The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Clinical Neuroscience - 2019;72(05-06)
Content
[In memoriam Mátyás Papp]
[Mátyás Papp died on 4th of April, 2019, at the age of 92, following a long disease. He was working for nearly 60 years in the Department of Neurology, Semmelweis University. He was known about his works on the inclusion bodies in multiple system atrophy (Papp-Lantos bodies). He was a honorary member of the International Society of Neuropathology. ]
[The effect of bevacizumab monotherapy on progression free survival in recurrent glioblastoma]
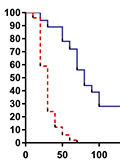
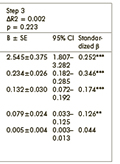
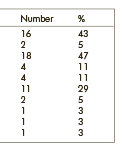
[Introduction, the aim of study - Glioblastoma, WHO grade IV is the most frequent primary malignant brain tumor in adults. There are few articles and result about the efficacy of bevacizumab monotherapy. The aim of our paper is to examine the effect of bevacizumab therapy on progression free and overall survival in an extended database of recurrent glioblastoma patients. Patients and methods - In our retrospective study, patients with recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab had been collected. All of our patients received first line chemo-irradiation according the Stupp protocol treatment. The histological diagnosis was primary or secondary glioblastoma in every patient. The prognostic features of primary and secondary glioblastomas were statistically analyzed. Results - Eighty-six patients were selected into the retrospective analysis. The histological diagnosis was primary glioblastoma in 65 patients (75.6%) and secondary glioblastoma in 21 patients (24.4%). The mean follow up period was 36.5 months. The mean second progression free survival beside bevacizumab therapy was 6.59 months and the mean overall survival was 24.55 months. In secunder glioblastoma cases, the mean second progression free survival was 6.16 months and the mean overall survival was 91.94 months. Conclusion - The bevacizumab therapy is a safe option in recurrent glioblastoma patients. Bevacizumab therapy has a positive effect both on progression free and overall survival and our results confirm the findings in the literature. There is no statistically significant difference in the second progression free survival between glioblastoma subtypes.]
Mid-term oral isotretinoin therapy causes a predominantly sensory demyelinating neuropathy
Aim - The purpose of this prospective study was to investigate whether mid-term treatment with oral isotretinoin may impact peripheral nerve function. Methods - In this study, we included 28 patients with no apparent neurological or neurophysiological findings. The patients received treatment with oral isotretinoin for papulopustular or nodulocystic acne. The patients with normal findings in the first examination were given 1 mg/kg/day oral isotretinoin. Neurological examinations and electroneurographic studies were performed before and 6 months after the onset of isotretinoin treatment. Results - Clinical examinations and electroneurographic evaluations prior to treatment revealed no abnormalities in any of the patients. However, 20 patients (72%) displayed one or more abnormal values in the tested parameters after treatment. Although the mean amplitudes of compound muscle action potential of the ulnar and median nerves did not vary, significant decreases were observed in the mean sensory conduction velocities of median, ulnar, sural, medial plantar, medial dorsal cutaneous, and dorsal sural nerves 6 months after the onset of treatment. Conclusion - Systemic use of isotretinoin may cause electroneurographic changes. Probable electroneurographic alterations may be detected at a much earlier period via dorsal sural nerve tracing when electrophysiological methods used in routine clinical practice cannot detect these changes.
Somatosensory amplification absorption contribute to electrosensitivity
Background - Two trait-like characteristics, somatosensory amplification and absorption, have been associated with symptom reports and idiopathic environmental intolerances in past research. Purpose - As the two constructs are not connected with each other, their independent contribution to symptom reports and electromagnetic hypersensitivity, as well as their interaction can be expected. Methods - On-line questionnaire. Patients - 506 college students completed an on-line questionnaire assessing absorption, somatosensory amplification, negative affect, somatic symptoms, and electromagnetic hypersensitivity. Results - Somatosensory amplification (β = 0.170, p < 0.001) and absorption (β = 0.128, p < 0.001) independently contributed to somatic symptoms after controlling for gender and negative affect (R2 = 0.347, p < 0.001). Similarly, somatosensory amplification (OR = 1.082, p < 0.05) and absorption (OR = 1.079, p < 0.01) independently contributed to electromagnetic hypersensitivity after controlling for somatic symptoms, gender, and negative affect (Nagelkerke R2 = 0.134, p < 0.001). However, no interaction effects were found. Discussion - Somatosensory amplification and absorption independently contribute to symptom reports and electromagnetic hypersensitivity. Conclusion - The findings suggest that psychological mechanisms underlying symptom reports and electromagnetic hypersensitivity might be heterogeneous.
