The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2001;11(05)
Content
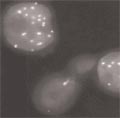
[Molecular morphological methods in laboratory medicine]
[Today, the increasing technical arsenal of molecular morphology has not only methodological importance, but also a revolutionary role in diagnostic laboratory medicine. Techniques previously used only in basic research have become widespread in routine diagnostics by now. The development of methodology for detection of genetic alterations has enabled laboratory tests not only to define disease associated pathobiochemical alterations, but also to identify the genetic background of diseases as well. Evolution of these methods caused qualitative changes not only in detection of disease specific alterations, but also in revealing increased individual susceptibility (sometimes at population level) indicating genetic predisposition to the disease. Recently, the classical methodology based on genetic microscopic morphology has been gradually supplemented or even replaced by different in situ hybridization techniques in many laboratories. Using these techniques chromosomal alterations in cells and tissues (including tumor cells) can be detected within one day (or maximum 1-2 days) without in vitro manipulation of cells. These improved techniques allow us to monitor chromosomal changes after the treatment of genetic diseases or define these alterations induced by environmental exposures.]
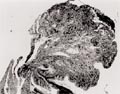
[Case report: gastrointestinal pyogenic granuloma]
[In this presentation authors would like to report a case with a lesion related to a ventricularly located pyogenic granuloma. A 65-year-old man was hospitalized with symptoms of acute gastritis. Despite symptomatic treatment for two days he was still in poor condition. Upper panendoscopy revealed Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis and a polypoid lesion with the size of a bean close to the cardia. The histology examination of the lesion verified pyogenic granuloma with gastric localization. After complete Helicobacter pylori eradication followed by PPI and H2 blocker-therapy, the polypoid configuration gradually decreased and after approximately one year it could not be detected and the patient remained symptomfree. According to literature data, pyogenic granuloma is extremely rare in the gastrointestinal tract except for the oral cavity which is the reason why authors intended to call the attention for this rare occurrence.]
[Helicobacter pylori infection and practical questions of therapy]
[According to our knowledge, Helicobacter pylori is a major factor in the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer disease. The prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection is 70-80% in ulcer patients with the bacteria colonising the mucous surface of the antral mucosa. Eradication therapy against the bacteria leads to complete healing of ulcer disease in about 85-90% of cases. Indications for the eradication and recommended treatment modalities are outlined in several consensus reports; however, in everyday practice a case by case decision is necessary. Present paper summarises two different cases. In the first, the patient has suffered from several relapses of ulcer disease and a successful eradication was performed. Despite of the healing of the ulcer, this patient continued to have prolonged dyspeptic symptoms which called for maintenance antisecretory therapy. The second case is an example that even in a Helicobacter pylori infected patient there could be other reasons for the ulcer pathogenesis. Thorough examinations revealed duodenal manifestation of Crohn’s disease as the background. The message of presented cases is that in each patient individual adaptation of diagnostic and therapeutic algorithms is recommended.]
[Diagnostic problems of ischemic colitis]
[Ischemic colitis is mainly caused by the impaired circulation of the inferior mesenteric artery. Most frequently it occurs as part of general arteriosclerotic disease or impaired left ventricular function, but it may also occur after abdominal aortic reconstruction. In connection with cocaine users, thrombophylia and vasculitis can also happen among young patients. Colonoscopy plays the most important role in making the diagnosis. In case of transitional ischemia conservative treatment is recommended, but surgery is needed in the progressive gangrenous form or when stricture in the colon developed. Authors describe the case of an 80-year-old man and discuss the etiology, clinical aspects, classical and up-to-date methods of diagnostics and the possibilities of conservative treatment.]
[Selective abortion in twin pregnancies discordant for congenital fetal anomaly]
[INTRODUCTION - In special cases of twin pregnancy where one of the fetuses is affected by severe congenital anomaly or disease confirmed with prenatal diagnostic methods and the other fetus is healthy, selective abortion has been accepted as the method of choice for twenty years to save the healthy sibling and to improve its life expectations. PATIENTS AND METHODS - The authors present their clinical experience of the past 15 years from 14 cases of selective abortion performed in twin pregnancies discordant for congenital fetal anomaly. Indication for the intervention was the anomaly of the second fetus in eleven cases and the anomaly of the first twin fetus in three cases. RESULTS - Out of eleven selective abortions performed on the second twin fetus, only one ended with the loss of the entire pregnancy. All three cases of selective abortion performed on the first twin fetus resulted in abortion of the entire twin pregnancy. All ten surviving fetuses were born living and healthy, followed by unharmed infant and childhood development. CONCLUSIONS - To offer the possibility of selective abortion to the parents seems to be indicated only in those cases of twin pregnancy where the discordant fetal disease or congenital anomaly is severe, placentation is dichorionic or at least diamniotic and where the second twin is affected.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]