The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Specialities
Psychiatry
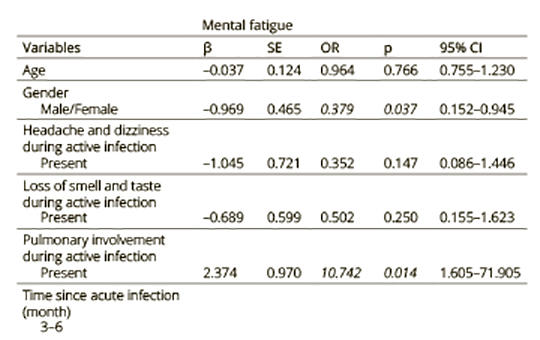
Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 in young adults: Mental fatigue and decreased cognitive flexibility
Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) describes the occurrence of persistent symptoms following COVID-19 infection. Neurological and psychiatric symptoms may include fatigue, post-exertional malaise, cognitive complaints, sensorimotor symptoms, headache, insomnia. The aim of this study was to evaluate the long-term effects of COVID-19 infection on mental fatigue and cognitive flexibility in young adults.
[Desmopressin may counteract polyuria in lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Review of the literature]
[Lithium is a simple ion that remains the best, safest and least expensive treatment for the prevention of recurrent episodes of bipolar disorder. However, in many patients administration of lithium is associated with renal side effects. The most frequent side effect is a defect in urinary concentration which may lead to permanent lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Patients suffer from a disturbed night therefore it is an eminent goal to secure them some rest. In our previous work administration of excessive doses of desmopressin resulted in clinically relevant antidiuresis in lithium-induced nephrogenic insipidus enhanced by indomethacine The purpose of the present paper is to review the literature concerning the use of desmopressin in lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.]
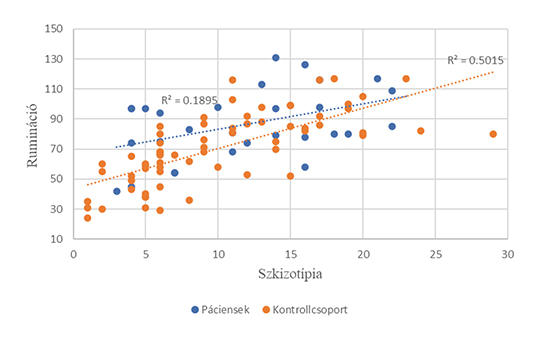
[Rumination and schizotypal personality traits]
[Although rumination and schizotypal traits can be considered transdiagnostic phenomena and can occur within non-clinical population as well, a relatively small number of research has been carried out on the topic involving both patient and non clinical participants. The aim of this study is to examine the relationship between schizotypal traits and rumination using a transdiagnostic approach, involving participants living with psychotic disorders and sine morbo individuals.
We recruited participants living with psychotic disorders (paranoid schizophrenia, hebephrenia, schizoaffective disorder, etc.) (n = 30) and controls who had not been diagnosed with any mental illnesses (n = 67). The connection between rumination and schizotypal traits was examined by self-report questionnaire method in a cross-sectional arrangement. The Oxford-Liverpool Inventory was used to measure schizotypal traits, and the Ruminative Thought Style Questionnaire was used to determine the level of rumination.
Schizotypal symptoms (β = 0.575; p < 0.001), especially cognitive disorganization (β = 0.459; p < 0.001) and unusual experiences (β = 0.221; p = 0.029) significantly explained the degree of rumination.
Our results support the hypothesis that the association between rumination and schizotypic traits is due to decreased cognitive inhibitory functions.]
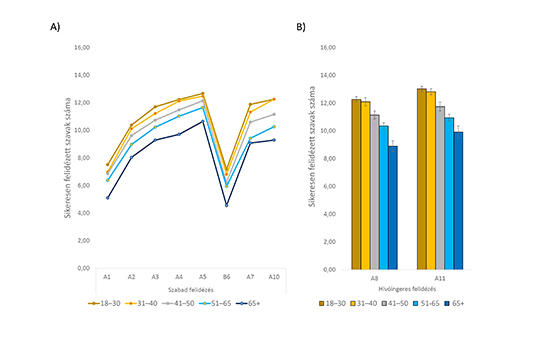
[Verbal Episodic Memory Test]
[The decline of episodic memory is one of the earliest cognitive markers of mild cognitive impairment and various types of dementia. Until today, however, there is no standardized Hungarian episodic memory test that takes into account the characteristics of the Hungarian language. The study presents the structure and standardized use of a new memory test (Verbal Episodic Memory Test, VEMT) as well as normative data in Hungary.
The VEMT is suitable for the comprehensive examination of verbal learning abilities in a broader sense, and more specifically, for the neuropsychological measurement of verbal list learning abilities. In the present study, we constructed a normative database consisting of data from 385 participants.
We showed that the VEMT is sensitive to demographic factors (e.g., age) which are linked to differences in episodic memory performance. Open access to the test is provided, and the normative scores are presented as well.
The indicators of the test are suitable for drawing a learning curve, for showing the interaction of new and previously learned information (interference effects), and for measuring differences between free recall and cued recall. Furthermore, the test scores are appropriate for distinguishing the effects of different types of memory encoding forms (phonological, semantic, and episodic), for measuring the ability to reconstruct the presentation of a sequence (memory order information), for detecting the rate of forgetting, for measuring recognition abilities, and for detecting hippocampus-related mnemonic pattern separation and completion functions. ]
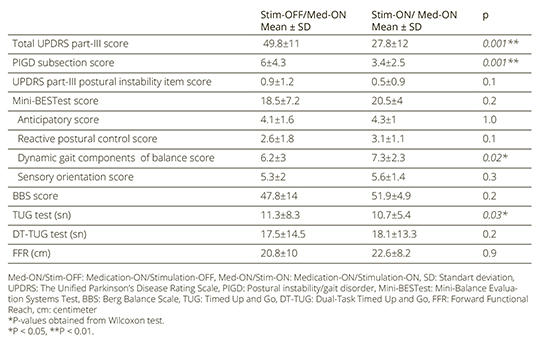
Effects of the combined treatment of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation and levodopa on balance and mobility in Parkinson’s disease
Background and purpose – To evaluate the efficacy of the combined therapy of bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation (STN-DBS) and dopaminergic medication on balance and mobility in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD).
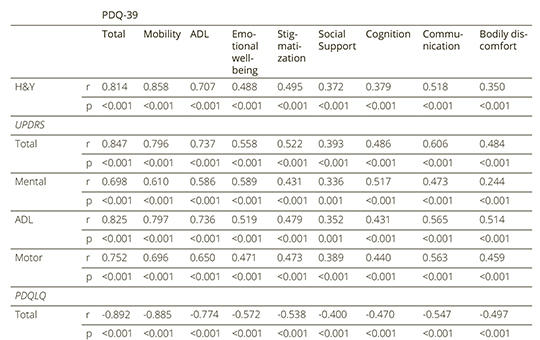
Reliability and validity of the Turkish version of the 39-item Parkinson Disease Questionnaire
This study aims to investigate the validity and reliability of the Turkish Version of the 39-item Parkinson Disease Questionnaire. A total of 100 patients with Parkinson’s disease who were admitted to the outpatient neurology clinic in Koc University and Istanbul University were enrolled. 39- item Parkinson Disease Questionnaire, Parkinson Disease Quality of Life Questionnaire, Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale, Hoehn-Yahr Scale, and Short Form Health Survey-36 were administered to all participants.
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
3.
4.
5.