[Decreasing Fever now and then: The Past Living with us]
SIMON János
DECEMBER 18, 2023
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2023;36(6)
SIMON János
DECEMBER 18, 2023
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2023;36(6)
Szöveg nagyítása:
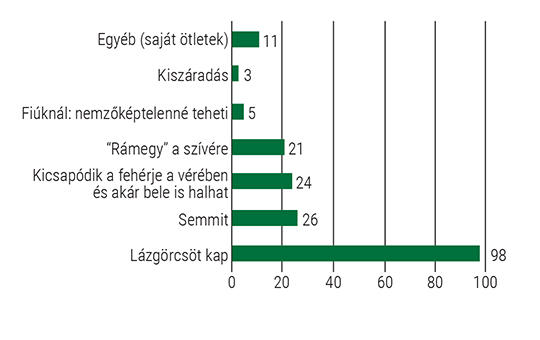
[To assess lay parents’ knowledge and attitudes towards fever; to find out to what extent they know and use fever control recommendations for their children; to assess whether the perceptions of parents who manage their children’s fever independently have changed. And to put this snapshot into context, it summaries how the perception of fever has changed through history to the present day.
The cross-sectional study was conducted between November 12, 2022 and December 24, 2022 through self-constructed online questionnaire among non-medical parents.
Most parents are not even aware of the basic concepts. If they do not have to manage their own fever, but their child’s, they will begin to reduce the fever much sooner. 58% of those surveyed also use physical methods (compresses, cooling baths) in addition to medication. Many misconceptions about fever persist. There is an opinion among parents that it is better to consult a physician than to manage fever on your own.
Disseminating knowledge about fever and tackling misconceptions would be vital to reduce the burden of overused emergency care.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The independent living of older people, who form an increasing proportion of society, is fundamentally determined by falls and the fear of falling. Fear of falling becomes pathological when loss of self-confidence and experience of fear of falling become persistent. Consequently, physical activity of older people becomes also limited, which compromises their future functional abilities and increases the risk of institutionalisation. This narrative review discusses the terminology used in the literature, the prevalence of fear of falling, and the methods used to evaluate it. It also outlines how it can be prevented and how it can be reduced (or even eliminated) based on current research.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[In the course of our research, we compared the pre-pregnancy test mass index of Hungarian women with the results of the National Nutrition and Nutritional Status Examinations.
Our cross-sectional study was conducted between 01.01.2020 and 01.08.2020. During the nonrandom, targeted, expert sample selection, the target group included pregnant women or mothers raising at least one minor child (N=1423). Exclusion criteria include the omission of mandatory questions. Our survey was done online, with a self-filled questionnaire, anonymously. In the questionnaire, we used sociodemographic, anthropometric, pregnancy and nutrition-related questions. The data were analyzed with IBM SPSS 25.0 statistical software, descriptive statistics and tables.
The normal BMI was typical only for those under 20 years of age (21 kg/m2). The largest proportion of people over 20 years of age were overweight (>25 kg/m2). Every fourth pregnant woman (43.4%) and every third mother (33%) reported that excess body weight does not bother them at all.
Based on the body mass index, Hungarian women are already overweight before pregnancy, which entails an increased health and financial burden.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Educational programs play a key role in managing the educational process. They contain important and useful information for training institutions, instructors and students, for organizing and conducting training. This issue is of particular importance nowadays, as the strengthening of the autonomy of vocational training institutions and the end of the compulsory nature of the program curricula present new challenges to schools. Based on the regulations, vocational training institutions must independently develop their training programs (of which the educational program is a part) based on the training and output requirements (KKK) and can no longer rely on the guidelines of the centrally issued program curricula (PTT).
The following summary study reviews methods and approaches that can assist educators in creating quality nursing education programs.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The aim of the research study was to get a better picture of the patient’s quality of life with Huntington’s disease and their caretaker’s. One of the main topics of the investigation was the family, because taking care of a Huntington’s patient can have a big impact on their lives. Our further concern was to introduce the concept for the families and test their open mindedness, if they would take assistance from nurse graduates to make the patient’s medical journey shorter and help with their everyday life challenges.
The cross-sectional research was done by validated tests, as well as, self-made tests which contained socio-demographic data and questions regarding the disease. The trial took place at Semmelweis University, at the Institute of Genomic Medicine and Rare Disorders in collaboration with the patients and their families.
According to the patients, their life quality is affected more physically than their mental health. The experiment showed that the disease has a big impact on the quality of life of the family members. The family members would be more open in regards to accepting help from advanced practice nurses.
