[Assessment of Attitude and Nursing Skills Based on Racial, Religious and Ethnical Attributes during Daily Practice ]
FIZESÁN Hilda1
JUNE 28, 2023
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2023;36(3)
FIZESÁN Hilda1
JUNE 28, 2023
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2023;36(3)
Szöveg nagyítása:
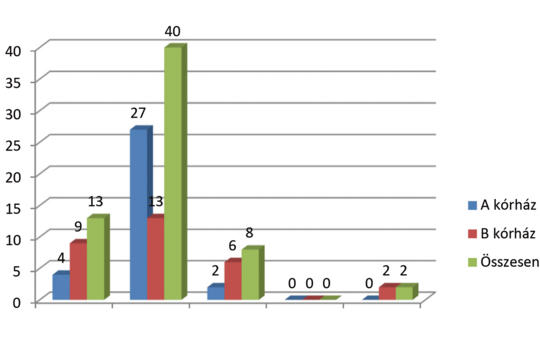
[Purpose: The aim of the study to gather detailed report about the knowledge and the manner of the nurses in patients from different cultures.
The study population consists of nurses from two different hospitals (Hospital A and Hospital B). Surveys were applied to assess the knowledge of intercultural nursing. Fifty questionnaires were sent each hospital. Finally, 63 completed questionnaires arrived from Hospital A (nA=33) and Hospital B (nB=30).
Most of the nurses have basic knowledge about transcultural nursing, but it should be improved furthermore.
According to the results, majority of the nurses have elemental experience in transcultural medical care, but it needs further development.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The use of fluorides is one of the most important areas of dental prevention. It has many beneficial effects on teeth, and it is worth using them starting from childhood. It has an important role in caries prevention and in ensuring the strength of the enamel. However, we must pay attention to take fluoride into our body in moderation. If we don’t act accordingly, we can damage the condition of the teeth and the structure of the bones, to which we should pay special attention during childhood. Fluorosis can be prevented by attention, but adequate information is essential for this, which can be provided by both dentists and dental hygienists.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[In Europe Hungary has the highest prevalence of oral cancer and mortality. That aforementioned case draws attention to the importance of oral screening tests because these types of tumors can be cured easily if we catch them in time. Stomato-oncology screening tests are one of the most painless and easiest examinations considering that it can be effectively done by non-professionals and healthcare workers outside of dentistry. This gives us the opportunity to filter out tumors in early states. This summary publication demonstrates the steps of extra- and intraoral examination and escalates to noticing periodontal deseases and oral cancer.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[To objectify the positive effect of individualized oral hygiene patient education on the condition of patients suffering from periodontal disease. Also to draw attention to the effectiveness and necessity of patient education in order to motivate the nurse and dental hygienist colleagues to implement individual patient education in practice.
Instrumental measurement-based impact assessment within a focus group with periodontal disease, observing the differences between the condition of patients who received patient education (n=108) and patients who did not received patient education (n=113).
Individual patient education is effective, individual patient compliance is higher and periodontal disease status shows a significantly greater improvement in patients who participated in individual patient education.
The education carried out by clinical dental hygienists can effectively improve the oral health of periodontal patients, thus reducing the disease burden and decreasing the periodontal disease risk effect on the development of other disease affecting the entire human body.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The incidence of oral cavity tumors is showing an increasing trend, with cause including harmful behaviors, improper nutrition, and inadequate lifestyle. There are many known pre-cancerous conditions, the early diagnosis and treatment of which can prevent malignant degeneration. This is only possible if people conciously pay attention to their oral hygiene and do not neglect regular dental chech-ups. It is important to draw the attention of lay people to this issue in all areas of healthcare.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT), as one of the methods of modern wound treatment, is widely used for the treatment of complex wounds both in inpatient and outpatient care and in home care.
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to assess the knowledge of nurses working in the surgical department and who encounter this treatment every day, about wound care with negative pressure.
Cross-sectional, qualitative method with structured interviews. The study sample is nurses working in the surgical department with a minimum OKJ Nursing professional qualification, who have encountered NPWT treatment during their practical work. The investigation took place in July and August of 2021.
