The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2003;13(08)
Content
[ACTUAL OBJECTIVES OF CARDIAC REHABILITATION]
[Cardiac rehabilitation programs are performed to decrease the physiologic and psychological effects of cardiac illness, reduce the risk of reinfarction and cardiac symptoms, stabilize the arteriosclerotic process and enhance the psychosocial status of selected cardiac patients. The cardiac rehabilitation intervention should be integrated into multifactorial secondary prevention program involving hospital phase, medical evaluation and adequate oral and interventional treatment, risk factor modification, prescription of exercise training, education and psychosocial counseling. These rehabilitation programs should be followed by long term risk reduction and secondary prevention program directed by the family physicians. On the basis of the review of scientific literature, the authors present the important components of cardiac rehabilitation and address actual objectives like new indications, selection of a professional rehabilitation team, appropriate training programs, counseling and education.]
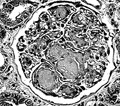
[THE VALUE OF RENAL BIOPSY IN DIABETES]
[The relentless increase of patients with kidney failure requiring renal replacement therapy has been documented world-wide. Recently, diabetic renal diseases has become the major cause of end-stage renal disease in the United States and in western Europe and is forecasted to become the most frequent cause of end-stage renal disease in Hungary. The most common renal lesion in type 1 as well as in type 2 diabetes is diabetic nephropathy. However, in the last few years numerous studies have demonstrated that there is a difference between patients with type 1 and those with type 2 diabetes in the expression and frequency of their renal disease. In type 1 diabetes a histological examination should only be made when a patient has features atypical of diabetic nephropathy and the indications of renal biopsy are well known. At the same time there is no agreement on renal biopsy indications in type 2 diabetes. In this review, we will summarise the characteristic features of diabetic nephropathy and other kidney alterations in the diabetic patient. Furthermore, we will raise the question of the renal biopsy indications and the more extensive use of the renal biopsy in type 2 diabetic patients for more effective prevention and treatment strategies.]
[EXERCISE-INDUCED BRONCHOCONSTRICTION]
[Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction describes the transient narrowing of the airways occurring during and most often after vigorous exercise. The mechanism of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction remains elusive, although airway drying and cooling plays a prominent role. The severity of this reaction depends on the temperature and the water content of the inspired air, the type and concentration of air pollutants inspired and the intensity of the exercise. Diagnosis of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction should include baseline spirometry followed by an exercise challenge test. The exercise can be a free-running test or a laboratory based test using a cycle-ergometer or a treadmill. Pre- and post-exercise pulmonary function should be compared, 10%-15% postexercise fall in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) is used as a diagnostic criteria (10% in laboratory test, 15% in free-running test). Heat loss, water loss, post exertional airway rewarming and the role of several mediators have been proposed as possible mechanisms responsible for the airway obstruction induced by exercise. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction can be easily diagnosed and treated in the majority of patients. When properly treated, asthmatic individuals should be able to participate or compete in the majority of sports.]
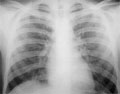
[PRESENTATION OF DIFFUSE INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES BY THE NEW CLINICORADIOLOGICAL- PATHOLOGICAL ASPECT]
[The aim of the authors was to overview the different forms of diffuse interstitial lung disease based on newly established radiological (HRCT) pattern and histopathological analysis beyond the clinical picture. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is emphasized having also historical importance and possible therapeutic antifibrotic interventions are discussed as well.]
[NEW DISORDERS OF EATING AND OF BODY IMAGE]
[Eating disorders show an important change in the last few decades concerning their frequency and clinical picture, as well. Besides bulimia nervosa, which was described two decades ago, muscle dysmorphia appeared ten years ago as a special body image disorder of males, regarded as a reverse form of anorexia nervosa in females. Eating disorder, body builder type was described only in 2000, meaning an overconcern about the body composition and muscle mass, accompanied by strict dieting rules. Another type of these disorders was described also in 2000, the nontraditional gender role in women, which is a strong preference for male characteristics and activities, the person being comfortable with her sex, while there is no intersex condition. This overview discusses the proposed diagnostic criteria and the role of some sociocultural factors in these recent disorders.]
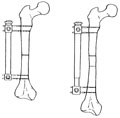
[LIMB LENGTHENING]
[The method of gradual limb lengthening plays a significant role in equalizing limb discrepancies, making dwarfs taller, correcting axial and other deformities coexisting with limb deficiency. Limb lengthening is carried out by one of two basic methods: diaphyseal lengthening with the Wagner unilateral distraction apparatus or metaphyseal lengthening with a series of rings and crossed K-wires. Gradual limb lengthening is presently having its golden days. At our institution 302 limb lengthening intervention were done between 1977 and 2002, 164 cases with Wagner, 137 cases with Ilizarov method, and one distraction epiphyseolysis. In average, 4.1 cm lengthening was achieved, 18.4% of the original length of the bone. The high incidence of complications was due to superficial infections at the entry points of the Kwires, infrequently worsening the outcome of the operation. Operative limb lengthening performed with appropriate indications and technique is a successful and rewarding area of orthopaedic surgery.]
[CEREBRAL AMYLOID ANGIOPATHY - A FATAL CASE OF RECURRENT MULTIFOCAL CEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE]
[Atherosclerosis and hypertension are the leading etiological factors in the pathogenesis of cerebral hemorrhage. With old age though, several other factors may appear of which cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) is of major importance. This condition is characterized by the deposition of β-amyloid in the leptomeningeal vessels as well as in the small and medium sized arteries of the cerebral cortex and it is not associated with systemic amyloidosis. This pathological protein is also seen in the brains of otherwise healthy older individuals and may also appear in other diseases such as Alzheimer disease, Down-syndrome, vascular malformations, spongiform encephalopathy and dementia pugilistica. The condition may be asymptomatic but it may also cause cerebral hemorrhage, dementia or various transient neurological symptoms. Most cases are sporadic, but familial subtypes have also been described.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]