The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2006;16(10)
Content
[CHEMOPREVENTION OF COLORECTAL CANCER]
[Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer mortality in developed countries; in Hungary, the mortality has almost tripled in the past four decades. A decrease in mortality can only be expected from a consistently applied diagnostic and management strategy, including preventive measures. Primary prevention is defined as dietary, medicinal and lifestyle actions that can reduce the risk of developing cancer in people with average risk. Secondary prevention is the prophylactic treatment of high-risk patients or praecancerous lesions; tertiary prevention is the prevention of recurrence in patients cured of colorectal cancer. Drugs or dietary supplements used for chemoprevention block, delay or reverse the process of carcinogenesis. The most important drugs used for chemoprevention are aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Long-term administration of these drugs reduces the risk of developing colorectal cancer or adenoma both in the high-risk and in the average-risk population. The risk-lowering effect seems to be in positive correlation with the dose and the duration of use. Other chemoprophylactic drugs such as calcium, folate, oestrogen and antioxidants, as well as 5-aminosalicylates in patients with ulcerative colitis are also discussed in this review. Based on the current knowledge, chemoprophylaxis of colorectal cancer is recommended as secondary prevention in patients at high risk (e.g., familial adenomatous polyposis, extensive ulcerative colitis). In contrast, based on adverse event profile and cost-effectiveness analysis, primary prevention with chemopreventive drugs is currently not recommended in the averagerisk population.]
[THE PRESENT STATE AND CURRENT PROBLEMS OF HUNGARIAN PSYCHIATRY]
[The changes in attitude that occurred in general medicine 2 to 3 decades ago had a fundamental impact on psychiatry by giving it a greater emphasis due to the wider acceptance of the bio-psycho-social model. In parallel with this change an English-speaking professional dominance took over the former German-French traditions. Hungarian psychiatrists keep pace with the development of psychiatry, with remarkable achievements in some areas. In everyday patient care and clinical practice, however, severe difficulties are encountered. The paper reviews the trends in practice, education, research, and also the development of professional organizations. Certain ethical implications of the sociocultural changes and future trends of national psychiatry are also summarized.]
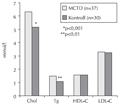
[STUDY OF PARAOXONASE ACTIVITY IN MIXED CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISEASE]
[INTRODUCTION - Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) is an inflammatory autoimmune disease with multiple organ involvement. Immune- inflammatory processes play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. The connection between inflammatory parameters and atherosclerosis in MCTD has not yet been studied. Lipid abnormality is an important risk factor of atherosclerosis. Among the lipids, HDL is protective, which is in part due to the antioxidant effect of paraoxonase. In this paper, the lipid profiles and paraoxonase activities of MCTD patients were studied and the factors causing abnormalities were investigated. PATIENTS AND METHODS - Thirty-seven patients with MCTD, who had not taken any lipid lowering drugs in the past 2 months, were enrolled in the study. Thirty healthy individuals served as controls. At the time of the study the mean age of the MCTD patients was 51.2 ± 9.5 years, and the mean disease duration was 11.0 ± 7.2 years. Paraoxonase activity was determined by spectrophotometry, lipid profiles were determined by a Cobas Integra 700 Analyser, the von Willebrand factor antigen (vWFAg) was measured by turbidimetry in platelet-poor plasma and the thrombomodulin and anti-endothelial cell antibody (AECA) measurements were carried out by ELISA methods. RESULTS - Paraoxonase activity in the MCTD patients was lower than in the control population (118.5 ± 64.6 U/l vs. 188.0 ± 77.6, p<0.001). The arylesterase activity was also significantly lower in the patients (p<0.001). The reduction of paraoxonase activity was in correlation with the age of the patients, the duration of the disease and with vascular (eye, cardiac, cerebral) disorders. The total cholesterol and triglicerid levels of the patients were significantly increased compared to the control group, while in the apoA1 levels a significant reduction was seen. A very strong correlation was observed between the reduction of paraoxonase activity and the increase of endothelial cell activation markers (thrombomodulin, vWFAg, AECA). There was no difference in the values of patients with or without corticosteroid treatment. CONCLUSIONS - The results suggest that in MCTD there is an increased risk for atherosclerosis. Apart from an elevated cholesterol and triglicerid level, a reduced paraoxonase level and activity may also play a role in the development of atherosclerosis,. Therefore, in patients with MCTD, due to the increased oxidative processes and the impaired elimination of free radicals, a sustained damage to the endothelial cells occurs, which is indicated by increased levels of thrombomodulin, vWFAg, and anti-endothelial antibody.]
