[The Comprehensive Aphasia Test in Hungarian]
ZAKARIÁS Lilla1,2,3, RÓZSA Sándor4, LUKÁCS Ágnes3,5
NOVEMBER 30, 2020
Clinical Neuroscience - 2020;73(11-12)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18071/isz.73.0405
Journal Article
ZAKARIÁS Lilla1,2,3, RÓZSA Sándor4, LUKÁCS Ágnes3,5
NOVEMBER 30, 2020
Clinical Neuroscience - 2020;73(11-12)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18071/isz.73.0405
Journal Article
Szöveg nagyítása:
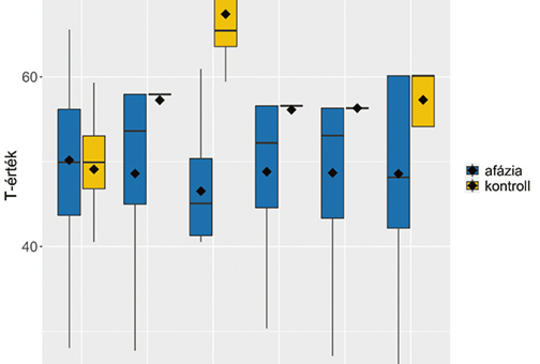
[In this paper we present the Comprehensive Aphasia Test-Hungarian (CAT-H; Zakariás and Lukács, in preparation), an assessment tool newly adapted to Hungarian, currently under standardisation. The test is suitable for the assessment of an acquired language disorder, post-stroke aphasia. The aims of this paper are to present 1) the main characteristics of the test, its areas of application, and the process of the Hungarian adaptation and standardisation, 2) the first results from a sample of Hungarian people with aphasia and healthy controls. Ninety-nine people with aphasia, mostly with unilateral, left hemisphere stroke, and 19 neurologically intact control participants were administered the CAT-H. In addition, we developed a questionnaire assessing demographic and clinical information. The CAT-H consists of two parts, a Cognitive Screening Test and a Language Test. People with aphasia performed significantly worse than the control group in all language and almost all cognitive subtests of the CAT-H. Consistent with our expectations, the control group performed close to ceiling in all subtests, whereas people with aphasia exhibited great individual variability both in the language and the cognitive subtests. In addition, we found that age, time post-onset, and type of stroke were associated with cognitive and linguistic abilities measured by the CAT-H. Our results and our experiences clearly show that the CAT-H provides a comprehensive profile of a person’s impaired and intact language abilities and can be used to monitor language recovery as well as to screen for basic cognitive deficits in aphasia. We hope that the CAT-H will be a unique resource for rehabilitation professionals and aphasia researchers in aphasia assessment and diagnostics in Hungary. ]
Clinical Neuroscience
[The well-known gap between stroke mortality of Eastern and Western European countries may reflect the effect of socioeconomic differences. Such a gap may be present between neighborhoods of different wealth within one city. We set forth to compare age distribution, incidence, case fatality, mortality, and risk factor profile of stroke patients of the poorest (District 8) and wealthiest (District 12) districts of Budapest. We synthesize the results of our former comparative epidemiological investigations focusing on the association of socioeconomic background and features of stroke in two districts of the capital city of Hungary. The “Budapest District 8–12 project” pointed out the younger age of stroke patients of the poorer district, and established that the prevalence of smoking, alcohol-consumption, and untreated hypertension is also higher in District 8. The “Six Years in Two Districts” project involving 4779 patients with a 10-year follow-up revealed higher incidence, case fatality and mortality of stroke in the less wealthy district. The younger patients of the poorer region show higher risk-factor prevalence, die younger and their fatality grows faster during long-term follow-up. The higher prevalence of risk factors and the higher fatality of the younger age groups in the socioeconomically deprived district reflect the higher vulnerability of the population in District 8. The missing link between poverty and stroke outcome seems to be lifestyle risk-factors and lack of adherence to primary preventive efforts. Public health campaigns on stroke prevention should focus on the young generation of socioeconomically deprived neighborhoods. ]
