The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Specialities
Psychiatry
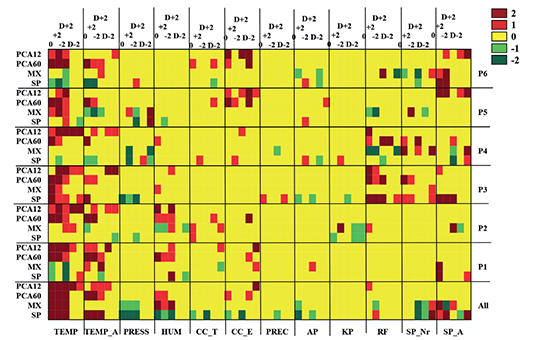
Personalized analysis of pain–weather associations: a pilot study
It is a wellknown belief that weather can influence human health, including pain sensation. However, the current data are controversial, which might be due to the wide range of interindividual differences. The present study aimed to characterize the individual pain–weather associations during chronic pain by utilizing several data analytical methods.
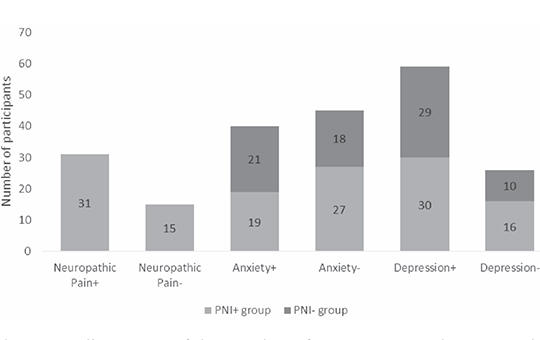
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, frequently result in mood disorders among affected individuals. It is established that neuropathic pain arising from traumatic neuropathies is also linked to mood disorders. This study investigates the influence of neuropathic pain on the development of mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries, following the earthquake centered in Kahramanmaraş on February 6, 2023.
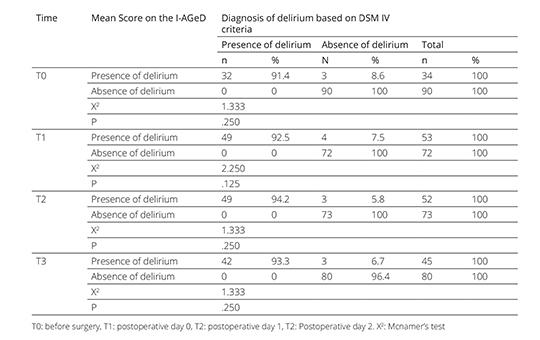
Validity and reliability of the Turkish version of the Informant Assessment of Geriatric Delirium Scale
Delirium is a common complication developing in elderly patients. Therefore, it is important to diagnose delirium earlier. Family caregivers play an active role in early diagnosis of delirium and build a bridge between health professionals and patients. The purpose of this research was to achieve the validity and reliability of the Turkish version of the Informant Assessment of Geriatric Delirium Scale (IAGeD).
[Blooming again – women’s life paths after brain injury ]
[After a serious brain injury or trauma, there is damaged the functional capacity of the affected persons and their self-image too. Traditional rehabilitation pays little attention to the female patients’ lost femininity. The aim of this study was to present the way of supporting women to realize again their femininity psychologically and physically alike after a brain injury.
In the Brain Injury Rehabilitation Unit of the National Institute for Medical Rehabilitation, the authors completed the female patients’ rehabilitation with special group sessions once a week. The topics were tailored to the needs of participants. There were targeted two specific objectives: achieving to perceive femininity in an autonomous way and regaining the feeling of femininity in the changed life circumstances due to the injury.
Occupational therapist, physiotherapists and nurses provided service to develop functional abilities. A psychologist helped the participants in trauma processing. Since the beginning in January 2022, two therapy cycles have been completed so far, each of which with 10-12 sessions. A total of 31 female patients and 8 supporting team members participated in these two groups so far.
Personalised rehabilitation was adjusted to the involved persons’ life circumstances, individuality, personality, family and social relations. Our experimental female group helped the participants to experience their femininity physically, mentally and psychologically too, according to their feedback.]
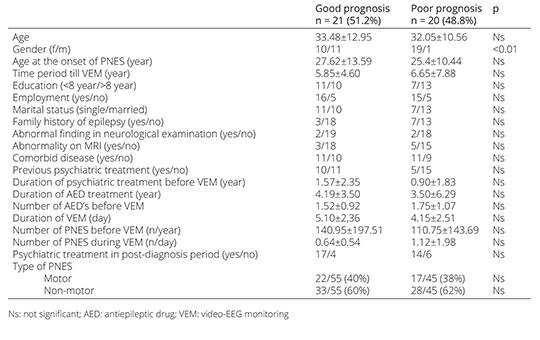
Factors affecting long-term prognosis in adult patients with psychogenic non-epileptic seizures
Among epileptic patients who are monitored using the video-electroencephalography monitoring (VEM) technique, in some patients a psychogenic non-epileptic seizure (PNES) can be identified as a definitive diagnosis. The longterm prognosis of these patients is not well known. In this study, we aimed to determine the factors that affect the prognosis of PNES. Forty-one PNES patients diagnosed using VEM between 2012 and 2022
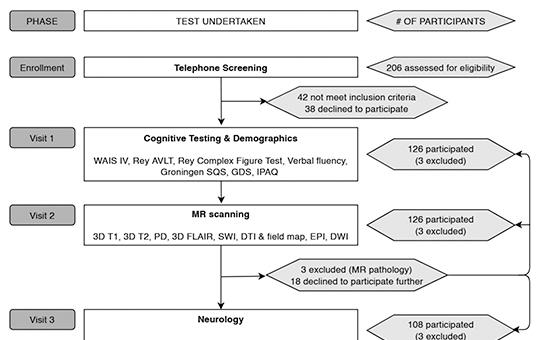
Study protocol of the Hungarian Longitudinal Study of Healthy Brain Aging (HuBA)
Neurocognitive aging and the associated brain diseases impose a major social and economic burden. Therefore, substantial efforts have been put into revealing the lifestyle, the neurobiological and the genetic underpinnings of healthy neurocognitive aging. However, these studies take place almost exclusively in a limited number of highlydeveloped countries. Thus, it is an important open
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
3.
4.
5.