[How and what can we do together for the care of hypertensive patients in communities of practice?]
TORZSA Péter, CSATLÓS Dalma, MÓCZÁR Csaba
TORZSA Péter, CSATLÓS Dalma, MÓCZÁR Csaba
Szöveg nagyítása:
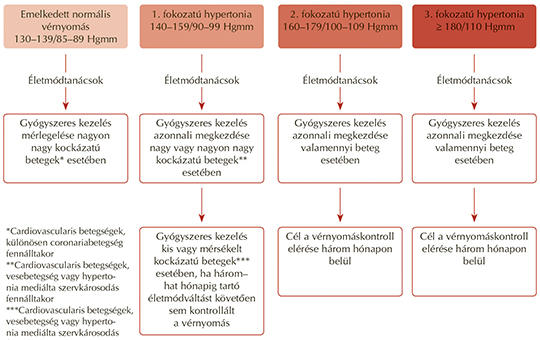
[As the first step in the transformation of primary care, the first communities of practice were set up to seek ways of expanding the competences, the range of equipment and the services provided by primary care. The structure of these no longer resembles the previous model of general practice, with teams of two or three doctors working in isolation from each other. The new form is a network of community practices. The care and management of hypertensive patients is a typical area of community work. In this article, the authors aim to illustrate the role of community practices in the care and management of hypertensive patients.]
Lege Artis Medicinae
[The diagnosis of hypertension is important, as high blood pressure is the most frequent and consequently the most important risk factor of cardiovascular diseases leading to mortality. The basis of diagnosis is the correct blood pressure measurement. Recent guidelines underline the importance of out of office (home and ambulatory) blood pressure monitoring besides the traditional office measurements. These methods have not only additive prognostic value, but with the help of these measurements, special hypertension forms (white coat and masked hypertension) can be diagnosed. On top of all these, home monitoring increases the patient’s compliance to the therapy. This short review summarizes the most important information on blood pressure measurement.]
Lege Artis Medicinae
[In this paper I summarise the currently valid guidelines for the pharmacotherapy of hypertensive patients, and in separate part, those for hypertensive urgencies and emergencies.]
Lege Artis Medicinae
[Childhood hypertension was previously regarded as a rare disease, caused primarily by renal or renovascular diseases. However, in the past 10-15 years due to increased prevalence of childhood obesity and the associated metabolic abnormalities, elevated blood pressure has become significantly more common. This highlights the public health significance of high blood pressure, and it also determines the screening protocols, which varies by age groups. The child's development should be taken into account when establishing normal blood pressure in childhood. In addition to the definition of hypertension, the characteristics of blood pressure measurements must also be known. Before adolescence, hypertension is most likely caused by an organic cause. During puberty and postpuberty, hypertension is primarily associated with obesity. The tests and their evaluation should be performed in a centre familiar with the examination of children, and where the childhood normal values are known. The goal of therapy is to prevent the organ-damaging effects of hypertension in a population where the disease is expected to persist for decades. Customized and realistic lifestyle changes are essential during treatment, but it may be necessary to introduce drug therapy as well. The medication should start as a monotherapy with the lowest necessary dose. If this does not achieve an adequate therapeutic effect, the treatment is supplemented with another class of antihypertensive medication.]
Lege Artis Medicinae
[Hypertension, which is the most important independent risk factor of cardiovascular mortality, affects approximately 3.5 million people in Hungary. Among them the rate of the unknown, known, but untreated or uncontrolled hypertensive patients is more, than 50%, a fact, which underlines the importance of screening and proper treatment. Since 2017, there is a difference in the classification of hypertension between Europe and the United States, based mostly on SPRINT study, which was published in 2015. However, in the treatment recommendations more similarities are present. Risk stratification must be the part of hypertension care. In risk communication as an alternative, the concept of vascular age was introduced, which mirrors more suggestively the patients' vascular hazard. In this review the author overviews the novelties in hypertension epidemiology, classification, and risk stratification.]