Clinical Neuroscience
Background: This overview provides a summary of the applications of transcranial Doppler (TCD) in ischemic stroke. Results: A fast-track neurovascular ultrasound protocol has been developed for detecting occlusion or stenosis. The technique is more reliable in the carotid area than in the posterior circulation. By monitoring the pulsatility index the increased intracranial pressure can be diagnosed. TIBI score was developed for grading residual flow. TCD has been shown to accurately predict complete or any recanalization. Regarding recanalization, TCD has a sensitivity of 92%, a specificity of 88%, a positive predictive value of 96%, a negative predictive value of 78% and an overall accuracy of 91%, respectively. Sonothrombolysis seemed to be a promising application but randomized controlled trials have shown that it does not improve clinical outcome. TCD examination can detect microembolic signals (MES) which are associated with an increased risk of stroke. Microemboli were detected in symptomatic and asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis and during carotid endarterectomy. The number of microemboli can be decreased by antithrombotic therapy. Contrast enchanced examination and Valsalva maneuver with continuous TCD monitoring can accurately screen for right-to-left shunt.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The clinical signs of SARS-CoV-2 infection has become more recognisable in recent times. In addition to common symptoms such as fever, cough, dyspnea, pneumonia and ageusia, less common complications can be identified, including many neurological manifestations. In this paper, we discuss three Covid-19 associated neurological disorders (Case 1: Covid-19 encephalitis, Case 2: Covid-19 organic headache, Case 3: SARS-CoV-2-infection and ischaemic stroke). We emphasize in our multiple case study that during the present pandemic, it is especially important for neurologists to be aware of the nervous system complications of the virus infection, thus saving unnecessary examinations and reducing the frequency of patients’ contact with health care personnel. ]
Clinical Neuroscience
Background – Up to now, the risk factors related to intracranial infections after transsphenoidal pituitary adenomectomy remain controversial. Purpose – To analyze the risk factors related to intracranial infections after transsphenoidal pituitary adenomectomy under an endoscope, and to provide evidence for preventing and controlling the occurrence and development of infections. A total of 370 patients receiving endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary adenomectomy in our hospital from January 2014 to October 2017 were selected. The risk factors related to postoperative intracranial infections were analyzed. The hospitalization lengths and expenditures of patients with and without intracranial infections were compared. Of the 370 patients, 18 underwent postoperative intracranial infections, with the infection rate of 4.86%. Intraoperative blood loss >120 mL, cerebrospinal leakage, diabetes, preoperative use of hormones, macroadenoma as well as surgical time >4 h all significantly increased the infection rate (P<0.05). Preoperative use of antibacterial agents prevented intracranial infection. Compared with patients without intracranial infections, the infected ones had significantly prolonged hospitalization length and increased expenditure (P<0.05). Discussion – It is of great clinical significance to analyze the risk factors related to intracranial infection after endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary adenomectomy, aiming to prevent and to control the onset and progression of infection. Intracranial infections after endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary adenomectomy were affected by many risk factors, also influencing the prognosis of patients and the economic burden.
