The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Clinical Neuroscience - 2024;77(9-10)
Content
Role of the video head impulse test in the evaluation of vestibulo-ocular reflex in individuals with Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the most common movement disorder and the second most common neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system. Dizziness is frequently reported by PD patients, yet there is a paucity of research focusing on the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) in this population using high-frequency vestibular testing. This study aims to investigate the VOR in individuals with PD using the video head thrust test with and without suppression.
Forty individuals with PD and 40 healthy individuals were included in the study. According to the Hoehn-Yahr Scale, individuals with PD were defined as early stage with a score of 1–2.5 and middle to late stage with a score of 3 to 5. The Head Impulse Testing Paradigm (HIMP) and Suppression Head Impulse Testing Paradigm (SHIMP) were applied to all individuals.
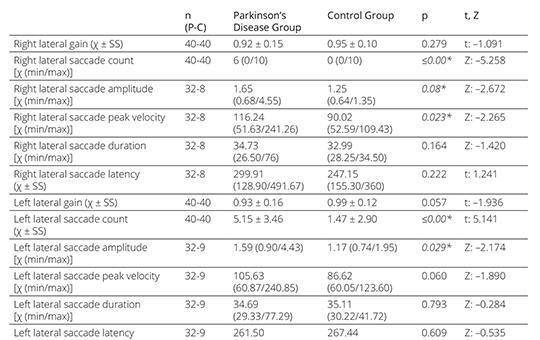
No statistically significant difference was observed between the PD group and the control group in terms of semicircular canal (SCC) gains in both HIMP and SHIMP tests. No catch-up saccades were observed in the right anterior, right posterior, left anterior, and left posterior SCC planes in the PD and control groups. However, in the right lateral SCC plane 32 patients in the PD group had saccades, while 8 patients in the control group had saccades. In the left lateral SCC plane, 32 patients in the PD group and 9 patients in the control group had catch-up saccades. A statistically significant difference was observed in the number and amplitude of saccades in the right and left lateral SCC planes compared to the control group (p<0.05). In addition, in the PD group, the amplitude, peak velocity, and latency of the anticompensatory saccades seen in SHIMP showed a statistically significant difference compared to the control group (p<0.05).
VOR in the vertical SCC plane was not affected in individuals with PD. However, VOR in the lateral SCC plane was affected. It was concluded that when evaluating VOR with both HIMP and SHIMP in individuals with PD, the presence of catch-up saccades should be focused on and evaluated for possible vestibular dysfunction, even though SCC gains are normal. This study will contribute to a deeper understanding of vestibular function in PD, potentially informing better management strategies for dizziness in this population.
The effect of body position, leg dominance, and automatic releasing mechanism on quadriceps muscle tone assessed by Pendulum Test in able-bodied persons
Quadriceps femoris muscle spasticity is commonly measured by the Wartenberg pendulum test. It is generally assumed that lower values of the number of swings of the leg and lower relaxation indexes are associated with higher muscle tone and more spasticity. Still, there is incoherence regarding the test’s applications with various body positions and starting mechanisms. This study aims to investigate the influence of body position, leg dominance, and automatic leg-releasing mechanism on muscle tone measured by pendulum test in healthy population whose muscle tone is often compared to the spastic muscle tone of patients with neurologic disorders.
15 healthy adults (age: 19-32 years, 9 males, 6 females) participated in this study. A Zebris 3D ultrasound-based motion analysis system was used to record kinematic data during the pendulum test. The number of swings of the leg and the relaxation index were computed from the collected data. The pendulum test was completed in eight conditions: in supine and semi-supine positions on the dominant and non-dominant leg separately and with investigator-release and automata-release mechanisms. Paired t-tests and Wilcoxon test with the significance level of .05 were applied in comparison of pairs of the pendulum test condition.
1) Applying automata-release mode, in the non-dominant leg the number of swings (p=0.03) and the relaxation index (p<0.001) were significantly higher in semi-supine than in supine position. 2) The non-dominant leg had significantly more swings than the dominant leg in both body positions with automata-release mode (p=0.009, p<0.001). In investigator-release mode this occurred in supine position (p<0.001). 3). Regarding the number of swings in investigator-release versus automata-release mode, no significant differences were found in any test condition, but the relaxation index showed significant difference for the non-dominant leg (p=0.01, p=0.009). 4) The values of the relaxation index didn’t support in all test conditions the results what the number of swings provided about the muscle tone. In automata-release mode, the dominant leg has a lower number of swings and a higher relaxation index than the non-dominant leg.
