathy. In human studies the examined probiotics are safe, tolerable and seem to be effective in conditions of diarrhea caused by antibiotics, traveller's diarrhea and pouchitis. In other above-mentioned conditions further randomized and controlled clinical trials are needed to evaluate their efficacy. Based on these results, in the research and manufacturing of genetically-engineered probiotic bacteria a major leap is expected.]
[THE ROLE OF THE CONSUMPTION OF HOT FOOD AND DRINK IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF OESOPHAGEAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA]
[INTRODUCTION - Potential risk factors leading to the development of squamous cell carcinoma in the oesophagus have been analyzed and summarized in a number of epidemiological studies. Authors disagree as to the pathogenic significance of the individual risk factors in various populations. However, it is commonly accepted that alcohol abuse and smoking play a significant role in the development of this disease. Several reports have suggested a positive relationship between oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma and the consumption of hot food and drink. A recent publication, however, claims that the consumption of hot drink is not a pathogenic factor in itself. In our study we wished either to confirm or to rule out a positive relationship between the development of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma and the history of consuming hot food or drink. PATIENTS AND METHODS - During the study period (1 January, 1993 - 31 September, 2004) 449 patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma were examined in our endoscopy laboratory. Histories were taken according to a predefined scheme. The aim was to identify patients with a history of consuming hot food or drink and to determine their percentage within the study population. A group of 738 patients examined endoscopically for indications other than oesophageal cancer served as controls. RESULTS - In the control group a significantly higher proportion of patients tended to consume hot food or drink compared to patients with cancer. Among the patients with oesophageal tumour who consumed hot food or drink a higher proportion was addicted to smoking and alcohol compared to the control group. CONCLUSIONS - In our study population we failed to identify a positive relationship between the development of squamous cell carcinoma in the oesophagus and the habit of consuming hot food or drink. We suggest that consumption of hot food or drink may play some role in the development of oesophageal cancer if it is associated with simultaneous smoking and alcohol consumption.]
[A RARE CAUSE OF CYANOSIS - A CASE REPORT ON SULFHEMOGLOBINEMIA]
[INTRODUCTION - Sulfhemoglobinemia (SHb) is an uncommon cause of cyanosis that is predominantly caused by drugs in adults. CLINICAL CASE - We report on an unusual case of sodium sulfate induced sulfhemoglobinemia in a 61-year-old woman after surgical polypectomy. Fractional hemoglobin derivates were assayed by spectrophotometry and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The sulfhemoglobinemia ratio was 8.6% in the first sample, and 3.77% a month later measured by spectrophotometry. In the hemolysate a new peak was identified as sulfhemoglobinemia by HPLC. It showed the presence of 9.37% sulfhemoglobinemia in the first sample and 4.88% a month later. After omitting the suspected toxic agent the cyanosis decreased significantly. CONCLUSIONS - The findings underline the importance of routine sulfhemoglobinemia analysis in cases of cyanosis of unknown origin.]
[IN-FAMILY VIOLENCE IN CONNECTION WITH HEAVY DRINKING]
[The interdisciplinary question of in-family violence has been being researched for a long time. The major part of this problem is related to the connection between heavy drinking and infamily violence. The background of its importance can mainly be found in all of those social, economic and personal losses and expenses, which result in the number of missed working hours, the costs of sanitary, police, judicial, punishment cases, nonmaterial harms and personal tragedies. Considering that the question of in-family violence related to alcohol consumption has never been a subject to systematic research in Hungary, Research Institute of Addictology made an attempt to analyse the alcohological relations of in-family violence in course of the research project called 'Violent behaviour in family patients treated with alcohol problems in the domestic abuse'. Detailed plan of the research can be found on the webpage of the institute (www.adki.hu). Within the scope of this project we first surveyed the international technical literature of in-family violence. When editing the themes we worked according to the so-called Mendeleyev-table, which means the collection of technical literature from (mainly American) full-text databases accessible on the Internet while putting the possible themes into logical order.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
2.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]3.
4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]