The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2004;14(01)
Content
[THE METABOLIC SYNDROME CLINICAL APPEARANCE, DIAGNOSIS, PATHOMECHANISM]
[The metabolic syndrome has gone by several names over the past two decades. The diagnostic criteria were proposed by the ATP III of NCEP in 2001 and were accepted by European Society of Cardiology and European Society of Hypertension in 2003. The criteria (abnormal waist rate, HDLcholesterol, triglyceride, blood pressure and fasting glucose) are listed and the presence of any three of these factors is considered sufficient for diagnosis. The prevalence of syndrome affects about a quarter of the Hungarian population with hypertension. The metabolic syndrome is associated with premature cardiovascular morbidity and mortality including an excess of sudden deaths. According to the recent literature data the main component of the syndrome, the obesity, especially with abdominal fat distribution is associated with hypertension, hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance with related abnormalities of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. The low HDL cholesterol, high triglyceride level and the small, dense LDL cholesterol particles are the parts of lipid component of syndrome. A variety of environmental (obesity, smoking, physical inactivity) and genetic factors (genetic mutations of lipoprotein lipase, hepatic lipase, CETP and PPA receptors) and the impaired FFA metabolism have all been related to lipid abnormalities. Sympathetic hyperfunction participates in the pathogenesis and complications of metabolic syndrome. Possible factors augmenting sympathetic activation include alterations of insulin, leptin, FFA, cytokines, sleep apnoe. Other important factors as the endocrin concept, the hypothalamus-hypophysis- adrenal axis, endothelial dysfunction are discussed. The impaired muscle insulin stimulated glycogen synthesis (FFA induced GLUT-4 inhibition) is the major cellular factor of insulin resistance. There is a continuous process from the insulin resistance state (with hyperinsulinemia) into the 2T diabetes mellitus (with hypoinsulinemia).]
[DIAGNOSTICS AND THERAPY OF ACUTE BLEEDINGS FROM GASTRODUODENAL ULCERS; PROPHYLAXIS OF STRESS ULCER]
[Acute gastrointestinal bleeding is a life threatening condition. Almost 90% of the acute bleeding episodes originate from the upper gastrointestinal tract with a 5-10% mortality rate. Emergency endoscopy is capable to detect the bleeding source offering the chance of endoscopic therapy as well. Injecting epinephrine in a 1:10000 diluted solution into the mucosa surrounding the ulcer is the generally used endoscopic haemostatic method. In ulcer bleeding cases permanent protonpump- inhibitor infusion for 72 hours is the therapy of choice to increase gastric pH and for the stabilization of the coagulum covering the ulcers. Mortality can be decreased by surgery performed in an early elective manner. The most important aim of gastroenterological treatment in ulcer bleeders is to avoid the rebleeding episodes which increase the mortality. Acute bleedings resulting from stress ulcers are typical complications in patients undergoing major surgery and require intensive care unit treatment. The mortality rate of stress ulcer bleeders can reach or even exceed 50%. Occasionally stress ulcers have a large ulcer like appearance but in most of the cases they have an erosive confluent formation. For the prophylaxis of the stress ulcer development and bleeding an effective inhibition of gastric acid secretion is recommended in the perioperative period as well as during the intensive care. Considering gastroenterological aspects protonpump- inhibition therapy offers the most effective protection of gastric mucosal barrier by increasing gastric pH. Despite sucralfate is being frequently used, the recommended stress ulcer prophylactic therapy is permanent PPI (pantoprazole or omeprazole) infusion in a dose of 8 mg/hours. With this prophylactic medication for 48-72 hours stress ulcers can be prevented in most of the cases without any significant adverse event.]
[GENDER ASSOCIATED DIFFERENCES IN THE PROGRESSION OF RENAL DISEASES]
[Increasing evidence suggests an important role of gender in the incidence, progression and different therapeutic possibilities of several diseases. Recent data demonstrated gender associated differences in the development and progression of chronic renal diseases. Present work reviews sexual dimorphism in different chronic renal diseases, summarizes underlying pathophysiological processes and therapeutic possibilities focusing on the role of gender. New evidences may present the base of gender based therapies in the future.]
[A NEW DISCIPLINE IN THE CENTER OF MEDICAL RESEARCH AND CLINICAL PRACTICE - THOUGHTS ON BIOINFORMATICS]
[Bioinformatics is one of the most important element of genomic research revolutionising biomedical science. This review describes the phenomena of genomic variance and comparative genomics. Briefly, the review summarises the identification procedure of new genes and gene expression patterns highly important in diagnostics. Bioinformatic procedures make possible the rapid detection of pathogens and have principal role in molecular drug design technologies.]
[LEGIONNAIRES’ DISEASE]
[Legionellae are important causative agents of nosocomial and community acquired pneumonias, the prevalence varying between 2-30%. The number of verified infections are increasing from year to year, which may be the consequence of the more sensitive and commonly applied laboratorical methods or can be explained by the spread of non-natural living environments created by humans. The outcome of Legionella infections are strongly determined by the host immune system, the comorbidities, the time to the diagnosis made and the initiated treatment. This review focuses on the various clinical manifestations of the Legionella infections, and summarises the diagnostic criteria and therapeutic methods in practice.]
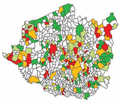
[LOCAL INEQUALITIES IN THE UTILIZATION OF SPECIAL HOME NURSING IN THE SOUTH-TRANSDANUBIAN REGION]
[INTRODUCTION - The aim of this study is to analyse the local inequalities in the access and utilization of special home nursing within Hungary focusing on the South-Transdanubian Region. DATA AND METHODS - In the first part of the study we compared the indicators of the access and utilizations of special home nursing at national and county level. In the second part of the analyses we made a detailed analyses of utilization data of home nursing in the three counties (Baranya, Somogy, Tolna) of the South- Transdanubian Region of Hungary. Data is derived from the financial database of the National Health Insurance Fund of Hungary for the period 1998-2002. RESULTS - The access of population to the special home nursing increased from 83,8% (1998) to 95,1% (2002). The utilization rate increased from 74,8% (1998) to 84,1% (2002). Within the South-Transdanubian Region we found significant local inequalities in the utilization of services (number of cases, number of visits), which were represented by the tools of geographical information system. CONCLUSIONS - There have been significant differences in the access and utilization of home nursing with remarkable within country inequalities.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]