The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Clinical Neuroscience - 2017;70(09-10)
Content
[Diabetes, dementia, depression, distress]
[The number of people living with diabetes continues to rise. Therefore neurologists or other health care practitioners may be increasingly faced with comorbid neuropsychiatric disorders commonly presented by diabetic patients. More recently there has been an increasing research interest not only in the interactions between diabetes and the nervous system, the fine structure and functional changes of the brain, but also in the cognitive aspects of antidiabetic treatments. Patients with both types of diabetes mellitus may show signs of cognitive decline, and depression. Comorbid insomnia, anxiety, and distress may also occur. The bi-directional relationships between all these phenomena as well as their connection with diabetes can lead to further health and quality of life deterioration. Therefore it is important that all practitioners involved in the care of diabetic patients recognize the presence of comorbid neuropsychiatric disturbances early on during the healthcare process. Identifying higher risk patients and early screening could improve the prognosis of diabetes and may prevent complications.]
[The Multiple Sclerosis Registry of Szeged]
[Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a rare disease of the central nervous system considering the total population, the prevalence in Hungary is 83.9/100.000. The first MS registry was established in Denmark in the middle of the 1950’s. This was followed by the establishment of several national, then international databases with the number of enrolled patients in the hundred-thousands. At the beginning, the primary goal of the registries were the epidemiological surveys, focusing on the number of patients, the prevalence, the incidence, the mortality and the co-morbidity. As of today, however, with the rapid advancement and development of new disease modifying therapies (DMT) with different effectiveness and adverse reactions, the therapeutic use of the registries became even more essential: the modern, up-to-date, well established registries become integral part of the DMTs’ monitorization. The Multiple Sclerosis Registry of Szeged was first established as a “paper-based” database, then, in 2012, it was upgraded to an electronic, easily contactable and useable internet-based registry. As of today, it contains the socio-demographic and clinical data of more than 600 patients; we constantly add new patients as well as keep the registry up-to-date with the refreshment of old patients’ data. Aside from the “classical” clinical data, it can be used for the recording and assessment of the MRI scans and the data on psychopathological and quality of life assessments, which are becoming more and more important in everyday MS management. The establishment of the internet-based registry incredibly helped both the monitorization of the effectiveness of DMTs, and the success of the new epidemiological and psychopathological surveys. ]
Health anxiety mediates the connection between somatosensory amplification and self-reported food sensitivity
Background - The frequency of self-reported food sensitivity (SFS) is increasing, and has a negative impact on the well-being and everyday functioning of the affected people. A considerable proportion of SFS cannot be medically explained. The lack of knowledge of its origin and treatment causes further stress in those affected. Purpose - This study aims to get a better understanding of the psychological background of the condition. Methods - A non-representative community sample (N=335; age: 35.1±13.18 yrs; 75.8% female) completed an English on-line questionnaire assessing somatosensory amplification, health anxiety, modern health worries (MHWs), beliefs concerning the scientific validity of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), holistic beliefs on health and illness. Results - In multiple binary logistic regression analyses, SFS were associated with CAM related beliefs, somatosensory amplification, and health anxiety after controlling for age and gender. The connection between somatosensory amplification and SFS were completely mediated by health anxiety. No differences between the two groups were found with respect to MHWs, worries about the harmful effects of various artificial components in food, and holistic health beliefs. Discussion: More positive attitudes toward CAM might be based on the lack of conventional treatment, rather than on higher levels of MHWs or a more holistic worldview. Both the existence of symptoms and the presence of health anxiety might be needed for the development and maintenance of SFS. Conclusions - The findings support the notion that somatosensory amplification and health anxiety might play a role in the development and maintenance of SFS.