[ENTERAL ADMINISTRATION OF N-3 POLYUNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS IN ACUTE PANCREATITIS]
[BACKGROUND - The main determinant of outcome in acute pancreatitis is the extent of inflammation and pancreatic necrosis. Early administration of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) may prevent the development of severe complications through modulation of eicosanoid synthesis and cytokine release. PATIENTS AND METHODS - In the prospective, randomised clinical trial 14 patients with acute pancreatitis received n-3 PUFAs (3.3 g/day for 5- 7 days) as a supplement to their enteral formula in the form of fish oil, and another 14 patients receiving enteral nutrition served as a control group. Measurements of erythrocyte superoxidedysmutase activity, serum total antioxidant status, C-reactive protein and praealbumin concentrations were performed at admission and at day 3, 7 and 14. Beside routine laboratory and imaging examinations, the fatty acid and vitamin A and E concentrations of the serum lipid fractions were also determined at admission and at day 7 of the jejunal nutrition. The endpoints of the study were the duration of hospitalisation, the duration of jejunal nutrition and the frequency of complications. RESULTS - A significantly higher superoxidedysmutase activity was observed in patients receiving n-3 fatty acids at day 3 of the treatment. The n-3 to n-6 long chain PUFA ratio increased significantly in the serum lipids of the patients receiving n-3 PUFA supplementation, whereas remained unchanged in the controls. Supplementation resulted in a significant decrease in the length of hospitalisation (13.1±6.7 vs. 19.3±7.2 days, p<0.05) and jejunal feeding (10.6±6.7 vs. 17.6±10.5, p<0.05). Complications developed in 6/14 (42%) of the treated group and in 9/14 (64%) of the control patients. CONCLUSION - Enteral administration of n-3 PUFAs in acute pancreatitis may promote earlier recovery by moderating inflammation.]
[SIMULTANEOUS PRESENCE OF GIST AND MALT-LYMPHOMA OF THE STOMACH IN A HELICOBACTER PYLORI NEGATIVE PATIENT]
[INTRODUCTION - The simultaneous presence of gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALT) and a gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is an extremely rare finding that has not been published until now. CASE REPORT - The authors report on a 78- year-old man who was referred to their department with an emergency upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Urgent gastroscopy revealed a bleeding ulcer in the middle third of the stomach. On the follow-up endoscopy 6 weeks later, an umbilicated polypoid lesion was found proximal to the healed ulcer, which was subsequently removed by elective surgery. Histology and immunohistochemical staining of the specimen for c-Kit confirmed the diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumour. A few weeks later the patient was readmitted because of haematemesis. Upon detailed histological examination of the biopsy specimens taken from the multiple superficial ulcers found near the previous lesion, MALT-lymphoma was diagnosed. The absence of Helicobacter pylori was confirmed by repeated histological examinations, serology and urea breath test. CONCLUSION - This is the first report on a patient with simultaneous presence of a gastrointestinal stromal tumour and gastric mucosaassociated lymphoid tissue lymphoma with H. pylori negativity. Several observations suggest that the development of malignant tumours of the stomach is also associated with H. pylori infection. In view of the reported case, the possibility of a common aetiology of these two neoplasms other than H. pylori infection is discussed.]
[EPITHELIAL CYST OF THE SPLEEN COMBINED WITH HAEMANGIOMA]
[INTRODUCTION - The most common symptom of spleen diseases is splenomegaly of various extent, which may be accompanied by pain in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, as well as by fever, jaundice, haemorrhages. CASE REPORT - A 24-year-old woman with an abdominal mass that could not be determined by imaging was operated on and an epithelial cyst of unusually large size was identified in the spleen. CONCLUSION - The pathological background, diagnostic possibilities, and treatment options are discussed for this rare disease.]
[’THE CYCLE OF VIOLENCE’ IN THE LIFE OF ALCOHOLICS]
[INTRODUCTION - ’The cycle of violence’ have long been a known phenomenon. The present research is aimed at answering the question of whether abuse suffered in childhood creates a tendency to aggressive behaviour in adulthood and whether there is a connection between these two forms of behaviour. METHODS - The sample studied comprised 235 clinically treated alcoholics. The instruments used for the investigation were the European Addiction Severity Index (EuropASI), the Buss and Perry Aggression Questionnaire, and the Janus Questionnaire. RESULTS - The most important finding is that persons who were physically abused in childhood by their parents were very likely to strike or beat someone in the course of their lives (χ2=9.79, p<0.001). Within the most aggressive group, 18 % had not suffered abuse in childhood, while 81 had been abused (χ2=13.25, p<0.001). If the patient had been physically abused, struck or beaten, that person later abused, struck or beat someone else (Pearson r=.397). CONCLUSION - The results draw attention to the importance of preventing and treating aggression in alcoholics undergoing clinical treatment.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]