[Breastfeeding Support in Postpartum care Units]
ANTALNÉ PETRIKÓ Emese Panna1
JULY 01, 2024
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2024;37(03)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.55608/nover.37.0012
Journal Article
ANTALNÉ PETRIKÓ Emese Panna1
JULY 01, 2024
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2024;37(03)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.55608/nover.37.0012
Journal Article
Szöveg nagyítása:
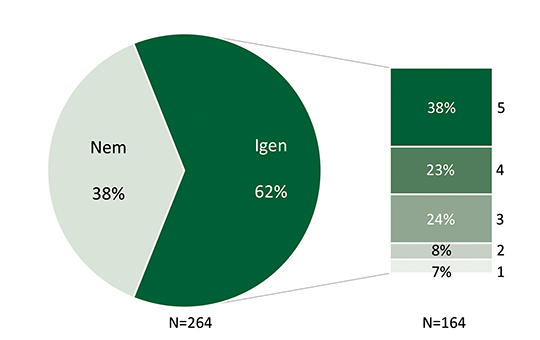
[Assess the quality and effectiveness of breastfeeding support in hospitals, and mothers’ satisfaction with the support they receive. Examine the relationship between the support provided by healthcare professionals and the success of breastfeeding and formula feeding.
The study was conducted using an internet-based, self-completed survey. 264 mothers took part in the research, who had given birth in Hungarian hospitals, from different parts of the country.
Based on the mothers’ experiences, the quality of breastfeeding support provided in hospitals is often inadequate and many cases mothers receive no help at all or not receive inadequate support to initiate breastfeeding. This can have a number of negative consequences, as insufficient support can contribute to premature cessation of breastfeeding and to the use of infant formula.
Providing appropriate professional support in the postpartum period is essential for the healthy development of children, therefore improvements and changes are needed in the field of hospital breastfeeding support.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Approximately 250-300 new paediatric cancer patients are diagnosed in Hungary every year. Due to the long-term treatment and to avoid frequent piercing of peripheral veins, long-term venous access (port-a-cath) is needed. These catheters are used in chemotherapy, cytostatic dilution therapy and palliative situations. Port-a-cath improves quality of life. The purpose of the study is to promote safe patient care by developing uniform guidelines.
I primarily used publications and guidelines published between 2018-2023, searching for uniform procedures and protocols related to the provision of port-a-cath.
The examination revealed that in modern care there are discrepancies and deficiencies in the care and management of these devices, which can lead to the development of catheter-related complications (e.g. CLABSI).
To provide safe patient care and to avoid complications, nurses need to be aware of important definitions and the correct procedure, which requires uniform guidelines.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The prevalence of asymptomatic, haemodynamically stable, septic, elderly patients in oxyological care is considerable. Our aim was to describe the prevalence, sociodemographic characteristics, triage category, disposition, and lactate level of these patients.
Our research method was a quanitative, retrospective document analysis. Our sample group consisted of patients treated for sepsis between 01/01/2024 and 29/02/2024, aged 65 years or older, with atypical symptoms (n=103).
Septicaemia BNO-code, 44.23% of patients diagnosed with septicaemia had elderly, cardiorespiratory stable, asymptomatic sepsis. The study found that residents of social institutions had a significantly higher proportion of deaths from sepsis (p=0.004). We found that the group of triage categories that were re-generated based on NEWS scores was significantly lower (p=0.000).
Asymptomatic sepsis in old age is a major disease process with a high mortality rate. The development of a standardised care protocol could be useful.
]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[This article discusses the etymology of the Hungarian word ‘nővér’ (sister, nurse). This word means a female sibling (‘woman+blood’), and its meaning later expanded to mean a sister (nun) in a religious order (from the Latin soror). Its usage to denote a woman tending to the sick derives from the fact that this job was done by nuns. In modern usage, members of the nursing personnel continue to be addressed as “nővér” (sister), although men have also appeared in their ranks in large numbers, but in the official job description they are referred to as “ápoló” (nurse).]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The events of the SARS-COV-19 pandemic have highlighted the need to focus on a number of tools and methods to improve the delivery of healthcare. Telemedicine can help in this innovation. The use of telemedicine during the Covid-19 pandemic was new in our country, but has long been used abroad. International experience, as well as that we gained during the covid pandemic, shows that the methodology is worth using in the domestic health care system in the future. The primary aim of this paper is to introduce the concepts related to telehealth. A sub-objective is to briefly review international practice. With our study we want to help to increase the knowledge of health professionals about telemedicine.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The aim of the research was to examine how well healthcare professionals can balance their work and personal life. The study also looked into the current health status, overall well-being, and satisfaction with life and work of the professionals.
