The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2003;13(01)
Content
[Cardiovascular diseaes and the kidney]
[From pathophysiological point of view, the kidney is an integral part of the cardiovascular system. Renal diseases adversely affect the cardiac functions, and disturbances of the cardiovascular system affect adversely renal functions, causing either the decrease of left ventricular functions or manifesting in overt chronic heart failure. Regarding the cardiac manifestations of renal diseases, characteristic features are the symptoms of left ventricular volume and pressure overload, the metabolic effects of the ”uremic toxins” and the frequent infections associated with dialysis and compromised immunologic state, the secunder hyperparathyreosis, as well as the associated conditions like hypertension, diabetes mellitus and coronary atherosclerosis. All these can be the explanation for the frequent cardiovascular death of chronic kidney disease patients. It also stresses the outstanding importance of the decrease of cardiovascular hazard of chronic renal disease patients. The strategy should comprise of an adequate antihypertensive treatment (ACE-inhibitor, AT-II blocking and calcium antagonist), strong antidiabetic control of diabetic patients and the adequate treatment of dyslipidaemia (if exists), as well as antithrombotic aspirin treatment.]
[Errors and mistakes in laboratory medicine]
[The unacceptable results of laboratory testing derive from the insufficient preanalytical, analytical and postanalytical processes. In addition to the analytical errors, there are inappropriate testing orders which reflect the failures of diagnostic strategy, and either result in excess testing orders without additional new informations, or in the lack of testing order that would be necessary for efficiency of patient's care. An increasing number of study demonstrate that in majority of cases the cause of erroneous results can be traced back to mistakes in the preanalytical phase (preparation of patient, sample collection). The total quality of the diagnostic strategy depends both on the compliance of tests according to the health condition of patient and the quality performance of laboratory processes. The elimination of the preanalytical errors and the formulation of proper diagnostic strategy requires a close cooperation between physicians and the diagnostic workplaces as well as the application of multidisciplinary guidelines which specify the quality requirements of the whole diagnostic process. Such guidelines are not prepared for specific professional activities and do not replace lower-level professional standards (e.g. for test procedures). Based on evidence-based medicine and the recommendations of international experts such guidelines should cover all elements of quality assurance necessary to achieve efficient diagnostic strategy and testing. There is little doubt that such recommendations will also be useful for rational financing of the health care system.]
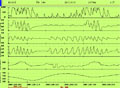
[Advances in sleep diagnostics]
[Despite the insufficient financial support, the number of the laboratories for sleep diagnostics and the examined patients are rising. The CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) equipment playing the main role in the treatment of the obstructive sleep apnoe syndrome (OSAS) is recently available from three neurological centres (Budapest, Debrecen, Pécs). These centres can prescribe the machine as a ”model experiment” with 85% support given by the State Health Care. The increase of the number of the licensed hospitals is expected in the near future, the only condition is the polysomnography background. Differential diagnostics (narcolepsy, RLS, PLMS, sleepdependent laryngospasm, disorders of the circadian rhythm) and the follow-up of the CPAP using patients (indication, contraindication, compliance, CPAP pressure setting, CPAP therapy control) have been emphasized.]
[The prevention of eating disorders]
[Eating disorders (obesity, anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa) present an increasing public health problem. Research relating to the prevention of these disorders show controversial results. On the basis of some observations prevention programs performed in young populations are effective, other studies present paradoxical effect. The present overview summarises the prevention strategies and discusses a complex program developed in Norway as well as the recommendations of the British Medical Association. In primary prevention reactive and proactive strategies can be distinguished. It is essential that prevention strategies should be realised at a macrosocial level. The real and effective prevention must involve the change in the attitude of the sociocultural environment and the influence of the cultural values mediated by mass media.]
[Hungarian Hypertension Study - EMMA]
[INTRODUCTION - Ischaemic heart disease and stroke show rapidly increasing incidence and lead mortality statistics in developed countries. Hypertension is the main risk factor for both diseases. With the support of Hungarian Society of Hypertension we performed a public opinion survey on hypertension and on the medicines of its treatment among Hungarian adults between October and December 2001. SUBJECTS AND METHODS - The Omnibus investigation using standardised questionnaires was carried out by monthly home interviews of 5000 participants. RESULTS - One aim of the study was to determine the prevalence of hypertension and the usage of drugs in the population over 35 years. Persistent high blood pressure had been diagnosed in 39% of these population (n=1360). When choosing drugs the lack of side effects is the most important characteristic beside efficacy in this age group. As the study results show, physicians consider regular blood pressure control and screening programs as most important factors for patients with hypertension. CONCLUSION - The results of EMMA study revealed habits and attitudes of regular drug intake. Results also outline the characteristics of the desirable drug that are best accepted by patients - drugs, which patients are faithful to.]
[Evidence-based practice guidelines for nursing and rehabilitation of stroke patients]
[Stroke is a common problem, being the third most frequent cause of death in the United Kingdom and Hungary, accounting for about 20% of bed occupancy. It is also an important cause of morbidity and disability mainly for those aged over 65. As a result, stroke care constitutes as an important part of health services use. Home care services working in the field of stroke rehabilitation have not used a unified evidence-based approach and well-described professional principles and protocols. There was little cooperation between the teams working in the institutional rehabilitation and home care rehabilitation services. No agreed rehabilitation processes, and standardised scales and documentation, showing the change of quality of life, were in use. There were no quality indicators and efficiency measures of nursing and no provision of services either. The Hungarian Nursing Association played a pioneering role in the introduction and dissemination of Evidence Based Nursing in Hungary and in adopting it into routine clinical practice. The successful implementation of the Association's project could be a good example for another field of care and nursing in Hungary and other countries in Europe. Our projects are supported by the Department For International Development (UK) in the framework of the TUDOR project. The Hungarian Nursing Association (HNA) developed a postgraduate training programme entitled "Evidence based nursing in practice". The participants were required to be members of the HNA, have a degree in the field of nursing (nurse teacher, degree nurse, nurse director). Members of the target group were all working in the field of stroke rehabilitation at hospitals or out-patient clinics and home nursing. The Hungarian Nursing Association's professional group developed an evidence based practice guideline for rehabilitation of stroke patients, which was published in the Bulletin of the Ministry of Health (11/2002, 23rd May, 2002). These evidence-based stroke rehabilitation guidelines focused on bladder management, position therapy and patient information.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]