Clinical Neuroscience
The relationship among obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) and obesity is very complex and multi-directional. Obesity and increased visceral fat are important perpetuating factors for DM2 in patients with OSAS. On the other hand, OSAS itself leads to obesity by causing both leptin and insulin resistance as a consequence of activation of the sympathetic nervous system. Risk for developing DM2 further increases in patients with OSAS and obesity. Data regarding effects of positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy, gold standard treatment for OSAS, on glycemic control were inconsistent due to variability in duration of and adherence to PAP therapy. In our cohort study we investigated effects of PAP treatment on glucose metabolism in normal-weighted non-diabetic OSAS patients, in obese non-diabetic OSAS patients, and in OSAS patients with DM2. We prospectively analyzed 67 patients diagnosed with OSAS and documented to be effectively treated with PAP therapy for three months. Apnea-hypopnea index was highest in the diabetic group, being significantly higher than in the normal-weighted group (p=0.021). Mean HOMA values were significantly higher in obese (p=0.002) and diabetic group (p=0.001) than normal-weighted group; the differences were still significant after PAP therapy. HbA1c levels were significantly higher in diabetic group compared to those in normal-weighted (p=0.012) and obese (p=0.001) groups. After PAP treatment, decrease in HbA1c levels were significant in normal-weighted (p=0.008), obese (p=0.034), and diabetic (p=0.011) groups. There was no correlation with the change in HbA1c levels and age (p=0.212), BMI (p=0.322), AHI (p=0.098) or oxygen levels (p=0.122). Our study showed that treatment of OSAS by PAP therapy offers beneficial effect on glucose metabolism, not only in diabetic patients, but also in obese and normal-weighted OSAS patients. Although data regarding overall effects of PAP therapy on glycemic control present contradictory results in the literature, it should be emphasized that duration and adherence to PAP therapy were main determinants for beneficial outcome of treatment.
Clinical Neuroscience
Atrial fibrilla- tion diagnosed after stroke (AFDAS) is a new term used for AF resulting from autonomic dysregulation. It is associated with a lower stroke recurrence compared to patients with known AF before a stroke (KAF). The aim of the study was to explore the characteristics and mortality rates in AFDAS patients. 134 ischemic stroke patients (66.1±14.2 years old, n=73 male) were consecutively included in the study.
Clinical Neuroscience
Stigma is a widespread phenomenon in Parkinson’s disease (PD) and has been shown to affect the quality of life of individuals. This study aims to assess the level of stigma and identify the factors contributing to stigma in patients with PD in Turkey. A total of 142 patients diagno¬sed with PD between June 2022 and March 2023 were included in the study. Sociodemographic data were collected using a sociodemographic information form.
Clinical Neuroscience
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, frequently result in mood disorders among affected individuals. It is established that neuropathic pain arising from traumatic neuropathies is also linked to mood disorders. This study investigates the influence of neuropathic pain on the development of mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries, following the earthquake centered in Kahramanmaraş on February 6, 2023.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Pain intensity is the most frequently assessed health domain in clinical studies among patients with low-back pain. Visual analogue scale (VAS) and Numeric rating scale (NRS) have been the mostly used measurement tools for pain intensity. We proposed to correlate these instruments to a generic health-related quality of life measurement tool in order to show the scale with superior clinical relevance.
We used cross-sectional, convenience sampling. 120 patients with chronic low-back pain administered the 29-item Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Profile with NRS included, and the VAS scale in the National Institute of Mental Health, Neurology and Neurosurgery. We determined the correlation between PROMIS domain T-scores and VAS and NRS scores.
We performed Spearman rank correlation test to calculate the correlation coefficient. We found VAS scales measuring pain had weak to moderate correlations with all PROMIS health domains (r = 0.24–0.55). Therefore, we compared correlation of PROMIS domain scores with PROMIS pain intensity numeric rating scale and VAS scales. PROMIS domains had moderate to strong correlations with pain intensity scale (r = 0.45–0.71). PROMIS physical function short form [r = –0.65, 95% CI (–0.75) – (–0.55)] and PROMIS pain interference short form (r = 0.71, 95% CI 0.63 – 0.79) had the strongest correlation with pain intensity item.
NRS has showed greater correlation with PROMIS domain T-scores than VAS scale. This may prove that NRS has greater connection to another health domains, thus it correlated more to health-related quality of life than visual scale. We recommend NRS to use in further clinical studies conducted among patients with low-back pain.]
Clinical Neuroscience
The aim of this study is to comprehensively determine the types of affected fibers in Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients by employing nerve conduction studies (NCS), sympathetic skin response (SSR) examinations, and current perception threshold (CPT) testing and to analyze the correlation between levodopa use and nerve involvement. This retrospective study included 36 clinically diagnosed PD patients who were recruited between January 2018 and April 2019.
Cognitive impairment in long-COVID
Personality traits and psychological complaints under patients suffering from headaches
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]
COMMENTS
0 comments