The effect of body position on the quadriceps muscle tone can be assessed by applying the pendulum test with an automatic leg-releasing mechanism even when the application of conventional investigator-release mode does not show a significant effect. The pendulum test is more sensitive to assess spasticity with automatic-release than with investigator-release mode.
[Quality of life in acute ischaemic stroke patients treated with recanalisation]
[Stroke is a serious health problem that has a significant impact on health-related quality of life. Despite the increasing popularity of measuring quality of life among patients, it is not routinely measured in clinical practice, and therefore little is known about how well clinical measures reflect quality of life after stroke. The aim of this study was to investigate the quality of life of patients with acute ischaemic stroke.
For the prospective study, patients diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke at the Neurology Clinic of the Clinical Center of the University of Pécs were selected through convenience sampling between June 2022 and May 2023. Based on the treatments, patients were divided into three groups: mechanical thrombectomy (MT), intravenous thrombolysis (IVT), and standard care (SC). Modified Rankin Scale (Pre-mRS, Follow-up mRS), NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS), and European Quality of Life 5 Dimensions Scale (EQ-5D-5L) were used in the research. Descriptive statistics, paired T-tests, Wilcoxon tests, McNemar tests and Pearson correlation analysis were applied for the analysis (SPSS 25.0; p <0.05).
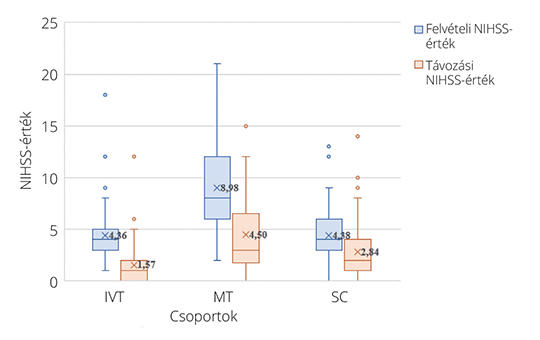
A total of 198 participants (115 males, 83 females) took part in the study (MT: 50, IVT: 69, SC: 79). The Pre-mRS and follow-up mRS values indicate that the majority of patients in all three groups fell into the mild category (Pre-mRS: 176 participants; 88%, follow-up mRS: 158 participants; 80%). There was a significant improvement in NIHSS scores in all three groups (IVT: 4.36 vs. 1.57, p<0.001; MT: 8.98 vs. 4.50, p<0.001; SC: 4.38 vs. 2.84, p<0.001). The EQ-5D-5L value also significantly increased for all groups (IVT: 0.82 vs. 0.88, p<0.001; MT: 0.63 vs. 0.73, p<0.001, SC: 0.76 vs. 0.80, p=0.014). Patients admitted with lower NIHSS values reported better quality of life at the end of our study (r: -0.43451).
At 30 days, significant improvement was observed in MT, IVT and SC groups when measured with EQ-5D-5L, but the extent of improvement was highest in the MT group.]
Effect of inflammatory response before mechanical thrombectomy on prognosis in stroke patients
Mechanical thrombectomy is the most important treatment modality in acute stroke; despite successful thrombectomy, good functional outcome is not achieved in a significant proportion of patients. This study examined the effect of neutrophil lymphocyte ratio (NLR) values at admission on functional outcomes in successfully recanalized patients.
Patients who underwent mechanical thrombectomy due to anterior system major vessel occlusion were retrospectively analyzed and compared with the admission NLR values and 3-month clinical modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores of successfully recanalized patients.
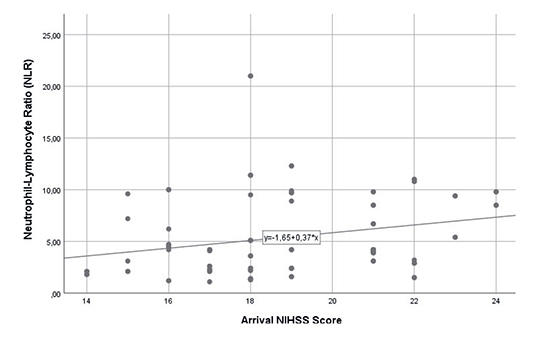
Of a total of 126 patients who underwent thrombectomy within the specified period, 97 patients with successful recanalization were included in the study. The overall successful recanalization rate was calculated as 77%. The mean NLR of patients with mRS ≤2 (n=65) was found to be significantly lower than patients with mRS≥3 (n=32) (p<0.001). A weak and significant correlation was found between National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) value and NLR (r= 0.315, p=.002).
