[Dietetic Aspects of Hospice-palliative Care]
TÓDOR Annamária 1,2
AUGUST 30, 2024
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2024;37(4)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.55608/nover.37.0017
Review
TÓDOR Annamária 1,2
AUGUST 30, 2024
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2024;37(4)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.55608/nover.37.0017
Review
Szöveg nagyítása:
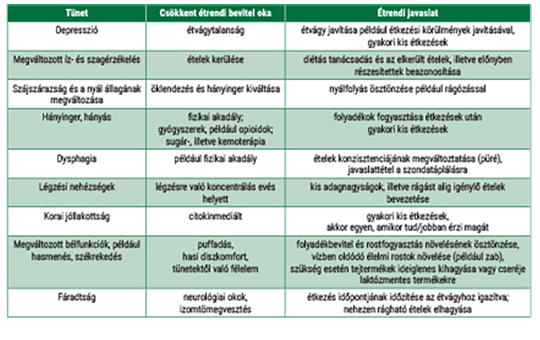
[Patients in hospice-palliative care are treated with the help of a multidisciplinary team, which includes dietittian too, as a member. The tasks of the dietitian are complex, they participate in the malnutrition screening, maintaining and reaching the patients’ appropriate nutritional status, exploring and solving different nutritional problems, shaping the diet according to individual needs, recommending clinical formula, if needed.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The number of individuals diagnosed with cancer among working-age populations is alarmingly increasing, and cancer remains one of the leading causes of death. Over the past few decades, the topic of staying in the labor market has become a worldwide subject of discussion regarding improving the quality of life for employees suffering from terminal illness. In this context, the importance of workplace rehabilitation, a supportive environment, and occupational health care is being increasingly recognized. With appropriate training, occupational health nurses could play a key role in collaborating with affected employees, as they can assist in assessing individual needs and ensuring reasonable accommodations in the workplace. Through their activities, the working conditions designed for terminally ill employees can simultaneously enhance quality of life and enable productive work at the end of life.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Postnatal palliative care is a very under-researched and under-represented area of paediatric palliative care in Hungary.
Aim: The examination was carried out to assess, in the absence of relevant Hungarian protocols, the professional and psychological duties of nurses working in neonatal and pediatric intensive care units regarding the physical, mental, and emotional support of the child and their parents. Additionally, it aimed to identify which support programs and professional training opportunities assist these professionals who are under significant psychological stress.
The quantitative, cross-sectional, comparative study was conducted on a voluntary basis with the participation of 41 individuals, using an anonymous questionnaire method. Additionally, interviews were conducted with professionals in the helping professions (n=3) regarding their duties, experiences, opinions, and knowledge.
In terms of outcomes, it is difficult to draw any conclusions due to low participation, however, questions on newborn pain and behaviour assessment, parent support and caregiver involvement incare fortunately paint a positive picture of neonatal palliative care in this country, in contrast to the lack of supervision and training for professionals in supportive processing which can lead to distress, and burnout.
The quintessence of the research is that there is a need for guidance on the topic for both children, their parents and caregivers, as well as for professional training and supportive environments to ensure more effective bereavement processing and care.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[ ]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The aim of study is to sensitise society to the need for access to hospice care and to raise awareness of the right to end-of-life dignity through the provision of continuous information.
the method chosen was SWOT analysis and in-depth interviews. I asked 30 affected people to describe their own experiences, coping methods and the supportive environment they lived in.
The outcome is shown by the listenership of the podcast conversations, demonstrating that loss can and should be discussed in an open and honest dialogue, that the humane care of terminally ill patients at the end of life requires an open social context in addition to the provision of expertise.
The end-of-life dignity of patients with tumours, and the support of families in this process, is a fundamental task of the hospice palliative care system, which is constantly improving, with the opening of new units nationwide. The social innovation programs are the helping need for enlarging the hospice-palliative health system.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[ ]
Clinical Neuroscience
[Stroke is a serious health problem that has a significant impact on health-related quality of life. Despite the increasing popularity of measuring quality of life among patients, it is not routinely measured in clinical practice, and therefore little is known about how well clinical measures reflect quality of life after stroke. The aim of this study was to investigate the quality of life of patients with acute ischaemic stroke.
For the prospective study, patients diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke at the Neurology Clinic of the Clinical Center of the University of Pécs were selected through convenience sampling between June 2022 and May 2023. Based on the treatments, patients were divided into three groups: mechanical thrombectomy (MT), intravenous thrombolysis (IVT), and standard care (SC). Modified Rankin Scale (Pre-mRS, Follow-up mRS), NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS), and European Quality of Life 5 Dimensions Scale (EQ-5D-5L) were used in the research. Descriptive statistics, paired T-tests, Wilcoxon tests, McNemar tests and Pearson correlation analysis were applied for the analysis (SPSS 25.0; p <0.05).
