The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2020;30(06-07)
Content
[Treatment of hypercholesterolemia in the elderly]
[The percentage of population aged ≥65 years is mounting worldwide, among them those over 75 years is also growing. Atherosclerosis is one of the most important and common disorder in the elderly responsible primarily for premature death and cognitive declining and impaired quality of life. Adequate lipid lowering therapy can decrease the risk of cardiovascular events – the main cause behind mortality – can extend life expectancy and improve the quality of life of patients. Effect of dietary treatment on cardiovascular risk reduction is as beneficial as in the younger populations. Regular physical activity reduces the risk of cardiovascular and overall mortality by 26% in males and 20% in females aged ≥65 years. If the medical history is negative for vascular disorders, statin administration as a primary prevention is indicated for patients 65>years. In the population aged 75≥years individual benefit/risk assessment is needed before statin administration. Larger risk reduction can be achieved between 65-75 years than in subjects over 75 years. Concerning secondary prevention, statin treatment is of pre-eminent significance, and its administration is evidence-based in the elderly. For achieving the lipid goals, combined therapy with statin and ezetimibe is recommended in the primary as well as secondary cardiovascular prevention. ]
[The significance of the identification of SARS-CoV-2 virus and the possible errors of the sampling method]
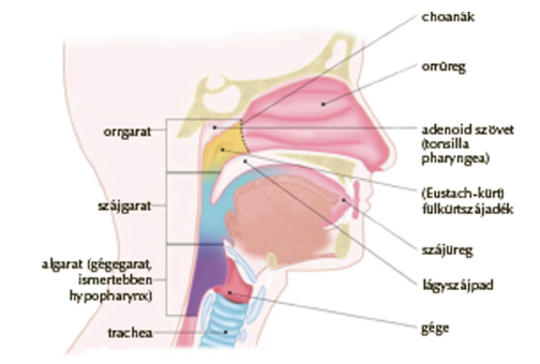
[The COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 virus while emerging suddenly and spreading throughout the globe challenged seriously also the modern medicine. Diagnostic methods recognising viral infections of the upper airways developed essentially in the last 20 years, and it was specifically progressing during the SARS and MERS epidemics thus facilitating the recognition and identification of infections by influenza, RS- and adenoviruses as well. Nevertheless the present novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) also demonstrated that the relatively simple procedures of naso- and oropharyngeal sampling are fallible too. Thus they may have a relatively high risk of false-negative outcomes. However the correct sampling prior the RT-PCR tests provides reliable diagnosis by high sensitivity and specificity. Thus improving the quality of sampling and avoiding failures by correct training and education of the personnel make more reliable the detection of viral infection or indicate recovery after the infection. Finally, this is a key issue while overcoming the present pandemic.]
[Sarcopenia – muscle loss – pathomechanism, clinical presentation and metabolic comorbidities]
[Sarcopenia, or the age-related involution of muscle strength and muscle mass, is a serious public health concern, due to the growing number of elderly population caused by nowadays demographic changes i.e. prolonged life expectancy. By ageing, the muscle tissue is shrinking gradually, leading to the loss of muscle strength and masses. This condition is called sarcopenia. Sarcopenia is the simultaneous decrease of muscle mass, muscle strength and functional independence. In parallel the physical performance deteriorates (weakness, slowness and poor physical balancing). Fatigue, elderly behaviour and weight loss are the consequences of these accumulating deficits, which associate with cognitive decline and result in increasing social isolation. The primary form of sarcopenia is the decrease of the energy production of muscle cells and then the death of muscle cells. Secondary, endocrine dysfunctions, diseases of the nervous system, decreased physical activity, malnutrition or malabsorption, chronic infection accelerate the process and aggravate the patient’s condition. Complex genetic, biochemical and endocrine mechanisms take part in the development of sarcopenia. This involution is due to the impaired balance of restoring and depleting processes of muscles. A questionnaire and algorithm have been developed to recognize, screen and diagnose the risks of sarcopenic condition; these separate the sarcopenic and non-sarcopenic patients with specific cut-off values. Sarcopenia can be diagnosed based on walking speed, decreased handgrip strength and measured or calculated muscle mass in persons over 65. Sarcopenia can be considered as a phenomenon of “physiological” aging, however, it becomes a disease when diagnostic cut-offs are exceeded and the patient experiences functional disability and declining quality of life. Prevention and treatment of sarcopenia and reducing the risk of falling are based on regular active resistance and coordination exercises. Options for pharmaceutical treatments are limited since despite of identified molecular targets there are no convincingly effective innovative therapy on the horizon. Nevertheless, there are some weak evidence for efficacy of the application of amino acids stimulating muscle cell differentiation, such as leucine or the analogue of beta-hydoxy-methylbutyrate beside exercise therapy.]