NLR value has been found to be associated with futile recanalization in mechanical thrombectomy patients. Therefore, we think that suppression of inflammation before thrombectomy will increase the chance of successful thrombectomy.
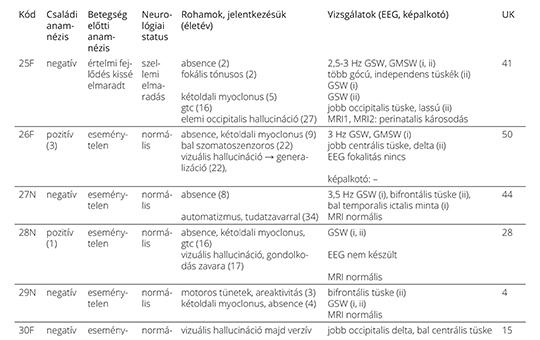
[Combined epilepsy with generalized and focal seizures]
[Combined epilepsy (with generalized and focal seizures) is a recently accepted and yet underreported epilepsy type. We intended to review the literature of combined epilepsy and to report the individual findings of the 31 combined epilepsy patients in our database. Thereafter, we investigated the characteristics of the patients at the group level.
The individual findings of the 31 patients were tabulated. We characterized the group with special reference to epidemiology, timing and the sequence of generalized and focal seizures, family history of seizures and severity of the electro-clinical phenotype. The variables were compared to those of the generalized epilepsy and the focal epilepsy groups of our database. We carried out statistical analyses by the two-sided Fishers’s exact test and the Kruskal-Wallis and post-hoc Dunn tests.
The prevalence of combined epilepsy was 1.56% within the total sample of the classifiable epilepsy patients. Females were affected more often than males (67.7% and 32.3%, respectively). Statistically significant associations emerged firstly between the “short interval” subgroup (where the generalized and focal seizures occurred with short time difference) and the lack of other cerebral abnormality, and secondly between the “long interval” subgroup (where 4 to 37 years elapsed between the occurrence of the two seizure types) and the presence of other brain abnormality (p = 0.02). The proportion of patients with positive family history of seizures was greater in the combined epilepsy- than in the generalized epilepsy group (p = 0.03) and the focal epilepsy group (p < 0.0001) of the database. The electro-clinical phenotype of the absence seizures showed more atypical findings (indicating poor prognosis) in combined epilepsy than in the generalized absence epilepsy patients of the database (p < 0,0001). Despite dissimilar patient selection and study design, our main findings were in accord with those of prior studies. The dissection of the combined epilepsy group into the “long interval” and “short interval” subgroups was a novel approach that highlighted the dissimilar pathogenetic and clinical correlates of each.
The case reports might facilitate the spread of information about combined epilepsy in the medical community. Analyses of the patients at the group level resulted in clinically useful pieces of evidence.]
Predictors of pneumonia in stroke patients with dysphagia: A Turkish study
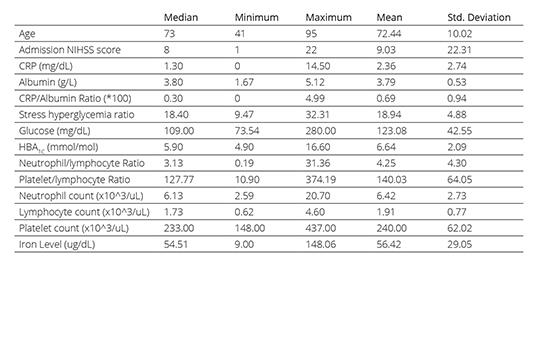
Dysphagia, characterized by difficulty in swallowing due to neurological deficits, stands out as the foremost contributor to stroke associated pneumonia (SAP) development. Recent investigations have explored the utility of blood tests, including parameters like neutrophil count, leukocyte count, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and the CRP to albumin ratio (CAR), at the time of admission as potential markers for predicting SAP development. This study is set out to assess predictors of SAP in patients with acute ischemic stroke and dysphagia.
