The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2005;15(12)
Content
[ABNORMAL ALBUMINURIA IS A CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTOR IN DIABETIC PATIENTS - ACHIEVING THERAPEUTIC GOAL IN PRACTICE]
[The stages of abnormal albuminuria are microand macroalbuminuria. The isolated abnormal albuminuria is a special form of proteinuria. For the detection of abnormal albuminuria one can use immunological or liquid chromatographic methods. The latter seems to be more appropriate than the immunological methods for the measurement of albuminuria in normo- and microalbuminuric diabetic patients. In diabetes mellitus, the circulating glycated and oxidized albumin is degraded and eliminated in the kidney. Decrease of the glomerular filtration rate is a valuable measure of renal insufficiency and this loss of kidney function is followed by the decrease of albuminuria as a sign of the glomerular closure. Albuminuria is an important cardiovascular risk factor and the decrease of the abnormal albuminuria is associated with a diminishing cardiovascular risk. Thus, albuminuria is a cardiovascular therapeutic target, as well. Therefore, the major points of the management of diabetic albuminuria are the achievement of euglycaemia, the use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and/or angiotensin receptor blockers.]
[LINKAGE OF POSTPRANDIAL LIPAEMIA AND GENES MUTATIONS IN FAMILIAL DYSLIPIDEMIA]
[The familial combined hyperlipidemia (FCH) is the most common form of heritable lipid disorder. The prevalence of FCH is 0.5 to 2.0% in the general population, and 15 to 20% in the survivors of myocardial infarction before the age of 60 years. Healthy people spend most part of their life in postprandial state, which is the sum of the 6-8 hours after each main meal spanning over 20 or 24 hour per day. After the ingestion of the fat rich meal the intestinal chylomicrons disturbs the balance of lipid metabolism. The disorder of the lipid transport does not always manifest itself in the fasting state when the lipid transport system is yet at poise. So, the measuring of fasting triglyceride does not reflect exactly the metabolic capacity and the true atherogen risk of the subject. The healthy FCH family members may have got abnormal higher and extended postprandial lipemia contrast of the normal fasting triglyceride levels. The distributions of PvuII and HindIII polymorphisms in FCH are different from normolipidemic controls. At the same time, there is significantly higher incidence of the apo e4 allele. The apo E4/3 genotypes have got higher and extended postprandial lipemia in FCH subjects. In the investigated international and Hungarian FCH groups have got the minor allele of apolipoprotein AV T/C polymorphism more frequently. The carrying status of the minor allele is accompanied with higher fasting lipid levels and associated with higher and extended postprandial lipemia. The Hungarian results suggest a decreased and extended catabolism of the remnants in FCH caused by apoAV T/C promoter variation that seems to have a more direct effect on the postprandial status than that of apoE 3/3-4/3 polymorphism. The knowledge of characteristics of postprandial lipemia influenced by the mutations of genes described by us are more useful as only the fasting triglyceride level and it is as effective as LDL- or HDL-cholesterol value in the measuring of prognosis of development of vascular disease with athero-thrombotic origin.]
[PRECONDITIONING AND CARDIOPROTECTION WITH VOLATILE ANESTHETICS]
[A rapidly growing body of experimental evidence indicates that volatile anesthetics protect the myocardium against reversible and irreversible ischemia and reperfusion injury. Volatile anesthetics exerted preconditioning effects, resembling to ischemic preconditioning in different animal models. This results in direct protection against ischemic damage, or an indirect enhancement of the ability of myocardial mitochondrial KATP channels to open in response to an agonist. In addition, volatile anesthetics also reduce the severity of reperfusion injury when administered only during reperfusion. These findings might expand our clinical possibilities in the perioperative management of ischemic cardiac dysfunction. Indeed, several recent publications reported on improved postoperative hemodynamic function and lowered level of ischemic cardiac biomarkers in patients anesthetized with volatile anesthetics during coronary artery bypass grafting. The potential applicability of these finding is subject of further research.]
[PRIMARY CARE EVALUATIONS OF THE NUTRITION AND HEALTH OF THE ELDERLY]
[In this comprehensive study the worldwide medical and social consequences of aging population are analysed. The physiological changes, deteriorations in the elderly, the relation of nutritional habits and lifestyle are also discussed according to the results of major epidemiological studies. The nutrition related morbidities, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases are analysed in detail. The most important observations of Europe-wide studies and the limited Hungarian epidemiological surveys are compared. The author also emphasizes the importance of medical support, health education and nutritional advices in different generations, especially in the elderly population.]
[THE EFFECT OF BALNEOTHERAPY AND HIDROTHERAPY IN LOCOMOTOR DISEASES - AN OLD THERAPY REBORN]
[Hungary is respected as an “Empire of thermal water” and balneotherapy has been an important part of health tourism. Recently, an increasing number of articles have been published which investigate the effect of thermal water on patients suffering from locomotor diseases. Balneotherapy has a beneficial painkiller effect and improves the quality of life in several cases of inflammatory and degenerative disorders of joint and bone diseases. The physical effect in its mechanism plays much greater role than the chemical one. A great number of evidence can be found in the medical databases proving the positive effect of balneotherapy in musculoskeletal diseases. Balneotherapy stands as an important factor in the National Development Plan of Hungary but we should like to emphasise that without basic research there is no effective balneotherapy.]
[SEROTYPE AND ANTIBIOTIC SENSITIVITY DETERMINATION OF SELECTED ISOLATES OF INVASIVE STREPTOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAE STRAINS]
[INTRODUCTION - Streptococcus pneumoniae (S. pneumoniae) is a very important pathogene of community acquired invasive infections. The aim the study was to collect data on the serotype distribution of invasive S. pneumoniae strains in Hungary and their resistance. In the light of the results it can be determined how effective the currently available polysaccharide vaccine is against the infections caused by invasive S. pneumoniae strains. MATERIALS AND METHODS - The seroprevalence and antibiotic sensitivity of 44 randomly selected isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from sterile sites of human body were analysed over a 4 year period (2000-2003). Samples were randomly analysed by the Quellung method. Detection of sensitivity of S. pneumoniae to penicillin and erythromycin were carried out by disc diffusions and E-test method in the microbiological laboratory of the St. Laszlo Hospital. RESULTS - The invasive isolates belong to 22 different serotypes. The prevalence of penicillin and erythromycin sensitivity was 79,5%, and 68% respectively. CONCLUSION - The 23 valent polysaccharide vaccine could provide coverage of 82% of invasive pneumococcal diseases caused by strains analysed in this study.]
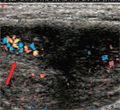
[PENILE VEIN THROMBOSIS AT YOUNG AGE]
[INTRODUCTION - Mondor’s disease is an uncommon disorder occuring mostly in middleaged women and characterized by superficial thrombophlebitis classically involving the thoraco- epigastric veins. Rarely, cases have been reported in atypical sites (upper arms, abdomen, groin and penis). CASE REPORT - This is the first case being published in the Hungarian literature. The young male patient's complaints were caused by penile vein thrombosis which was demonstrated on physical examination and Doppler ultrasonography. Since hereditary thrombophilia and malignancy has been ruled out, we assume that local trauma and venous stasis caused by previous abdominal surgery have been the etiological factors of the disease. CONCLUSION - We give a review of the literature and would like to draw the attention to this rare type of thrombosis, its risk factors and the difficulties of the therapy.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.