The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Clinical Neuroscience - 2023;76(1-2)
Content
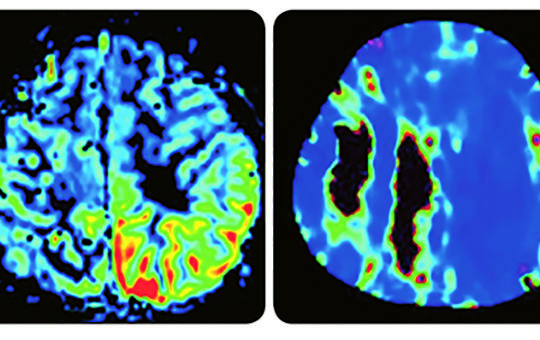
Characteristics of stroke-like lesions on cerebral imaging
Stroke-like lesions (SLLs) are pathognomonic for mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) syndrome but occur in other mitochondrial and non-mitochondrial disorders as well. This mini-review aims at summarising and discussing recent findings to open up future perspectives how to manage this fleeting phenomenon.
[The effects of mindfulness-based interventions in post-stroke rehabilitation]
[Stroke is nowadays one of the most prevalent diseases worldwide causing devastating impairments and negative consequences for survivors. It is a main cause of adult onset disability and it can have a negative impact on psychological health, cognitive function and quality of life. Post-stroke rehabilitation may reduce long-term disability, and in recent years several innovations have emerged to improve recovery. Decades of research suggest that mindfulness-based interventions support a greater capacity to live with chronic medical conditions and contribute to lowering stress levels. Previous works report positive results amoung stroke survivors, improvements in mood, mental fatigue and in some degree in cognitive and physical functioning, plus represent a promising option in secondary prevention. Since the early 2000s, numerous clinical studies have investigated the efficacy of mindfulness-based interventions in post-stroke rehabilitation. In this paper the main results of the relevant international research is reviewed and also, the main modalities of the mindfulness-based interventions are presented. Our primary goal is to evaluate the results in order to draw attention to the importance of rehabilitation of patients with stroke and hopefully the theoretical and practical knowledge of the review will contribute to development effective and secure protocols in future research. Mindfulness-based techniques can become clinically valuable complementary therapeutic interventions in post-stroke rehabilitation. More research in this area is warranted: to evaluate these specific practices and their suitability; using randomized, controlled, follow up designs, rigorous methods, and different treatment settings; expanding outcomes to include physiological, health care use, and health-related outcomes; exploring mediating factors; and discerning dose effects and optimal frequency and length of practice. ]
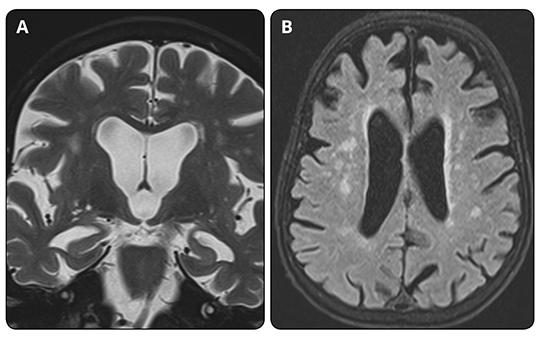
Interrater reliability of modified visual mrı rating scale assessing atrophy and white matter changes
Cortical atrophy and white matter changes are common findings on magnetic resonance imaging among elderly. Several visual scales have been proposed to evaluate these changes using neuroimaging. We have recently proposed a scale (Modified Visual Magnetic Resonance Rating Scale) recently which allows us to evaluate atrophy, white matter hyperintensities, basal ganglia and infratentorial infarcts together. Our aim in this study was to evaluate the interrater reliability of magnetic resonance visual assessment using this scale between two neurologists and a radiologist.
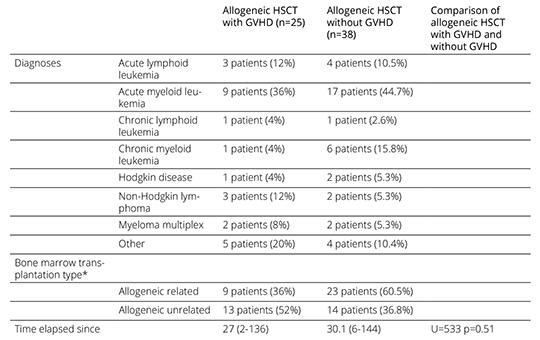
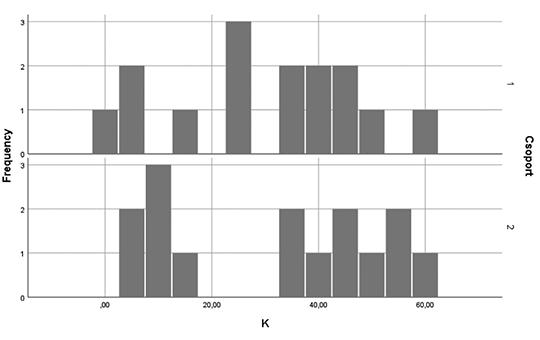
[Impact of the type of hematopoietic stem-cell transplant on quality of life and psychopathology]
[Despite the decrease in transplant-related mortality, patients who receive hematopoietic stem- cell transplants often suffer from short-and long-term morbidities, poorer quality of life, and psychosocial functioning deficits. Several studies have compared the quality of life and affective symptoms of patients after under- going autologous and allogeneic hematopoi- etic stem-cell transplants. Some studies have reported similar or greater quality of life im- pairments in allogeneic hematopoietic stem- cell recipients, but the findings have been inconsistent. Our purpose was to examine the influence of the type of hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation on the quality of life and affective symptoms of patients.]
