The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2019;32(04)
Content
[The effect of an alternative training method on the pelvic floor muscle]
[Aim: In our study we analysed an alternative training method alone or in combination with pelvic floor muscle (PFM) with deep abdominal muscle strengthen the PFM better. Material and Methods: The study was conducted on women (n=5, mean age ±SD: 51,8 years, ±9,23 years). The Callanetics® gymnastics consisted of training sessions of 2x1 hours (10 weeks only Callanetics® exercises, 10 weeks in combined with PFM contractions). The subjects completed a questionnaire (risk factors, symptoms) and to measure the body parts’ circumference at 0. and 20. weeks. The measurement of the conditional capacitance of the PFM was performed by EMG before the gymnastics, then at weeks 10 and 20. We used R Statistics Software. Results: Significant decreseing were observed in the circumference of extremities and on isometric contraction improves (p=0.036). The dynamic strength showed an increasing tendency. Conclusion: The alternative training method significantly increased the maximum contractions of the PFM.]
[Dangerous beauty - Health risks of beauty salon workers ]
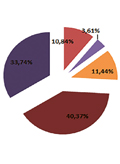
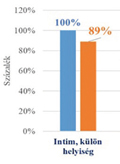
[The aim of the study: The aim was to assess the health status and working conditions of the beauty salon workers (hairdressers, barbers, beauticians, manicurists and pedicurists), and their knowledge regarding workplace risk factors. Methods: The survey was conducted in December 2018 - January 2019 through self-constructed online questionnaire among Hungarian beauty salon workers which covered socio-demographic data, workers’ health issues and occupational health issues. Data were analysed with SPSS 22.0. Results: The online questionnaire filled out by a total of 166 beauty salon workers. workers (165 women and 1 man). The respondents had an average age of 35.21 years. The average working hours of the workers was 8.88 hours. 33.73% of the sample did not visited the occupational health setting at all. It can conclude that all of the respondents have chronical disease. Conclusions: The research confirmed that the employees of the beauty industry are exposed to a lot of health damaging factors, which is primarily the permanent contamination with chemical substances. The test results prove, that more emphasis should be placed on prevention and appearance in occupational health tests, as well as order to the personal protective equipment to use for healthy and safe working.]
[How to break sensitive news in the Ophthalmology, specifically at diabetic retinopathy ]
[The aim of the study: To investigate the circumstances of breaking bad news by health care professionals and the conditions of communication at the Ophthalmology Clinic of the University of Pécs, among diabetic retinopathy patients. Material and method: Quantitative and cross-sectional examination, February-December 2018. Statistical methods: descriptive and mathematical statistics (χ2-test), SPSSv22, (p<0,05). Results: Most of the examined medical professionals working at the clinic (20 persons/90.90%) can’t be supported by a protocol for breaking bad news, however, the need for a protocol is formulated as more than half of the respondents (11 persons/59.09%). Conclusions: Health care professionals would need to develop a protocol to break bad news in health care institutions, also in the Clinic of Ophthalmology, furthermore, attention should be paid to improving the circumstances during providing information to patients.]
[Meta-analysis about the Incontinence-associated dermatitis prevention ]
[Background: The maintenance of tissue integrity is an essential part of qualitative nursing. There is a wide scale of products serving the prevention of Incontinence-associated Dermatitis (IAD). However, there is little evidence nurses know about them, making their choice of strategy difficult. Aim: To produce an evidence based publication about the preventive products of IAD, helping nurses in their choice of strategy. Method: In our meta analysis we examined the content of the Medline and Scopus database with special focus on English and Hungarian publications from the last ten years. From the 17459 articles relevant in this topic we analyzed and included 9 studies serving our criteria. Records: We found several methods of prevention; Washing without water, special absorbent pants, protocols and a study about the ’perineal pouch’. The studies were compared from the aspect of IAD prevalence, severity and cost effects. The 3in1 products and protokolls are should be used is the hungarian nursing practice.]
[The effect of whole body electrostimulation for the pelvic floor muscles ]
[The aim of the study: Few studies research the effects of trunk stabilizer muscle strengthening on pelvic floor dysfunctions. We assessed a new core strengthening method on the pelvic floor muscles. Material and method: Female patient (70 years) with stressincontinence and low back pain received the Whole Body Electric Muscle Stimulation for 10 weeks (2x25 minutes/week). The EMG (for the conditioning ability of pelvic floor muscle such as maximal isometric contraction, dynamic endurance and relaxation values), urodynamic assessment, introitus and the transabdominal ultrasound were used before and after training. Results: The patient’s the stressincontinence, low back pain and the conditioning ability of pelvic floor muscles improved. The urodynamic and ultrasounds values showed improvement in functions of the bladder neck and deep abdominal muscle. Conclusion: This method would increase the trunk stabilization and pelvic floor muscle strength of the eldery age group, which might decrease the prevalence of urinary incontinence.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]2.
3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aspects of Occupational Health Nursing for Incurable Patients ]