A total of 198 participants (115 males, 83 females) took part in the study (MT: 50, IVT: 69, SC: 79). The Pre-mRS and follow-up mRS values indicate that the majority of patients in all three groups fell into the mild category (Pre-mRS: 176 participants; 88%, follow-up mRS: 158 participants; 80%). There was a significant improvement in NIHSS scores in all three groups (IVT: 4.36 vs. 1.57, p<0.001; MT: 8.98 vs. 4.50, p<0.001; SC: 4.38 vs. 2.84, p<0.001). The EQ-5D-5L value also significantly increased for all groups (IVT: 0.82 vs. 0.88, p<0.001; MT: 0.63 vs. 0.73, p<0.001, SC: 0.76 vs. 0.80, p=0.014). Patients admitted with lower NIHSS values reported better quality of life at the end of our study (r: -0.43451).
At 30 days, significant improvement was observed in MT, IVT and SC groups when measured with EQ-5D-5L, but the extent of improvement was highest in the MT group.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The aim of the research study was to get a better picture of the patient’s quality of life with Huntington’s disease and their caretaker’s. One of the main topics of the investigation was the family, because taking care of a Huntington’s patient can have a big impact on their lives. Our further concern was to introduce the concept for the families and test their open mindedness, if they would take assistance from nurse graduates to make the patient’s medical journey shorter and help with their everyday life challenges.
The cross-sectional research was done by validated tests, as well as, self-made tests which contained socio-demographic data and questions regarding the disease. The trial took place at Semmelweis University, at the Institute of Genomic Medicine and Rare Disorders in collaboration with the patients and their families.
According to the patients, their life quality is affected more physically than their mental health. The experiment showed that the disease has a big impact on the quality of life of the family members. The family members would be more open in regards to accepting help from advanced practice nurses.
Huntington’s disease has a negative impact on the quality of life of the patients and their families. It would be adequate to study if the provided help of advanced practice nurses could improve their quality of life. ]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The purpose of the study is to investigate the quality of life of young adults in relation to oral health and how smoking affects this. The aim is to explore the differences in oral health-related quality of life between smokers, non-smokers, and quitters in a given age group.
The survey was conducted using a self-designed online questionnaire that included the Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP-14) questionnaire. The survey was conducted from May 01 to June 30, 2023, using a nonrandom sampling method that relied on easily accessible subjects. Data were processed and analysed using IBM SPSS 20.0 statistical software, descriptive statistics, Kruskal-Wallis test, and Spearman’s rank correlation analysis (p<0.05).
Based on the 317 assessable responses, smokers had a higher average OHIP-14 total score than non-smokers and quitters, but there were no significant differences in oral health-related quality of life between the groups (p=0.540). Four self-reported questions were added to the OHIP-14 questionnaire: dissatisfied with the colour of their teeth; afraid of communicating with others without seeing their teeth being seen; afraid of having a serious oral problem; afraid of losing their teeth. These issues are highly correlated with the OHIP-14 questionnaire and fear of oral lesions appears to be present among smokers.
Young adults do not yet show a significant deterioration in oral quality of life due to smoking, but additional questions are worth considering to assess the quality of life in smokers.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The high blood pressure disease is one of the primary risk factors for the development of other cardiovascular diseases. The aim of the present study was to assess the medication habits, sleep quality, and quality of life of patients aged 45 and older living with hypertension.
Our study was a quantitative descriptive cross-sectional survey conducted in 2022 in the form of an online questionnaire among patients aged 45 and older suffering from hypertension (n=143). The data collection tools included the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (8 items), the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, EQ-5D-5L, and a self-designed questionnaire.
Lower age was associated with higher levels of medication adherence (R=-0.36; p=0.024). Patients who regularly visited their general practitioner showed more consistent medication intake (p=0.048). Adequate sleep quality positively influenced the quality of life (p<0.001).
Regular visits to the general practitioner not only facilitate medication adherence but also provide an excellent opportunity for patient education and health promotion. Therefore, it has paramount importance to draw the attention of hypertensive patients to the role of regular check-ups with their general practitioner, which can contribute to the prevention of complications arising from hypertension.]
Clinical Oncology
[Background: The increased number of cancer survivors and the recognition of physical and psychosocial challenges, present from cancer diagnosis through active treatment and beyond, led to the discipline of cancer survivorship.]
Novel approach of screening and chronic care of hypertension patients in pri- mary care
ESMO Expert Consensus Statements on Cancer Survivorship: promoting high-quality survivorship care and research in Europe
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]4.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Fear of Falling among Geriatric Patients: a Narrative Review]1.
2.
3.
4.
5.