The prevalence of sarcopenia and dynapenia according to stage among Alzheimer-type dementia patients
Aim - In this study, the aim was to identify the prevalence of sarcopenia and dynapenia according to disease stage among Alzheimer-type dementia (AD) patients and collect data to suggest precautions related to reducing the disease load. Method - The study was completed with 127 patients separated into stages according to Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR) criteria and 279 healthy volunteers aged 18-39 years and 70-80 years abiding by the exclusion criteria who agreed to participate in the research. Our prospective and cross-sectional study applied the CDR and mini mental test (MMSE) to patients with disorder in more than one cognitive area and possible AD diagnosis according to NINCDS-ADRDA (National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke-Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders Association) diagnostic criteria. The patient and control groups had skeletal muscle mass index (SMMI), muscle strength and physical performance assessed with sarcopenia diagnosis according to European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People (EWGSOP) diagnostic criteria. Results - In our study, in parallel with the increase in disease stage of AD patients, the prevalence of sarcopenia (led by severe sarcopenia) and dynapenia was higher compared to a control group of similar age. Conclusion - In chronic, progressive diseases, like AD, identification of changes in parameters, like muscle mass and strength and reductions in physical performance in the early period, is important for identification and to take precautions in the initial stages considering the limitations of the preventive effects of treatment applied after diagnosis of AD.
The methylation status of NKCC1 and KCC2 in the patients with refractory temporal lobe epilepsy
Purpose - Methylation is a key epigenetic modification of DNA and regarding its impact on epilepsy, it is argued that “DNA methylation may play an important role in seizure susceptibility and maintenance of the disorder”. DNA methylation status of KCC2 (SCL12A5) and NKCC1 (SCL12A2) associated with refractory temporal lobe epilepsy was investigated in our study. Materials and methods - Thirty-eight patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) who were diagnosed by video EEG monitoring and 32 healthy control subjects were included in the study. Twenty-three patients in TLE group were men and the remaining 15 were women. Among them, 27 had unilateral temporal focus (9 with right; 18 with left) and 11 patients had bilateral TLE. We analyzed promoter region methylation status of the KCC2 (SCL12A5) and NKCC1 (SCL12A2) genes in the case and control groups. Gene regions of interest were amplified through PCR and sequencing was accomplished with pyro-sequencing. Results - We found a significant relationship between TLE and methylation on the NKCC1. However, there was no association between TLE and methylation on the KCC2 gene. Also, we found no association between right or left and unilateral or bilateral foci of TLE. There was no relationship between TLE and methylation on the NKCC1and KCC2 genes in terms of mesial temporal sclerosis in cranial MRI, head trauma or febrile convulsions. Conclusion - The methylation of NKCC1 can be a mechanism of refractory temporal lobe epilepsy. There are limited findings about DNA methylation in TLE. Therefore, further studies with large sample sizes are necessary.
[Dopamine agonists in Parkinson’s disease therapy - 15 years of experience of the Neurological Clinics from Tîrgu Mureș. A cross-sectional study ]
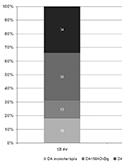
[Background and purpose - There is relatively few data regarding the usage of dopaminagonists for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease; furthermore, there are no publications regarding Central- and Eastern-European countries. The aim of the study was to evaluate the use of dopamine agonists as a therapeutic option amongst Parkinson’s disease patients admitted to the Neurological Clinics of Tîrgu Mures during the last 15 years. Methods - In our study we investigated the data of all Parkinson’s patients treated at our clinics between the 1st of January 2003 and the 31st of December 2017. We analyzed the particularities of dopamine agonists’ usage based on the therapeutic recommendations from the final report of these patients. Regarding time since the diagnosis, we divided the patients in two groups: less than or equal to 5 years and more than 5 years. Results - During the studied period a total of 2379 patients with Parkinson’s disease were treated at the Clinics. From the 1237 patients with disease duration under 5 years 665 received dopamine agonists: 120 as monotherapy, 83 together with monoamine oxidase inhibitors and in 234 cases associated with levodopa. The remaining 228 patients were treated with a triple combination of levodopa, dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase inhibitors. In patients suffering from Parkinson’s disease for more than 5 years, in 364 cases out of 653 a dopamine agonist was part of the therapy. Conclusion - The usage of dopamine agonists was similar to the data presented in other studies. We consider that clinicians treating the disease should, with the necessary prudence, use the available and recommended dopamine agonist with the utmost courage to their maximum therapeutic potential.]
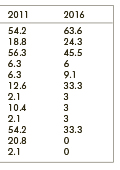
Population-based stroke screening days in the 12th district of Budapest in 2011 and 2016 - What have and what have not changed?