The cross-sectional study was conducted among Hungarian healthcare professionals between February 18 and March 10, 2024, using simple random sampling technique. Data collection was done through a web-based anonymous, self-administered questionnaire application. Data analysis was carried out using the SPSS 25.0 statistical software with the application of the Chi-square test. The significance level was set at p≤0.05.
A total of 224 individuals completed the survey. Their average age was 49.99 (±9.49) years and 93.8% of them were female. In the work-family conflict scale, respondents scored an average of 10.96 (±3.04) points on the ’Work-to-Family Conflict’ subscale, while they scored an average of 5.9 (±2.2) points on the ’Family-to-Work Conflict’ subscale. On average, the healthcare professionalss rated their health status as 3.48, and 59.4% of them have chronic illnesses.
The results point to the importance for healthcare organizations to address the work-life balance of healthcare professionals. The compatibility of work and family life (flexible working hours, part-time positions) is a critical factor in attracting and retaining new talents, as well as in retaining skilled workforce.]
Clinical Neuroscience
Stigma is a widespread phenomenon in Parkinson’s disease (PD) and has been shown to affect the quality of life of individuals. This study aims to assess the level of stigma and identify the factors contributing to stigma in patients with PD in Turkey. A total of 142 patients diagno¬sed with PD between June 2022 and March 2023 were included in the study. Sociodemographic data were collected using a sociodemographic information form.
Clinical Neuroscience
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, frequently result in mood disorders among affected individuals. It is established that neuropathic pain arising from traumatic neuropathies is also linked to mood disorders. This study investigates the influence of neuropathic pain on the development of mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries, following the earthquake centered in Kahramanmaraş on February 6, 2023.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The purpose of the study is to find correlations between sarcopenia, falls, falls and social isolation in the elderly population.
This study chose a genre of literature review, in which seven articles were analyzed.
Weakness, falls and social isolation are closely related, which is also supported by statistical calculations.
The results of the literature review will help all professionals working in the care of the elderly to understand how different geriatric complex conditions are related to each other.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[To assess lay parents’ knowledge and attitudes towards fever; to find out to what extent they know and use fever control recommendations for their children; to assess whether the perceptions of parents who manage their children’s fever independently have changed. And to put this snapshot into context, it summaries how the perception of fever has changed through history to the present day.
The cross-sectional study was conducted between November 12, 2022 and December 24, 2022 through self-constructed online questionnaire among non-medical parents.
Most parents are not even aware of the basic concepts. If they do not have to manage their own fever, but their child’s, they will begin to reduce the fever much sooner. 58% of those surveyed also use physical methods (compresses, cooling baths) in addition to medication. Many misconceptions about fever persist. There is an opinion among parents that it is better to consult a physician than to manage fever on your own.
Disseminating knowledge about fever and tackling misconceptions would be vital to reduce the burden of overused emergency care.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The field of healthcare is constantly developing, and the role of nurses is of paramount importance in the optimal care and treatment of patients. Practical education for nurses is essential to acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to provide complex health care to patients. However, traditional hands-on teaching methods are time-consuming and sometimes offer limited opportunities to practice in varied and critical clinical situations.
This article reviews the place and benefits of simulation in the practical education of nurses. The simulation gives nurses the opportunity to practice handling different cases in a realistic, controlled environment, thus improving their decision-making skills and communication skills. After a brief historical overview, it will be presented what types of simulation tools and methods are available for the practical education of nurses and how they support the students’ knowledge acquisition and development.]
Epilepsy in women – Part 2
An update on approved and emerging drugs for the treatment of postpartum depression
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]