Correlation of vitamin D levels with electrophysiological findings and pain in the patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Objective - This study aimed to assess the correlation between vitamin D deficiency and electrophysiological findings and pain level in patients with symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Patients and method - A total of 131 patients with symptoms of CTS, 70 with vitamin D deficiency and 61 without vitamin D deficiency, were included in the study. Using demographic data and findings from electrophysiological examinations, the patients were divided into two groups based on their vitamin D level (Group 1: <20 ng/ml; Group 2: ≥20 ng/ml). The Boston Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Questionnaire was used to assess their CTS- related pain level. Results - Although the rate of CTS in the patients with a low vitamin D level was found to be high, no statistically significant correlation was observed between low vitamin D level and the frequency and severity of CTS. Additionally, the pain and functional loss ratio induced by CTS was found to be higher in the group with a lower vitamin D level than in the group with normal levels. Conclusion - Low vitamin D levels may increase the severity of CTS symptoms. Treatment of vitamin D deficiency in patients with CTS can play a role in reducing pain and disability.
[Current diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension]
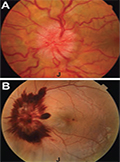
[Background - Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is cha-racterized by raised intracranial pressure of unknown origin, leading to persisting visual loss if left untreated. Purpose - We assessed timing of surgery, and the efficacy and safety of ventriculo-peritoneal shunt. Methods - Retrospective analysis of 65 patients treated at our Neuro-ophthalmology Clinic between 2009 and 2017. Patients - We treated 15 children and 50 adults, 42 patients conservatively, and 23 surgically. The median age at presentation was 27 years for adults, 88% were obese, and 86% female. The age of children was 5-17 years, 40% were obese, and 53% girl. The commonest presentation symptom was headache in both groups (64%), followed by obscuration (33%), and double vision (22-31%). Subjective visual loss was only experienced in the surgical group (50%). The time until diagnosis was 2 weeks in both groups. However, the conservative group presented to our institute significantly earlier (3 weeks), than the surgical group (8 weeks). The follow-up time was 25 months. Results - In the conservative group papilla edema was 2D, visual acuity ≥0.7, and visual field loss was only mild. Time to cure was 3 months. In the surgical group both preoperative papilla edema (3D), and visual function were significantly worse. Indications for surgery were papilla edema, deteriorating visual function or relapse resistant to conservative treatment. Papilla edema disappeared 3 months after surgery, and visual field deficit improved significantly. We detected significant improvement in all aspects of visual function even at first neuro-ophthalmic control 4 days after surgery. However, visual acuity only improved in cases of preoperative acuity ≥0.3. Shunt revision occurred in 17%, and shunt infection in 8.5%. One patient suffered from persistent visual deterioration after surgery, and asymptomatic complication (epidural hematoma) was found in another patient. There was no surgical mortality. Conclusions - This is a curable condition with early diagnosis and adequate treatment, and persistent visual loss can be prevented. Surgery is effective and safe, close neuro-ophthalmic monitoring is mandatory for its optimal timing. Visual function of all patients can be preserved when operated on in time, whereas severe visual loss appears to be irreversible despite surgery.]
Does the comparison of median-to-ulnar nerve sensory conduction add an additional value in electrodiagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome?
Background and purpose - Distal sensory onset latency (DSOL), conduction velocity (SCV) and nerve action potential (SNAP) amplitudes are used in electrodiagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) beside motor conduction data. The aim of our study is to search whether the comparison of median-to-ulnar nerve sensory conduction adds an additional diagnostic value in CTS or not. Methods - Median and ulnar nerve were stimulated on wrist, and SNAPs were recorded on second and fifth fingers, respectively. Best cut-off points for the searched parameters and their diagnostic efficiencies were determined. The cut off points were also stratified according to the age and gender, and their diagnostic efficiencies were calculated again. Results - The study includes 415 hands belong to 344 subjects. Best cut off points for median nerve DSOL and SCV were 2.7 msec and 49.0 m/sec with the diagnostic efficiencies of 87.7% and 88.7%, respectively. Best cut off points for DSOL difference and SCV difference were 0.62 msec and 4.0 m/sec, and efficiencies were 89.6% and 84.3%, respectively. Conclusion - Determining the relative elongation of median nerve DSOL to the ulnar nerve one has a little additional value in electrodiagnosis of CTS, whereas any additional value is not obtained from SCV comparison.
