The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2014;24(05-06)
Content
[Diclofenac/orphenadrin as a combined analgetics in relief of pain Systemic literature review]
[The objectives of this paper are to discuss the safety and tolerability of combined infusion -Neodolpasse(®) - containing non-steroidal antiinflammarory drug, diclofenac and central muscle relaxant orphenadrin on the basis of recent data. The author reviewed phase IV randomised, controlled studies published on Medline and in the Hungarian literature. On the basis of the available data, diclofenac/orphenadrin infusion is an effective and safe analgesic, which is easy to administer and to combine with other painkillers in acute low back pain and other painful rheumatic conditions, as well as postoperative pain.]
[Epidemilogy of hepatitis C virus and possibilities of transmission]
[The medical impact of hepatitis C (HCV) is significant worldwide. The main consequences are chronic hepatic injury, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma formation. The estimated global prevalence is 3% with 180 million infected people worldwide. The prevalence <1% in Hungary. The prevalence increased between 1990 and 2005 in East Asia, Western Europe, and West sub-Saharan Africa. There is characteristic geographical distribution of the main HCV genotypes. The mode of transmission can not be identified of 40% of cases. The most frequent transmission is the intravénás drug injection in the developed countries, and unsafe health procedures in developing countries. The sensitive, nucleic acid amplification testing, identification of high-risk groups, development of vaccination would help the HCV prevalence in the future. ]
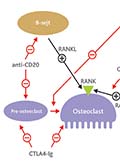
[The effect of biological therapy on generalised osteoporosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis]
[In rheumatoid arthritis, the inflammation and damage of multiple joints can lead to generalised osteoporosis. This process is mostly mediaated by cells and cytokines that are also important for maintaining inflammation, by inhibiting bone formation as well as stimulating bone resorption. Data from the literature show that biological therapies that effectively decrease inflammation can also stimulate bone formation and inhibit bone resorption. This results in an increased bone density and bone protection, which is highly important to prevent subseqent fractures.]
[Posttraumatic growth among cancer patients]
[In addition to studies of the negative effects of psychological trauma, recognition of benefit of highly distressing life experiences is increasingly becoming the focus in psycho-traumatology, usually under the name of posttraumatic growth (PTG). The recent review first demonstrates the domains of PTG and factors in the development of PTG. After this, the most frequent domains and the prevalence of PTG in the case of cancer patients are discussed. Finally, the paper tries to answer the question whether there is any relationship between PTG and physical health. ]
[Experiences from the dissection room. Quantitative and qualitative study among Hungarian medical students]
[BACKGROUND - The anatomy and pathology are the most outstanding field of the medical curriculum. These subjects mean the first practical experiences of dissection. The international literatures results shows that experience of dissection are important stages of becoming physician, but not always problemless. METHODS - Quantative (n=733) and qualitative (n=45) exploratory research among Hungarian medical students. We tried to present the effects and experiences of dissection pratcise using both analytical methods. Validity of the research was greatly improved by using the two methods. RESULTS - 50% of medical students reported that they were affected by dissection practice. The female students and those in clinical training (III-VI.years) reported about negative effects significantly more frequently. The results of the qualitative survey verified that dissection practices have decisive effect during the training and coping with experiences was often difficult especially for females students. CONCLUSIONS - Our research confirmed the hypothesis of dissection experiences play outstanding role in becoming physician. The successful coping isn’t the repression or ignorance of emotion, but understanding and finding effective solutions strategies for the negative emotions of experiences. Managing these experiences are a crucial factor of latter wellbeing of physicians and decisive factor of doctors-patient relationship.]
[What makes youth happy today? Relationships between religion, spirituality and mental well-being among high school students]
[INTRODUCTION - Studies suggest that traditional religiosity is more and more neglected among adolescents, however, not implying to the lack of religiousness or spirituality. Religion/spirituality is still a significant protective factor. Therefore, the main goal of the present paper was to analyze indicators of mental well-being in a sample of high school students in light of religious/spiritual variables. METHODS - The data collection of the questionnaire survey (2010) was going on among 656 high school students in Sze- ged (age range between 14-21 years, mean=16.5 years, S.D.=1.5 years of age, 49.1% of the sample was female). Depressive symptomatology, satisfaction with life and optimism were dependent variables and indicators of spirituality/religiosity were the independent ones. Beyond descriptive statistics, correlation and multiple regression analyses (stepwise method) were applied in the calculations. RESULTS - Our results show that for today’s youth happiness is primarily associated with their existential well-being: those who see a meaning in life, who have goals in life and believe that they are able to see through and understand life events, tend to be more satisfied with life, more optimistic and less depressed. Besides, spiritual belief may also contribute to life satisfaction whereas importance of religiosity may be a protective factor in the case of depression. CONCLUSIONS - Based on these results we may conclude that existential well-being (that is, finding a meaning in life) is a prominent spiritual variable. Data also suggest, however, that youth’s mental well-being only partially comes from religiosity, mostly it stems from other resources. More research is needed to detect this. All in all, as it appears that youth do need a belief in a meaning in life, similar to other age groups.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]