[Avoiding unlimited energy drink consumption is a matter of our heart]
[Energy drinks have been gaining unbroken popularity, especially among youngsters and children since they were introduced to the market. Manufacturers promise to improve performance and stamina with consuming the products, classified as non-alcoholic soft drinks. In addition to the vitamins and plant extracts, they contain a significant amount of caffeine and other stimulants (taurine, guarana). Among the active ingredients, caffeine has an outstanding effect and thereby a danger, since its overconsumption – in addition to milder hemodynamic changes – can cause severe cardiovascular consequences, cardiac arrhythmias, ion channel diseases, increased blood coagulation, myocardial infarction or reduced cerebral blood flow in susceptible consumers. Many case studies have also reported serious cardiovascular attacks among young chronic energy drink consumers. Health impairments of excessive and long-term consumption of energy drinks have been studied increasingly, however there is limited and contradictory evidence on the safety of consumption and the effectiveness of performance enhancement. ]
[Suicide endangering elderly people: risk factors, prevention and care]
[According to the data of the Hungarian Central Statistical Office (HCSO), the Hungarian citizens aged over 65 represented in 2001 11.8%, 2011 13.2% and 2019 19.3% of the total population. Providing services for aging (>60 years), aged (>75 years), very old (>90 years) and Matusalem (>100 years) individuals burdens heavily the health system and the socio-economic sector. Maintaining these people’s physical and mental health and self-perceived well-being is a pre-eminently important task. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) statistics based on data providing countries, the number of suicides committed in the population aged 60-79 has risen approximately by 21% between 1987 and 2006. The suicide rate in Hungary has decreased steadily and significantly since 1980 (4809 in 1980, 1656 in 2018, i.e. a decrease of 66%). Thus since 2018, Hungary is not among the top three countries in Europe and the top 15 in the world. However, the number of completed suicides and suicide attempts remains high and shows rising tendency in the elderly. Preventing suicide, exploring the risk factors and caring patients after attempted suicide we need to analyse thoroughly and disseminate widely the results of the recent researches. In this study, we reviewed international and domestic literature data to find answers primarily to prevention issues. ]
[Minority students in Hungarian medical training]
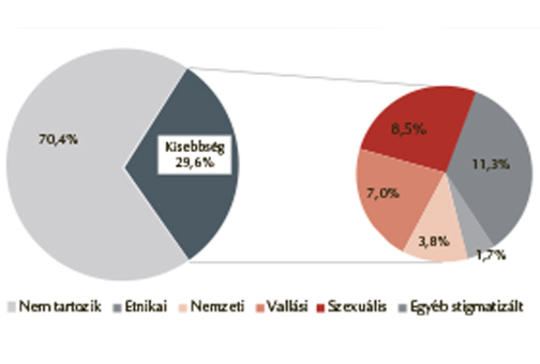
[General health of minority people is usually worse than that of their majority peers and they often expe rience discrimination in the healthcare system. According to international literature, physicians belonging to any minority group are more likely to care for other mi nority people, therefore they may play a key role in reducing healthcare inequities. Anonymous, online questionnaire was distributed to medical students of the four Hungarian universities with medical schools (response rate was 8.86%). In this paper, we analyze our collected data about perceived discrimination with descriptive statistical methods. Results of confirmative statistical analyses (statistical tests) were considered exploratory in nature. 29.6% of respondents self-identified as a member of any minority. 63.0% of minority students and 53.8% of women indicated that they realized discriminated or were harassed in the last 12 months, meanwhile, 37.8% of non-minority students and 31.9% of males have experienced discrimination. Discrimination related to ethnic origin, sexual orientation and disability are regarded as the most widespread forms of discrimination according to our respondents. Students are most likely to say that there is no age related discrimination on the grounds of age – both being under 30 years old (12.0%) and being over 55 (8.6%). Being the member of any minority group seems to have no effect on student’s/ one’s opinion how widespread the forms of dis crimination are. Minority students are more comfortable to work with a member of another minority. However male students feel more uncomfortable to work with a member of sexual or gender minorities compared to female counterparts. Minority students tend to be more critical to the universities’ efforts to enhance diversity. Minority students and females may play a key role in reducing discrimination in medical training and in the healthcare system and in providing high-quality care for individuals who belong to any minority. Although there are more females than males in medical training they still report higher occurrence of perceived discrimination. However, it is important to emphasize the low response rate in our study, which does not allow us to draw any general conclusions.]
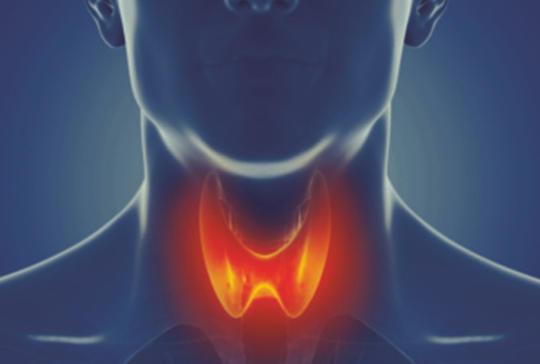
[Persisting Hashimoto’s thyroiditis converting to Graves’ disease]
[Graves’disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are the two most important types of autoimmune thyroid diseases. Autoimmune hyperthyroidism commonly leads later on to hypothyroidism. The conversion from persisting Hashimoto-thyroiditis to hyperthyroidism is rare in the literature. The author presents the cases of two patients, whose Hashimoto’s thyroiditis treated with thyroxin for years, changed into Graves’ hyperthyroidism spontaneously. CASE REPORT – The patients had been diagnosed with autoimmune hypothyroidism since several years. The clinical symptoms, the low peripheral hormone levels, the high level of antithyroid antibodies and the ultrasound imaging confirmed the hypertrophic form of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. After several years of high dose levothyroxin treatment, clinical symptoms of hyperthyroidism have appeared. After omitting the substitution, the thyroid hormone levelled off at high values and the level of anti-TSH receptor antibodies raised too. The diffuse, obviously increased blood flow of the thyroid glands, and in one of the patients the thyroid scan, confirmed the Graves’ disease. During the thyreostatic treatment, the symptoms of the patients disappeared, they became euthyreoid and the antibody levels decreased as well. The Graves’ disease and the Hashimoto’s thyroiditis have many common features. These immunological, genetic and other common features enable the mutual transition of these two diseases.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]4.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Fear of Falling among Geriatric Patients: a Narrative Review]1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Recurrent simultaneous central nervous system demyelination with possible peripheral demyelination / nodopathy in a seronegative patient2.
3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Predictors of pneumonia in stroke patients with dysphagia: A Turkish study4.
5.
Clinical Neuroscience
Effect of inflammatory response before mechanical thrombectomy on prognosis in stroke patients