We aimed to investigate the association between fluoxetine use and the survival of hospitalised coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia patients. This retrospective case-control study used data extracted from the medical records of adult patients hospitalised with moderate or severe COVID-19 pneumonia at the Uzsoki Teaching Hospital of the Semmelweis University in Budapest, Hungary between 17 March and 22 April 2021. As a part of standard medical treatment, patients received anti-COVID-19 therapies as favipiravir, remdesivir, baricitinib or a combination of these drugs; and 110 of them received 20 mg fluoxetine capsules once daily as an adjuvant medication. Multivariable logistic regression was used to evaluate the association between fluoxetine use and mortality.
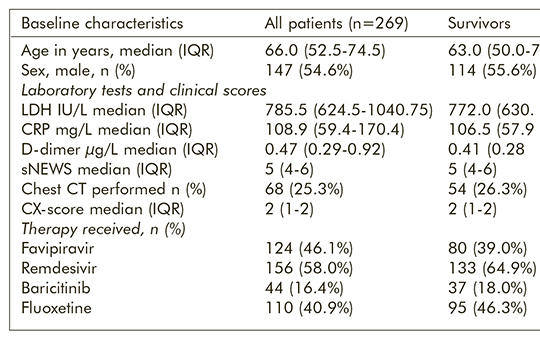
For excluding a fluoxetine-selection bias potentially influencing our results, we compared baseline prognostic markers in the two groups treated versus not treated with fluoxetine. Out of the 269 participants, 205 (76.2%) survived and 64 (23.8%) died between days 2 and 28 after hospitalisation. Greater age (OR [95% CI] 1.08 [1.05–1.11], p<0.001), radiographic severity based on chest X-ray (OR [95% CI] 2.03 [1.27–3.25], p=0.003) and higher score of shortened National Early Warning Score (sNEWS) (OR [95% CI] 1.20 [1.01-1.43], p=0.04) were associated with higher mortality. Fluoxetine use was associated with an important (70%) decrease of mortality (OR [95% CI] 0.33 [0.16–0.68], p=0.002) compared to the non-fluoxetine group. Age, gender, LDH, CRP, and D-dimer levels, sNEWS, Chest X-ray score did not show statistical difference between the fluoxetine and non-fluoxetine groups supporting the reliability of our finding. Provisional to confirmation in randomised controlled studies, fluoxetine may be a potent treatment increasing the survival for COVID-19 pneumonia.




COMMENTS
0 comments