[The aim of the research study was to get a better picture of the patient’s quality of life with Huntington’s disease and their caretaker’s. One of the main topics of the investigation was the family, because taking care of a Huntington’s patient can have a big impact on their lives. Our further concern was to introduce the concept for the families and test their open mindedness, if they would take assistance from nurse graduates to make the patient’s medical journey shorter and help with their everyday life challenges.
The cross-sectional research was done by validated tests, as well as, self-made tests which contained socio-demographic data and questions regarding the disease. The trial took place at Semmelweis University, at the Institute of Genomic Medicine and Rare Disorders in collaboration with the patients and their families.
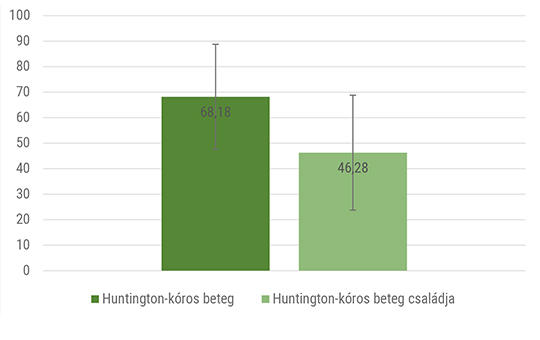
According to the patients, their life quality is affected more physically than their mental health. The experiment showed that the disease has a big impact on the quality of life of the family members. The family members would be more open in regards to accepting help from advanced practice nurses.
Huntington’s disease has a negative impact on the quality of life of the patients and their families. It would be adequate to study if the provided help of advanced practice nurses could improve their quality of life. ]