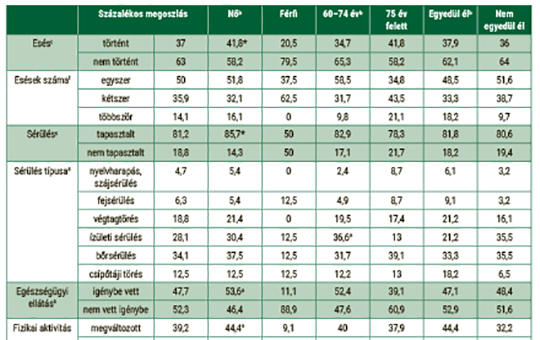
[To assess the prevalence of falls, knowledge of fall risk factors and daily fall prevention behaviour of elderly living in their own homes. 173 elderly people were surveyed. In addition to sociodemographic variables, we examined the prevalence of falls, risk of falling, knowledge of risk factors, modification of living environment, and daily fall prevention behaviors. Descriptive and mathematical statistics (chi-square, t-test, correlation analysis) were used (p<0.05). 37% of elderly people had a fall in the past year and 81.2% of them had experienced an injury. Among the risk factors, modifiable risk factors were the least accepted by the elderly. The idea of creating a safe environment was addressed by 72.8% of the sample, but only 52.9% had intervened. Changes were more likely to be adopted by women (p=0.025). Among the preventive activities, asking for help (12.1%) and using walking aids (18.5%) were the least adopted. Fall prevention programs that focus on modifiable risk factors are needed.]




COMMENTS
0 comments