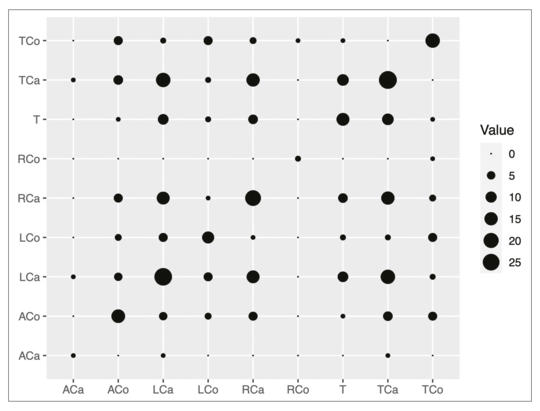
Clinical features of cervical dystonia patients classified by the COL-CAP concept and treated with ultrasound-guided botulinum neurotoxin
Cervical dystonia (CD) is the most common form of focal dystonias, where the identification of the involved muscles, the determination of optimal botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT-A) dose per muscle injection, and precise tar- geting may be challenging. The aim of the current study is to compare local centre data with international data, enabling the identification of population and methodolo gical factors behind the differences, thereby further improvement of the care of Hunga- rian patients with CD.
[The effect of surgical psychoeducation on the outcome of spinal surgery]
[Interdiscipli nary researches demonstrate that patients’ fears and anxieties about surgery play a key role in the success of postoperative recovery. Psychoeducation is a professional information transfer method that aims to increase patients’ knowledge about their dis ease, and how to cope with it, and to emo tionally process the problems associated with the disease. If patients feel competent in their own healing process after surgery, they will experience less pain and become selfsufficient sooner, thereby the number of nursing days spent in the clinic reduces.]
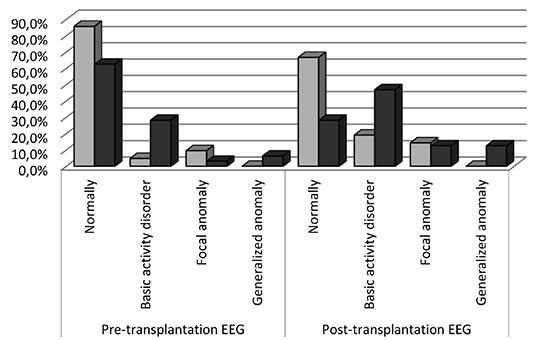
[Evaluation of pre- and post-transplant electroencephalographic examination in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients]
[Haemato poietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is one of the most effective treatment methods for many malignant and nonmalignant diseases. In this study, we aimed to detect electroencephalographic (EEG) anomalies at an early stage in patients who underwent allogeneic and autologous HSCT and required the management of potentially life threatening non-convulsive seizures.]
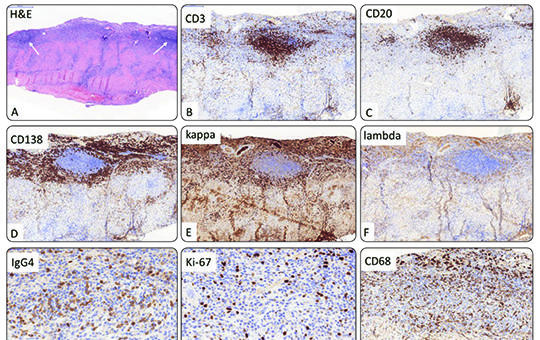
Isolated IgG4 hypertrophic pachymeningitis with cranial nerve involvement
IgG4-related (IgG4-RD) disease is a relatively newly identified, chronic autoimmune disorder that can affect any organ system. The disease is relatively rare. It has mostly systemic presentation, however it can also appear in isolated form in one single organ. In our report, we demonstrate an elderly male patient’s case with IgG4-RD presented in the form of diffuse meningeal inflammation and hypertrophic pachymeningitis with one-sided cranial nerve and intraventricular involvement.
Novel heterozygous STUB1 gene mutation causes SCA48 in a Hungarian patient
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 48 (SCA48) is an autosomal dominantly inherited disease characterized by gait and limb ataxia, cerebellar dysarthria, cognitive impairment, psychiatric abnormalities and variable types of movement disorders. To date, more than 30 STUB1 gene (NM_005861.4) mutations have been described in the genetic background of SCA48.
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
2.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]3.
4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]