The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2009;19(08-09)
Content
[The importance of vitamin D deficiency in practice]
[The effects of vitamin D in bone health have been known since the 1920s. Recently, it has been proven that its role in the body is much more complex. Activated vitamin D is a steroid hormone that regulates transcription of more than 200 human genes through its receptor that is detectable in almost all types of cells. In contrast to the former conceptions, it can be activated not only in the kidneys; moreover, local 1-α-hydroxylation plays a greater role in its extraskeletal effects. Vitamin D deficiency, currently defined as serum levels of <30 ng/ml, is caused by the lack of ‘effective’ sunlight exposition. Thus, vitamin D deficiency is one of the most frequent deficiencies in the developed world that plays a role not only in the development of skeletal conditions but many other diseases, as well. A low vitamin D level causes a reduced calcium absorption, a higher bone remodelling rate and increased bone loss. It also reduces muscle strength and increases the risk of falling. Normal vitamin D status is required for the effectiveness of drugs for osteoporosis treatment; however vitamin D treatment in itself is not effective in osteoporosis. An increasing number of studies show the benefits of vitamin D supplementation and treatment in extraskeletal conditions. Vitamin D plays an important role in the prevention of several auto-immune diseases, infections, cardiovascular diseases, and cancers. Therefore, all UV-B radiation-deprived adults require an intake of vitamin D to maintain a level of >30 ng/ml. Vitamin D3 treatment is safe. The necessary dose can be reliably approximated by the calculation that an incremental consumption of 100 IU/day raises serum vitamin levels by 1,0 ng/ml. Clinical trials suggest that for the vast majority of individuals, a prolonged intake of 10,000 IU/day does not pose any risk.]
[Up-to-date management of systemic sclerosis]
[Systemic sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by three major features: widespread fibrosis in the skin and internal organs, a non-inflammatory small vessel obliterative vasculopathy and immunological activation with disease-specific autoantibodies. It is necessary to take a systematic approach to the diagnosis and evaluation of each case in order to provide appropriate treatment. Disease-modifying approaches can be classified according to the underlying pathogenic process. Thus vascular therapies include agents used for Raynaud’s phenomenon, critical digital ischaemia and organ-based vascular complications such as scleroderma renal crisis and pulmonary hypertension. Immunosuppressive drugs are used in lung involvement or rapid skin progression. The results of different anti-fibrotic therapies are controversial. Finally in managing organ-based manifestations and complications a multidisciplinary approach to the therapy is useful with patient education as an integral component of successful management.]
[The role of neurohormonal regulation in the development of insulin resistance in chronic stress]
[The effects of the chronic stress could not be avoided recently. The pathognomic regulation of the neurohormonal events is responsible for the manifestation of diseases such as obesity, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus type 2, depression, tumors, inflammations, allergy. Two major regulatory systems are involved in the neuroendocrine alterations caused by stress: the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the sympathetic nervous systems. The chronic activation of the adrenocortical system leads to insulin resistance and obesity associating with vascular, arteriosclerotic and inflammatory symptoms. The revealing of the pathognomic events on time and the enhanced physical activity may provide the effective prevention of these frequent diseases.]
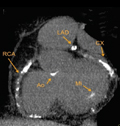
[Measurement of coronary artery calcification in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus using dual-source, multi-slice computed tomography]
[INTRODUCTION - Coronary artery calcification can be characterized non-invasively and numerically using computed tomography (CT). In adult patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, coronary atherosclerosis may be present without clinical symptoms. PATIENTS AND METHODS - Asymptomatic adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus (n=46) were investigated. Coronary artery calcification was expressed in Agatston-scores using a dual source CT scanner. RESULTS - Twenty-one patients had a coronary artery calcification score of ≥1 (range 1-2353), while in 25 patients no detectable calcium (score 0) was observed. Patients with vs. without coronary artery calcification had a higher age (51.0±9.9 vs. 42.8±7.8 years; p=0.0045), a longer duration of diabetes (30.6±9.2 vs. 24.2± 8.6 years; p=0.0238), a higher waist circumference (87.9±11.5 vs. 79.7±9.4 cm; p=0.0146), and a higher BMI (26.2±2.9 vs. 23.8±3.1 kg/m2;p=0.0109). Moreover, patients with vs. without detectable coronary artery calcification had higher serum lipid levels (LDL-cholesterol, 3.35±0.32 vs. 3.01±0.68 mmol/l; p=0.0069) and higher serum uric acid levels (228.4±48.7 vs. 195.1±39.4 µmol/l; p=0.0437). Hypertension was more common (p=0.0144) in patients with coronary artery calcification than in patients without it. There was no significant difference between the groups in HbA1c (7.97±0.85 vs. 8.26±1.28%; p=0.7491), however, estimated insulin sensitivity was lower in patients with vs. without detectable coronary artery calcification (7.15±2.09 vs. 9.20±2.03 mg/kg/min; p=0.0017). CONCLUSION - Our results suggest that coronary artery disease in type 1 diabetic patients is associated with higher age, longer duration of diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors rather than with long-term glucose control.]
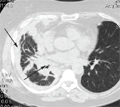
[Experience with bevacizumab in non-small cell lung cancer]
[INTRODUCTION - Bevacizumab, a recombinant anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, is the antiangiogenic drug used at advanced stage of non-small cell lung cancer. It is the only antiangiogenic therapy up till know available with reimbursement in Hungary. It is indicated in the first-line, platinum-based treatment of advanced stage non-squamous nonsmall cell lung cancer, and used together with chemotherapy. CASE REPORT - In this case report we present the case of a patient with advanced stage pulmonary adenocarcinoma, with a progressionfree survival of more than one year with bevacizumab- docetaxel-cisplatine therapy. CONCLUSION - Bevacizumab given together with combination chemotherapy is effective in advanced lung adenocarcinoma.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]