Introduction - Population-based screening is an option to identify persons at high risk for stroke. However it is associated with rather high expenses, necessitating the selection of effective methods that take local characteristics into account. The 12th district of Budapest has a long tradition of population-based screening for frequent and preventable diseases. The Szent János Hospital hosts an annual stroke screening day. In the present study, previously published data from the 2011 screening were compared with those obtained in 2016, looking for changes and tendencies throughout the examined period. Subjects and methods - The screening day was conducted in a generally similar way in 2011 and 2016. Similarly to the previous event, the program was organized on a Saturday, the call for the event was spread by the local newspaper. The crew composition was the same. As regards the components of the screening (currently including general history taking, risk status assessment, blood pressure measurement, BMI assessment, cholesterol and blood glucose tests, carotid duplex ultrasonography, and ophthalmological examination), the only difference was the absence of cardiologic examination (it was conducted on an independent day). The anonymous data sheet was the same. Results - The number of participants in the 2016 event was 33, to provide more comfortable conditions. The female predominance was slightly less pronounced but was still present in 2016 (60.6% vs. 72.9%). The mean age became substantially higher (71.2 y vs. 62.9 y). The ratios of participants with higher level of education (97% vs. 94%) and those who are married were still remarkable. The most frequent risk factors were the same; however the ratio of participants with hypertension, ‘other heart disease’, and diabetes increased, whereas that of with hyperlipidemia and obesity decreased. The incidence of atrial fibrillation was unaltered. None of the participants in 2016 admitted smoking (previously this ratio was 20.8%) or drinking heavily. The findings of the carotid ultrasonography revealed a more favorable vascular status. Ophthalmological assessments (predominantly hypertensive alterations on fundoscopy) revealed that the pathological vs. physiological ratio switched to 1:2 from 2:1. The final evaluation of the screening program likewise demonstrated an improved overall state of health of the population. Conclusions - We observed a more favorable stroke risk status of the population in 2016. Whether it is indeed a tendency unknown at present. The role of the local media in calling for screening is still decisive, and the cohesive power of the family is important.
Hyperhomocysteinemia in female migraineurs of childbearing ages
Background and purpose - Migraine is a risk factor for ischemic stroke in women of childbearing ages. Previous researches revealed a higher prevalence of hyperhomocysteinemia in migraineurs. Possible differences on the frequencies of hyperhomocysteinemia between migraine with aura and migraine without aura could contribute the established variances in stroke risk between these migraine types. Therefore, we aimed to search if the frequency of hyperhomocysteinemia was different between these subtypes of migraine or not. Methods - We analyzed the findings of serum homocysteine levels in female migraineurs of 16-49 years old who admitted to our outpatient clinic. Results - Homocysteine level was elevated in 13.3% of study population. There were not any significant differences on median serum homocysteine levels between migraine with aura (8.0 mikromol/L) and without aura (8.5 mikromol/L). (p=0.426) The frequencies of hyperhomocysteinemia were also similar (9.1% versus 16.7%, respectively; p=0.373). Correlation analyses did not reveal any linear correlation between ages and homocysteine levels either in group of migraine with aura or in group of migraine without aura (p=0.417 and p=0.647, respectively). Similarly, any linear correlation between disease ages and homocysteine levels either in group of migraine with aura or in group of migraine without aura was not detected (p=0.359 and p=0.849, respectively). Conclusion - The median serum homocysteine levels and the frequencies of hyperhomocysteinemia are similar between migraine with aura and without aura in women of childbearing ages. Therefore, the variances on stroke risk ratios between these types of migraine are probably not originated from the differences of serum homocysteine status.
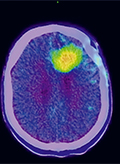
[F-DOPA PET/MR based target definiton in the 3D based radiotherapy treatment of glioblastoma multiforme patients. First Hungarian experiences ]
[Introduction - Radiotherapy plays important role in the complex oncological treatment of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). The modern 3D radiotherapy treatments are based on cross-sectional CT and MR information, however more attention is being paid to functional hybrid imaging describing the biological and functional morphology of tumor lesions. 18F-DOPA is an amino acid tracer with high specificity and sensitivity, which may play an important role in the precise definition of target volume in the irradiation process of GBM patients. Our study presents the first experiences with 18F-DOPA based PET/CT/MR 3D irradiation planning process. Methods - In Hungary the 18F-DOPA radiotracer has been available for clinical use since September 2017. Between September 2017 and January 2018, at the Somogy County Kaposi Mór Teaching Hospital Dr. József Baka Diagnostic, Radiation Oncology, Research and Teaching Center 3 histologically verified glioblastoma multiforme patients received 18F-DOPA based 3D irradiation treatment. In the contouring process the native planning CT scanes were fused with the PET/MR series (T1 contrast enhanced, T2 and 18F-DOPA sequences). We defined 18F-DOPA uptake volume (BTV-F-DOPA), the T1 contrast enhanced MRI volume (GTV-T1CE), and the volume of the area covered by oedema on the T2 weighted MRI scan (CTV-oedema) in all patients. We also registered the BTV-F-DOPA volumes not covered by the conventional MR based target volumes. Results - Examining the 3 cases, the average volume of 18F-DOPA tumor was 22.7 cm3 (range 15.3-30.9; SD = 7.82). The average GTV T1 CE was found to be 8.7 cm3 (range 3.8-13.2; SD = 4.70). The mean CTV oedema volume was 40.3 cm3 (range 27.7-57.7; SD = 15.36). A non-overlapping target volume difference (BTV-F-DOPA not covered by CTV oedema area) was 4.5 cm3 (range 1-10.3; SD = 5.05) for PTV definition. Conclusion - Based on our results the tumor area defined by the amino acid tracer is not fully identical with the MRI defined T2 oedema CTV. 18F-DOPA defined BTV can modify the definiton of the PTV, and the radiotherapy treatment. ]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
2.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]3.
4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]