Huntington’s disease has a negative impact on the quality of life of the patients and their families. It would be adequate to study if the provided help of advanced practice nurses could improve their quality of life. ]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[ ]
Clinical Neuroscience
We aimed to investigate the association between fluoxetine use and the survival of hospitalised coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia patients. This retrospective case-control study used data extracted from the medical records of adult patients hospitalised with moderate or severe COVID-19 pneumonia at the Uzsoki Teaching Hospital of the Semmelweis University in Budapest, Hungary between 17 March and 22 April 2021. As a part of standard medical treatment, patients received anti-COVID-19 therapies as favipiravir, remdesivir, baricitinib or a combination of these drugs; and 110 of them received 20 mg fluoxetine capsules once daily as an adjuvant medication. Multivariable logistic regression was used to evaluate the association between fluoxetine use and mortality. For excluding a fluoxetine-selection bias potentially influencing our results, we compared baseline prognostic markers in the two groups treated versus not treated with fluoxetine. Out of the 269 participants, 205 (76.2%) survived and 64 (23.8%) died between days 2 and 28 after hospitalisation. Greater age (OR [95% CI] 1.08 [1.05–1.11], p<0.001), radiographic severity based on chest X-ray (OR [95% CI] 2.03 [1.27–3.25], p=0.003) and higher score of shortened National Early Warning Score (sNEWS) (OR [95% CI] 1.20 [1.01-1.43], p=0.04) were associated with higher mortality. Fluoxetine use was associated with an important (70%) decrease of mortality (OR [95% CI] 0.33 [0.16–0.68], p=0.002) compared to the non-fluoxetine group. Age, gender, LDH, CRP, and D-dimer levels, sNEWS, Chest X-ray score did not show statistical difference between the fluoxetine and non-fluoxetine groups supporting the reliability of our finding. Provisional to confirmation in randomised controlled studies, fluoxetine may be a potent treatment increasing the survival for COVID-19 pneumonia.
Clinical Neuroscience
In aging societies, the morbidity and mortality of dementia is increasing at a significant rate, thereby imposing burden on healthcare, economy and the society as well. Patients’ and caregivers’ quality of life and life expectancy are greatly determined by the early diagnosis and the initiation of available symptomatic treatments. Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine have been the cornerstones of Alzheimer’s therapy for approximately two decades and over the years, more and more experience has been gained on their use in non-Alzheimer’s dementias too. The aim of our work was to provide a comprehensive summary about the use of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer’s and non-Alzheimers’s dementias.
Clinical Neuroscience
We review the literature on REM parasomnias, and their the underlying mechanisms. Several REM parasomnias are consistent with sleep dissociations, where certain elements of the REM sleep pattern emerge in an inadequate time (sleep paralysis, hypnagogic hallucinations and cataplexy) or are absent/partial in their normal REM sleep time (REM sleep without atonia, underlying REM sleep behavior disorder). The rest of REM parasomnias (sleep related painful erection, catathrenia) may have other still unclear mechanisms. REM parasomnias deserve attention, because in addition to disturbing sleep and causing injuries, they may shed light on REM sleep functions as well as the heterogeneous etiologies of parasomnias. One of them, REM sleep behavior disorder has special importance as a warning sign of evolving neurodegenerative conditions mainly synucleinopathies (some cases synucleinopathies themselves) and it is a model parasomnia revealing that parasomnias may have by autoimmune, iatrogenic and even psychosomatic etiologies.
Clinical Neuroscience
[In this paper we present the Comprehensive Aphasia Test-Hungarian (CAT-H; Zakariás and Lukács, in preparation), an assessment tool newly adapted to Hungarian, currently under standardisation. The test is suitable for the assessment of an acquired language disorder, post-stroke aphasia. The aims of this paper are to present 1) the main characteristics of the test, its areas of application, and the process of the Hungarian adaptation and standardisation, 2) the first results from a sample of Hungarian people with aphasia and healthy controls. Ninety-nine people with aphasia, mostly with unilateral, left hemisphere stroke, and 19 neurologically intact control participants were administered the CAT-H. In addition, we developed a questionnaire assessing demographic and clinical information. The CAT-H consists of two parts, a Cognitive Screening Test and a Language Test. People with aphasia performed significantly worse than the control group in all language and almost all cognitive subtests of the CAT-H. Consistent with our expectations, the control group performed close to ceiling in all subtests, whereas people with aphasia exhibited great individual variability both in the language and the cognitive subtests. In addition, we found that age, time post-onset, and type of stroke were associated with cognitive and linguistic abilities measured by the CAT-H. Our results and our experiences clearly show that the CAT-H provides a comprehensive profile of a person’s impaired and intact language abilities and can be used to monitor language recovery as well as to screen for basic cognitive deficits in aphasia. We hope that the CAT-H will be a unique resource for rehabilitation professionals and aphasia researchers in aphasia assessment and diagnostics in Hungary. ]
Clinical Neuroscience
Autism spectrum disorder is a neurodevelopmental disorder with a heterogeneous presentation, the etiology of which is not clearly elucidated. In recent years, comorbidity has become more evident with the increase in the frequency of autism and diagnostic possibilities of inborn errors of metabolism. One hundred and seventy-nine patients with diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder who presented to the Pediatric Metabolism outpatient clinic between 01/September/2018-29/February/2020 constituted the study population. The personal information, routine and specific metabolic tests of the patients were analyzed retrospectively. Out of the 3261 patients who presented to our outpatient clinic, 179 (5.48%) were diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder and were included in the study. As a result of specific metabolic examinations performed, 6 (3.3%) patients were diagnosed with inborn errors of metabolism. Two of our patients were diagnosed with classical phenylketonuria, two with classical homocystinuria, one with mucopolysaccharidosis type 3D (Sanfilippo syndrome) and one with 3-methylchrotonyl Co-A carboxylase deficiency. Inborn errors of metabolism may rarely present with autism spectrum disorder symptoms. Careful evaluation of the history, physical examination and additional findings in patients diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder will guide the clinician in the decision-making process and chose the appropriate specific metabolic investigation. An underlying inborn errors of metabolism may be a treatable cause of autism.
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.