Lege Artis Medicinae
[Arterial aging is a physiologic process coexisting with general aging of the human body, however arterial age of a given individual can be different from his chronologic age. The underlying causes are determined by genetic factors, cell biologic processes and several risk factors. While risk scores are invaluable tools for adapted preventive strategies, a significant gap exists between predicted and actual event rates. Therefore, it is necessary to refine the risk stratification at an individual level, the tools for this are biomarkers. Biomarkers are surrogate endpoints, which precede, substitute the real, hard endpoint clinical events. It has been proposed that numerous potential vascular biomarkers would have a role in primary and secondary cardiovascular prevention. Most of them fit in the concept of early vascular aging (EVA). Only carotid ultrasonography, ankle-brachial index and carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity meet perfectly the strictest criteria against the biomarkers. The process of arterial aging may be decelerated and beneficially influenced with non-pharmacologic and pharmacologic treatment strategies.]
Clinical Neuroscience
Atrial fibrilla- tion diagnosed after stroke (AFDAS) is a new term used for AF resulting from autonomic dysregulation. It is associated with a lower stroke recurrence compared to patients with known AF before a stroke (KAF). The aim of the study was to explore the characteristics and mortality rates in AFDAS patients. 134 ischemic stroke patients (66.1±14.2 years old, n=73 male) were consecutively included in the study.
Clinical Neuroscience
Stigma is a widespread phenomenon in Parkinson’s disease (PD) and has been shown to affect the quality of life of individuals. This study aims to assess the level of stigma and identify the factors contributing to stigma in patients with PD in Turkey. A total of 142 patients diagno¬sed with PD between June 2022 and March 2023 were included in the study. Sociodemographic data were collected using a sociodemographic information form.
Clinical Neuroscience
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, frequently result in mood disorders among affected individuals. It is established that neuropathic pain arising from traumatic neuropathies is also linked to mood disorders. This study investigates the influence of neuropathic pain on the development of mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries, following the earthquake centered in Kahramanmaraş on February 6, 2023.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The purpose of the study is to find correlations between sarcopenia, falls, falls and social isolation in the elderly population.
This study chose a genre of literature review, in which seven articles were analyzed.
Weakness, falls and social isolation are closely related, which is also supported by statistical calculations.
The results of the literature review will help all professionals working in the care of the elderly to understand how different geriatric complex conditions are related to each other.]
Clinical Neuroscience
[Pain intensity is the most frequently assessed health domain in clinical studies among patients with low-back pain. Visual analogue scale (VAS) and Numeric rating scale (NRS) have been the mostly used measurement tools for pain intensity. We proposed to correlate these instruments to a generic health-related quality of life measurement tool in order to show the scale with superior clinical relevance.
We used cross-sectional, convenience sampling. 120 patients with chronic low-back pain administered the 29-item Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Profile with NRS included, and the VAS scale in the National Institute of Mental Health, Neurology and Neurosurgery. We determined the correlation between PROMIS domain T-scores and VAS and NRS scores.
We performed Spearman rank correlation test to calculate the correlation coefficient. We found VAS scales measuring pain had weak to moderate correlations with all PROMIS health domains (r = 0.24–0.55). Therefore, we compared correlation of PROMIS domain scores with PROMIS pain intensity numeric rating scale and VAS scales. PROMIS domains had moderate to strong correlations with pain intensity scale (r = 0.45–0.71). PROMIS physical function short form [r = –0.65, 95% CI (–0.75) – (–0.55)] and PROMIS pain interference short form (r = 0.71, 95% CI 0.63 – 0.79) had the strongest correlation with pain intensity item.
NRS has showed greater correlation with PROMIS domain T-scores than VAS scale. This may prove that NRS has greater connection to another health domains, thus it correlated more to health-related quality of life than visual scale. We recommend NRS to use in further clinical studies conducted among patients with low-back pain.]
Risk factors of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with preeclampsia or eclampsia: A retrospective review
Results achieved with advanced practice nurses in general practitioner care for hypertensive patients
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]
COMMENTS
0 comments