[Childhood sporadic type of hemiplegic migraine with arteria cerebri media hypoperfusion]
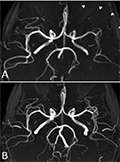
[Hemiplegic migraine is a rare subtype of migraine that is associated with reversible motor weakness in the aura phase. This is an uncommon form of migraine usually starting in childhood. The purpose of this case report is to highlight the differential diagnostic difficulty of the first attack. We describe a case, where the fluctuating unilateral motor weakness and aphasia suggested that the patient had ischaemic stroke. Nevertheless the brain MRI and MR angiography, the measured 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid (5-HIAA) concentration changes and the spontaneously improving clinical status proved the diagnosis of hemiplegic migraine. The MRI and MR angiography was very beneficial in establishing the correct diagnosis in this case. To distinguish between the familiar and sporadic type of hemiplegic migraine further genetic tests can be carried out.]
[Administration of idarucizumab in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage under dabigatran-therapy]
[Introduction - Among antidotes in development for reversal of novel oral anticoagulants, dabigatran-specific idarucizumab was the first one to reach the market. Case presentation - We present the first Hungarian case of intracerebral hemorrhage under treatment with dabigatran, where idarucizumab was administered to suspend anticoagulation. Discussion - Our report is concordant with prior publications, confirming the efficacy of the antidote in reversing the effect of dabigatran, and thus, preventing intracerebral hematoma progression in the acute phase. Conclusion - Since there is no proven alternative to idarucizumab, conducting randomized clinical trials would be unethical. Therefore, besides case reports, positive results of prospective studies could help us revise therapeutic guidelines, and thus, improve the prognosis of dabigatran-associated intracerebral hemorrhages.]
A case of secondary SUNCT syndrome
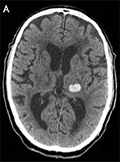
SUNCT syndrome, a rare form of primary headaches, may be secondary to pituitary tumours. The secondary forms usually related with prolactinomas. The response of dopamin agonists could be variable. In this study, we reported a case of SUNCT syndrome secondary to prolactinoma. Cranial magnetic resonance imaging was performed for this patient because of the increase in pain severity and frequency. A hemorrhage was detected into the prolactinoma ipsilateral to the pain. The headache attacks were taken undercontrol and remission was ensured with cabergoline in a short time.
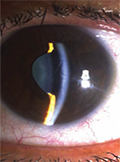
Title of the article: Bilateral acute angle-closure glaucoma induced by duloxetine
Introduction - To present a rare case of bilateral acute angle-closure glaucoma secondary to duloxetine administered for the treatment of depression. Case presentation - A 46 year old woman developed bilateral closed angle glaucoma after 15 days of duloxetine usage. Intraocular pressures (IOP) were 52 and 55 mm Hg in right and left eyes respectively, with shallow anterior chamber and angle closure on gonioscopy. Discontinuing duloxetine treatment, initiation of antiglaucomatous treatment and bilateral Nd:YAG Laser iridotomy obtained normalized IOP and anterior chamber depth. Conclusion - Duloxetine, used in the treatment of depression can be responsible for acute angle-closure glaucoma by leading to mydriasis and ciliary effusion.
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]1.
2.
Clinical Neuroscience Proceedings
[A Magyar Stroke Társaság XVIII. Kongresszusa és a Magyar Neuroszonológiai Társaság XV. Konferenciája. Absztraktfüzet]3.
4.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[A selection of the entries submitted to the literary contest "Honorable mission: the joys and challenges of our profession" ]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[End of Life and Palliative Care of Newborns in the Nursing Context]