[Education of Healthcare Professionals about Stomato-oncology Screening Tests]
HEGYI Virág1, FRITSCHEK Nóra Anna1, NÉMETH Anikó1,2
JUNE 28, 2023
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2023;36(3)
HEGYI Virág1, FRITSCHEK Nóra Anna1, NÉMETH Anikó1,2
JUNE 28, 2023
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2023;36(3)
Szöveg nagyítása:
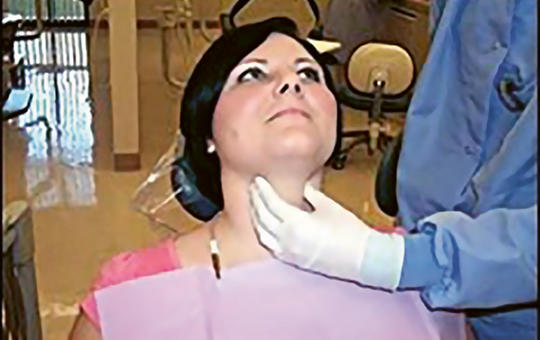
[In Europe Hungary has the highest prevalence of oral cancer and mortality. That aforementioned case draws attention to the importance of oral screening tests because these types of tumors can be cured easily if we catch them in time. Stomato-oncology screening tests are one of the most painless and easiest examinations considering that it can be effectively done by non-professionals and healthcare workers outside of dentistry. This gives us the opportunity to filter out tumors in early states. This summary publication demonstrates the steps of extra- and intraoral examination and escalates to noticing periodontal deseases and oral cancer.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The use of fluorides is one of the most important areas of dental prevention. It has many beneficial effects on teeth, and it is worth using them starting from childhood. It has an important role in caries prevention and in ensuring the strength of the enamel. However, we must pay attention to take fluoride into our body in moderation. If we don’t act accordingly, we can damage the condition of the teeth and the structure of the bones, to which we should pay special attention during childhood. Fluorosis can be prevented by attention, but adequate information is essential for this, which can be provided by both dentists and dental hygienists.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[To objectify the positive effect of individualized oral hygiene patient education on the condition of patients suffering from periodontal disease. Also to draw attention to the effectiveness and necessity of patient education in order to motivate the nurse and dental hygienist colleagues to implement individual patient education in practice.
Instrumental measurement-based impact assessment within a focus group with periodontal disease, observing the differences between the condition of patients who received patient education (n=108) and patients who did not received patient education (n=113).
Individual patient education is effective, individual patient compliance is higher and periodontal disease status shows a significantly greater improvement in patients who participated in individual patient education.
The education carried out by clinical dental hygienists can effectively improve the oral health of periodontal patients, thus reducing the disease burden and decreasing the periodontal disease risk effect on the development of other disease affecting the entire human body.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Purpose: The aim of the study to gather detailed report about the knowledge and the manner of the nurses in patients from different cultures.
The study population consists of nurses from two different hospitals (Hospital A and Hospital B). Surveys were applied to assess the knowledge of intercultural nursing. Fifty questionnaires were sent each hospital. Finally, 63 completed questionnaires arrived from Hospital A (nA=33) and Hospital B (nB=30).
Most of the nurses have basic knowledge about transcultural nursing, but it should be improved furthermore.
According to the results, majority of the nurses have elemental experience in transcultural medical care, but it needs further development.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT), as one of the methods of modern wound treatment, is widely used for the treatment of complex wounds both in inpatient and outpatient care and in home care.
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to assess the knowledge of nurses working in the surgical department and who encounter this treatment every day, about wound care with negative pressure.
Cross-sectional, qualitative method with structured interviews. The study sample is nurses working in the surgical department with a minimum OKJ Nursing professional qualification, who have encountered NPWT treatment during their practical work. The investigation took place in July and August of 2021.
Among the interviewed nurses, 9 out of 10 did not encounter this form of wound treatment in their previous jobs. 9 nurses knew the principle on which the equipment works and the effect it has on wound healing. All interviewed nurses were aware of what to pay attention to when caring for a patient receiving NPWT care. According to the nurses, their most important task is to monitor the secretions that empty into the collection tank, both quantitatively and qualitatively. Only 1 nurse out of 10 mentioned that when a large amount of blood appears, the machine must be stopped immediately and the doctor must be alerted immediately. 8 of the nurses were interested in additional information and useful information about NPWT.
The negative pressure therapy has not yet spread widely in Hungary, but at the same time, the nurses who have worked with this wound treatment method are aware of the working principle of the machine. Nurses consider it important to monitor all parts of the equipment, because they are aware that if any part is malfunctioning, the treatment is ineffective. Nurses’ knowledge is based only on their experience and they would like to expand their knowledge of negative pressure therapy.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The incidence of oral cavity tumors is showing an increasing trend, with cause including harmful behaviors, improper nutrition, and inadequate lifestyle. There are many known pre-cancerous conditions, the early diagnosis and treatment of which can prevent malignant degeneration. This is only possible if people conciously pay attention to their oral hygiene and do not neglect regular dental chech-ups. It is important to draw the attention of lay people to this issue in all areas of healthcare.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Drug use is still on the rise today, with designer drugs being particularly dangerous. In addition to the general effects on the body, we must also mention the negative effects on the oral cavity. Many people do not realise that oral health can also be at risk, although oral lesions can develop as a result of poor oral hygiene, infections or neurological symptoms caused by the way in which the drug is used, or even by the way in which it is taken. In addition to dental caries, it is important to mention oral infections, tooth wear, or even Kaposi’s sarcoma due to possible HIV infection. Recognition of these oral lesions and of illegal drug use is not only a task for dental professionals, but also for the whole health care system.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The purpose of the study is to investigate the quality of life of young adults in relation to oral health and how smoking affects this. The aim is to explore the differences in oral health-related quality of life between smokers, non-smokers, and quitters in a given age group.
The survey was conducted using a self-designed online questionnaire that included the Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP-14) questionnaire. The survey was conducted from May 01 to June 30, 2023, using a nonrandom sampling method that relied on easily accessible subjects. Data were processed and analysed using IBM SPSS 20.0 statistical software, descriptive statistics, Kruskal-Wallis test, and Spearman’s rank correlation analysis (p<0.05).
Based on the 317 assessable responses, smokers had a higher average OHIP-14 total score than non-smokers and quitters, but there were no significant differences in oral health-related quality of life between the groups (p=0.540). Four self-reported questions were added to the OHIP-14 questionnaire: dissatisfied with the colour of their teeth; afraid of communicating with others without seeing their teeth being seen; afraid of having a serious oral problem; afraid of losing their teeth. These issues are highly correlated with the OHIP-14 questionnaire and fear of oral lesions appears to be present among smokers.
Young adults do not yet show a significant deterioration in oral quality of life due to smoking, but additional questions are worth considering to assess the quality of life in smokers.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Diabetes affects the whole body, altering fundamental metabolic processes. The number of people with diabetes is gradually increasing, with a growing proportion of younger and younger people affected. While significant lifestyle changes are needed to manage diabetes, some form of medication is also essential. Often, only the importance of exercise and diet is brought to patients’ attention by professionals, overlooking the importance of oral prevention. A number of oral conditions (e.g. dry mouth, gingivitis) can occur in people with diabetes as a result of poor oral hygiene. It is important to raise awareness of these conditions and how to prevent them at all levels of healthcare.]
Effect of surgical mask and N95 respirator mask use on cerebrovascular reactivity
Work-life Balance among Healthcare Professionals
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]