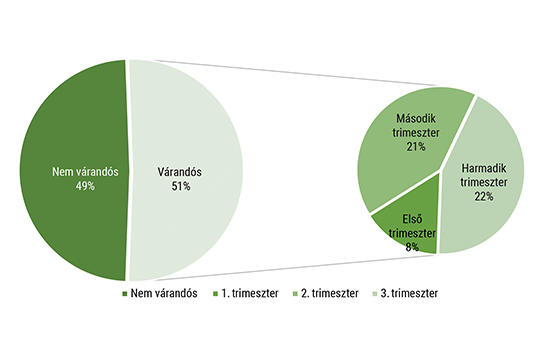
[In the course of our research, we compared the pre-pregnancy test mass index of Hungarian women with the results of the National Nutrition and Nutritional Status Examinations.
Our cross-sectional study was conducted between 01.01.2020 and 01.08.2020. During the nonrandom, targeted, expert sample selection, the target group included pregnant women or mothers raising at least one minor child (N=1423). Exclusion criteria include the omission of mandatory questions. Our survey was done online, with a self-filled questionnaire, anonymously. In the questionnaire, we used sociodemographic, anthropometric, pregnancy and nutrition-related questions. The data were analyzed with IBM SPSS 25.0 statistical software, descriptive statistics and tables.
The normal BMI was typical only for those under 20 years of age (21 kg/m2). The largest proportion of people over 20 years of age were overweight (>25 kg/m2). Every fourth pregnant woman (43.4%) and every third mother (33%) reported that excess body weight does not bother them at all.
Based on the body mass index, Hungarian women are already overweight before pregnancy, which entails an increased health and financial burden.]