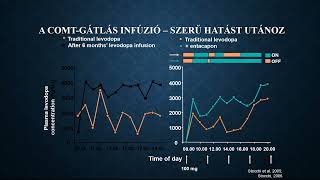
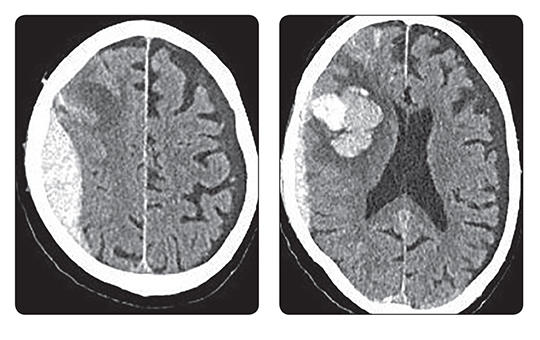
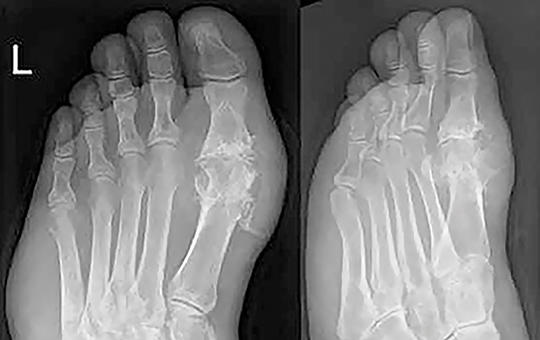
Több mint hét évvel rövidebb élethosszra számíthatott 2023-ban egy újszülött Magyarországon, mint Spanyolországban. Jelentősek a különbségek a férfiak és nők között is.
Az eLitMed.hu orvostudományi portál a böngészés tökéletesítése érdekében cookie-kat használ.
Ha bővebb információkat szeretne kapni a cookie-k használatáról és arról, hogyan módosíthatja a beállításokat, kattintson ide: Tájékoztató az eLitMed.hu Cookie-használatáról.