The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2001;11(08-09)
Content
[Risk to the fetus in the light of new data]
[Extensive research efforts based on principles of evidence-based medicine have helped lately to accumulate large amount of information on the risks to the fetus during pregnancy. As a result, the standpoints concerning risks to the fetus have become more precise in many respects. A number of earlier assumptions have been proven to be exaggerated or unfounded and the range of cases at risk has been narrowed down. This paper presents the most important data on potential risks to the fetus originating from hereditary factors, infections, maternal diseases, drugs, irradiation and special gestational anomalies. The data presented highlight the necessity of identifying the fetal damage during the pregnancy unequivocally, based exclusively on evidence of probative force and with realistic appraisal of the danger of any existent fetal damage.]
[Sentinel node biopsy in melanoma malignum]
[INTRODUCTION - For many decades there has been no adequate treatment for affected regional lymph nodes in melanoma malignum. In the last couple of years with the implementation of the sentinel lymph node biopsy technique, it became possible to perform selective lymphadenectomy, i.e. to perform radical block dissection only in cases of histologically proven metastases in the sentinel lymph nodes. Since the lymphatic involvement in melanoma malignum is the most important prognostic factor, it is essential to treat lymphatic etastases as early as possible to get the best results. PATIENTS AND METHODS - In the past two years we have removed the sentinel lymph nodes together with primary tumors being 1 mm or thicker, ulcerated and regressive, based on clinical appearance in 120 melanoma cases. RESULTS - Of the 120 sentinel lymph node biopsies 58 contained metastatic cells. Beside tumor thickness, histological features of regression were found to correlate with the positivity of the sentinel nodes in thin melanoma cases. CONCLUSIONS - Sentinel lymph node biopsy is a relatively simple procedure with minimal complication rate. It allows early therapeutical block dissection and the selection of patients who require adjuvant therapy. Our clinical observations suggest that beside tumor thickness and ulceration, the clinical and histological signs of regression are important factors to consider for the indication of sentinel node biopsy.]
[Chlamydia pneumoniae in coronary arteries of young adults]
[INTRODUCTION - An association of Chlamydia pneumoniae (C. pneumoniae) with coronary heart disease has been found with seroepidemiological methods. This organism was demonstrated in atheromatous plaques by electron microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and polymerase chain reaction. MATERIAL AND METHODS - To better understand the significance of the presence of C. pneumoniae in atheromatous plaques, we examined coronary artery segments from young adults (15-34 years) with and without atherosclerosis. 74 samples of left anterior descending artery were examined immunohistochemically for the presence of C. pneumoniae by the monoclonal antibody RR402. RESULTS - C. pneumoniae was identified in the atheroma in 11 of 17 cases (65%) and in preatheroma in 6 of 15 cases (40%), in fatty streak in 7 of 23 cases (30%) and in intimal thickening in 1 of 14 cases (7%). C. pneumoniae was not found in the intimal and medial layer of the normal-appearing coronary arteries. C. pneumoniae was detected in the adventitia in 51 cases (67%) of the coronary arteries: in the normal arteries and initial lesions in 27 of 42 cases (63%), and in the advanced lesions in 24 of 32 cases (75%). Correlation was observed between the C. pneumoniae positive cases and cigarette smoking. CONCLUSION - Our results suggest that C. pneumoniae may relate to the severity of atherosclerosis in the youth, thus may initiate atherosclerotic injury or facilitate its progression along with other risk factors.]
[Endothel dysfunction and hypertension]
[In the past two decade numerous data has been collected about the role of endothelium in the development of several cardiovascular disorders i.e. hypertension, congestive heart failure and atherosclerosis. Endothelial cells had been thought to be passive barriers only, but it turned out that through paracrine and autocrine hormone secretion they take part in modulating and regulating the vasodilator and vasoconstrictor effects being directed to vascular smooth muscle cells. The intact endothelium prevents the adhesion of platelets and monocytes, the platelet aggregation, as well as the migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. It has been shown that both in experimental and human hypertension the endothelial function i.e. the so-called endothel-dependent vasodilatation is damaged, being the main feature of endothelial dysfunction. In spite of extensive research it is not clear whether endothelial dysfunction is a cause or a consequence of hypertension, with exact pathomechanism being also unclear. Methods, by which this important parameter could be precisely measured are under development. Researchers also examine whether recently used antihypertensive agents could improve or eliminate endothelial dysfunction and whether this effect may offer benefit to patients in terms of morbidity and mortality. This article attempts to summarize the most up-to-date information about the endothelial dysfunction research.]
[Anti-atherosclerotic effects of Ca-antagonists in the light of new clinical data]
[Based on in vitro and animal research, it has been found that calcium antagonist drugs are capable of inhibiting directly the atherosclerotic process. In spite of their advantegous antiatherosclerotic effect, the fast-release, first-generation dihydropyridines had an unfortunate effect on the number of newly developed myocardial infarctions and on cardiovascular mortality. New, controlled clinical studies have found long acting calcium antagonists to decrease significantly the progression of the atherosclerosis in the carotid artery - verified with B-mode ultrasound scans - and the appearance of cardiovascular clinical events, when either proven coronary sclerosis (PREVENT, CAPARES studies) or hypertension (INSIGHT, ELSA, VHAS) was present. If further clinical trials (CAMELOT, NORMALISE - now under way) justify these promising clinical data, then long-acting calcium channel blockers may become new and significant tools in the prevention of the progression and clinical complications of atherosclerotic disease.]
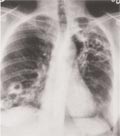
[Wegener’s granulomatosis: diagnostic questions]
[INTRODUCTION - Wegener’s granulomatosis is a disease of unknown origin classified as an immune vasculitis. The main pathologic feature is necrotising granulomatous small vessel vasculitis. Clinically the upper and/or lower airways are affected most often as well as the kidneys in the generalised form. The highly specific antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies have diagnostic significance beside the pathology and clinical symptoms. PATIENTS AND METHODS - We have studied the clinical and diagnostic characteristics of 15 cases diagnosed in our centre from the last 25 years. All patients had pulmonary manifestation. We analysed the organ involvement, clinical signs indicating the diagnosis, chest radiography, chances for biopsies of diagnostic significance and the difficulties of differential diagnostics. RESULTS - The diagnosis was made based on histological samples from the upper airways in three cases and from the lower airways in six cases (in four cases the bronchoscopic biopsies were diagnostic, in two patients thoracotomy was necessary). In six cases, clinical signs and typical organ manifestations were the basis of the diagnosis. CONCLUSION - This very rarely occurring disease which is difficult to recognise requires pulmonological examination due to the involvement of lungs. If this diagnosis comes to mind - based on findings of bilateral, multiplex, round pulmonal shadows with cavitation - the pulmonologist should search for other organ manifestations and involve respective specialists. Ideally, diagnosis is established by histopathology or by positive cytoplasmic antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]