The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Hypertension and nephrology - 2019;23(01)
Content
[Statins for elderly people, in primary prevention?]
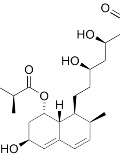
[In a recent, retrospective cohort study, statin usage in primary prevention was found being not beneficial for patients (i) without diabetes over 75 years of age, and (ii) with diabetes over 85 years of age (75-84 years total mortality of diabetics was also lower). These findings are in sharp contrast to the two outstanding, double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized, a primary prevention studies done with rosuvastatin. Of these, 50% reduction in LDL-C in JUPITER was associated with a 50% reduction in risk and 25% reduction in LDL-C in HOPE-3 with 25% reduction in risk. Furthermore, subgroup analyzes did not indicate lower efficacy for the elderly. The recommendation of the European Atherosclerosis Society for primary preventions of the elderlies recommending consideration of statin use in these cases (Class IIa) is particularly relevant, especially in the presence of other risk factors such as hypertension. In the primary prevention lipid treatment, we can see quite clearly till 75 years of age and hopefully, we will even further after learning about the results of STAREE, a study that is designed to elderly and in which 40 mg atorvastatin is applied.]
[The importance of statin therapy in hypertension]
[Hypertension and hypercholesterolaemia often co-occur and promote early cardiovascular disease. Previous studies have shown that antihypertensive treatment may be more effective if LDL cholesterol is also reduced. This may be due to the increased expression of angiotensin-1 receptor in hypercholesterolaemia, which increases peripheral vascular resistance through angiotensin-2, and adversely affects endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Other authors indicate that high cholesterol levels increase the production of angiotensin-2 through the activation of the chymase system. High cholesterol levels increase the amount of circulating oxidized LDL which binds to the transmembrane oxidized LDL receptor (LOX- 1) also activates the angiotensin-1 receptor. In addition, angiotensin-2 has an effect on intracellular cholesterol synthesis by enhancing the key enzyme of the synthesis of intracellular cholesterol, HMG-CoA reductase. The authors present the studies that support cholesterol lowering can contribute to lowering blood pressure and other major meta-analyses in which the beneficial effects of cholesterol lowering and lipid lowering on blood pressure reductions were not proven. In the background, it may well be that these studies are not designed to evaluate the effect of cholesterol-lowering drugs on hypertension in patients with hypercholesterolaemia, and non-statin-treated patients are not randomized.]
[Sexual problems in CKD – a narrative review]
[Sexual dysfunction is highly prevalent in patients with CKD, especially those receiving dialysis. Given the high prevalence of sexual problems in CKD patients, there has been growing interest in finding effective treatments for sexual dysfunction. PDE5i and zinc have been found promising interventions for treating sexual dysfunction in men with CKD in a systematic review of RCTs, but the evidence supporting their routine use in CKD patients is limited. In the Collaborative Depression and Sexual Dysfunction (CDS) Study, over a cohort of 1611 men in hemodialysis, 83% reported erectile dysfunction and 47% reported severe erectile dysfunction, with depression strongly correlated to this problem. Similarly, sexual dysfunction was highly prevalent in women undergoing hemodialysis. Of the 659 respondents, 555 (84%) reported sexual dysfunction and more than half of sexually active women reported sexual dysfunction, associated with age, depressive symptoms, menopause, low serum albumin, and diuretic therapy.]
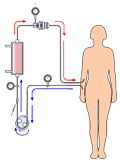
[Methods of using telemedicine devices (smartphones, tablets) during home blood pressure measurement]
[Despite the use of advanced antihypertensive drugs, patients with hypertension are still insufficient to reach the target blood pressure. In this area, home blood pressure measurement was a significant step forward, but it is not at all how the method of home blood pressure measurement is done, on the other hand, it needs to be much closer to the doctor-patient relationship. This is the goal of introducing telemedicine tools and methods into the every day clinical practice. Three methods are known: In the first one the user uses a special application on the smartphone and writes your data into the smartphone. Solution 2 is that data are automatically transferred from the measuring device into the smartphone in the third, the smartphone itself performs the measurement. Really, the first application can be disseminated with a broadly compatible doctor-patient collaboration strategy.]
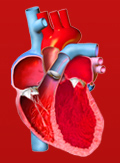
[Carvedilol in chronic kidney disease]
[Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is endemic affecting 850 million people worldwide. Adequate antihypertensive treatment slows the progression of the kidney disease and also decreases the mortality of this population. Because of the comorbidities and the high cardiovascular risk beta-blockers have to be administered frequently in these patients. Carvedilol is a 3rd generation non-selective beta-blocker with alpha- 1 receptor blocking and antioxidant properties. It is metabolically neutral, it does not increase the risk of new onset diabetes and it does not increase the patients’ body weight. In some animal models of CKD and in several human CKD studies carvedilol has shown to have nephroprotective properties and it also decreased the cardiovascular risk in combination therapies.]
[Hypertension and atrial fibrillation. Part 3. Screening of atrial fibrillation with active involvement of patients. New telemedicine devices]
[In the early detection of atrial fibrillation, new devices and methods with smart phone applications for patients’ self-control a regaining increasing role. The author provides a detailed description of a number of reliable, validated - working on smart phones or without her solutions - equipment with pulse or ECG recording and the irvalue in every day clinical practice. They promote closer physician - patient cooperation and signal the future of prevention and care of atrial fibrillation. In the early detection of atrial fibrillation, new devices and methods with smart phone applications for patients’ self-control a regain in gin creasing role.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]