Among the interviewed nurses, 9 out of 10 did not encounter this form of wound treatment in their previous jobs. 9 nurses knew the principle on which the equipment works and the effect it has on wound healing. All interviewed nurses were aware of what to pay attention to when caring for a patient receiving NPWT care. According to the nurses, their most important task is to monitor the secretions that empty into the collection tank, both quantitatively and qualitatively. Only 1 nurse out of 10 mentioned that when a large amount of blood appears, the machine must be stopped immediately and the doctor must be alerted immediately. 8 of the nurses were interested in additional information and useful information about NPWT.
The negative pressure therapy has not yet spread widely in Hungary, but at the same time, the nurses who have worked with this wound treatment method are aware of the working principle of the machine. Nurses consider it important to monitor all parts of the equipment, because they are aware that if any part is malfunctioning, the treatment is ineffective. Nurses’ knowledge is based only on their experience and they would like to expand their knowledge of negative pressure therapy.]
Clinical Neuroscience
[This research focused on the knowledge and attitude toward to electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) in the general population of Hungary. There are only a few studies in the international literature focusing on the public’s attitude towards ECT, and no such study has been published from Hungary. Participants were reached through social media and asked to fill out a semi-structured questionnaire on internet that comprised seventeen questions. Participation in the survey was entirely voluntary and anonymous. Participants of the survey were not working in health care; their answers to the questionnaire were compared to those of health-care workers. The result showed a significant difference between healthcare workers’ and lay people’s knowledge and attitude towards ECT. Two third of lay participants have never heard about ECT. Those familiar with ECT were relatively well-informed about its certain aspects yet rejection of ECT was significantly higher in the group of lay participants than in health-care workers. Lay people’s incomplete knowledge and negative attitude towards ECT was confirmed by this survey. The dissemination of reliable information – which should be the shared responsibility of mental health professionals and the media – would be vitally important to disperse the prejudices and doubts about ECT.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The aim of the authors is to call attention to the differences arising during nursing of patients of different culture. Regarding to the fact that in our healthcare system there are more and more patients with foreign customs, it is inevitable for the healthcare staff to acquire new knowledge and apply it during their work in an effective way. ]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aim of the research: Investigating nurse students’ attitude towards complementary and alternative medicine and their knowledge of and experience with it. Research and sampling methods: 171 Hungarian nurse (57 full time and 114 part time) students participated in our cross-sectional study using a self-administered questionnaire. Results: Nurse students’ attitude towards alternative medicine is positive. The most known alternative methods were massage, herbal medicine, acupuncture, homeopathy, relaxation and meditation. The most used practices were massage, herbal medicine and homeopathy and found them efficient. Full time students used the Internet and part time students used education as information sources. Most students agreed that the integration of alternative methods into health care would be effective, and it should be taught in higher education. Conclusions: Nursing student would get reliable knowledge by integrating alternative medicine into higher education system and it takes their work more effective. ]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aim of the study: To map out the motivation that drove BSc nursing students to choose a profession in the health sector and begin their college studies. The authors considered it important to include, in the scope of the study, an assessment of the perception and prestige of the chosen vocation, as well as the level of work satisfaction. Sample and methods: The self-completion questionnaire was filled out by BSc nursing students at the Faculty of Health Sciences and Social Studies of the University of Szeged (N=208). The sample consisted of correspondence (n=136) and full-time (n=72) students, who took part in the data gathering on a voluntary basis. Results: A helpful attitude and humanistic values are what most influenced the respondents in relation to their choice of career, and their enrolment in college studies was mainly motivated by their internal drive. These attitudes, however, do not fully offset the low prestige and the negative aspects of the profession. Conclusions: The results show that there is a need for comprehensive reform in the sector, in the interest of improving the prestige of the profession and preventing career abandonment.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Vaccination is one of the most effective public health interventions against infectious diseases, especially against vaccine-preventable paediatric diseases. However, there are parents either delaying or refusing recommended childhood vaccination due to the fear of a ‘link’ between vaccinations and autism or other diseases. Religious objection is often used as an excuse to avoid the vaccination. Opposition to vaccination dates back to the Victorian age. Since the 18th century, fear and controversy accompanied the introduction of every new vaccine. This has been compounded, in recent years, by a decreased trust in the vaccine manufacturing or distributing institutions. Although healthcare professionals are cited as the most influential source by parents and adult population on vaccine decision-making, mistrust of vaccinations is already occurs among health workers. It is important for health professionals to be well informed, to able to persuade parents and the targeted population to vaccine.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.