This retrospective cross-sectional study, conducted at the University of Health Sciences, Neurology Department of Erenkoy Mental Health Neurological Disorders in Istanbul, Turkey, between January 2021 and January 2023, assessed 65 individuals with acute ischemic stroke and dysphagia. Excluding specific criteria, clinical and laboratory data were collected. Patients were categorized into SAP and non-SAP groups based on diagnostic criteria. Results provide insights into risk factors of SAP.
In this study of 65 stroke patients with dysphagia, 27 (41.5%) developed SAP within the first week. No significant differences in age, gender, comorbidities, or infarct size were observed between the pneumonia-positive and pneumonia-negative groups (p > 0.05). HbA1c levels were significantly lower in the pneumonia-positive group (p = 0.02). Logistic regression revealed that NLR, CAR levels, and the presence of atrial fibrillation (AF) were significant predictors of pneumonia development (p < 0.001).
Dysphagia is considered one of the most significant risk factors for SAP. However not all ischemic stroke patients with dysphagia develop SAP; that is the reason we think NLR, CAR, and AF might be predictors of SAP in acute ischemic stroke patients with dysphagia.
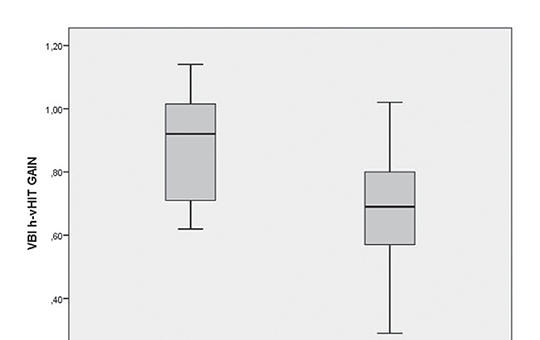
Evaluating vertebrobasilar insufficiency and Meniere’s disease: Insights from cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential and video head impulse test
This prospective study aimed to investigate diffe-rences in video head impulse test (vHIT) and cervical vestibular evoked myogenic poten-tial (cVEMP) findings between patients with vertebrobasilar insufficiency (VBI) and Meniere’s disease (MD) who experience episodic vertigo attacks.
A total of 27 patients with VBI and 37 patients with MD were enrolled into the study in a tertiary referral center. Inclusion criteria consisted of patients with a minimum of two previous vertigo attacks, unaccompanied by any neurological symptoms during an attack. All patients underwent horizontal canal h-vHIT and c-VEMP assessments following pure sound audiometric examinations. First, vHIT and cVEMP results for low and high flow sides in VBI patients were analyzed. Subsequently, data from the low-flow side in VBI patients and the affected side in MD patients were compared.
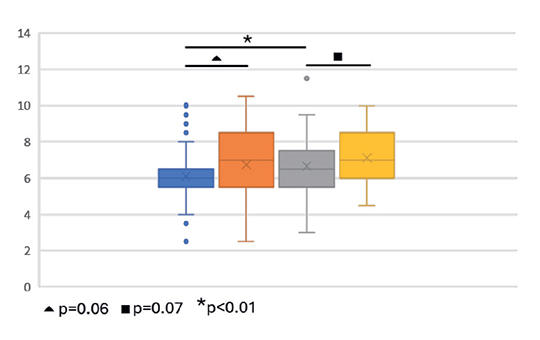
The mean vHIT values for low and high-flow volume sides in VBI patients were 0.68 and 0.88, respectively. In MD patients, mean vHIT values for affected and healthy sides were measured as 0.77 and 0.87, respectively. Abnormal results were observed in 66.7% of VBI patients and 51.4% of MD patients, with no statistically significant difference between the findings (p> 0.05). Upon examining the affected side, c-VEMP responses were absent in 41% of MD patients and 48% of VBI patients, with no statistically significant difference between the groups (p> 0.05).
vHIT and cVEMP assessments can be utilized as supplementary tools to radiologic investigations for the clinical diagnosis and follow-up of VBI. However, no significant differences were observed between vHIT and cVEMP findings in patients with MD and VBI.
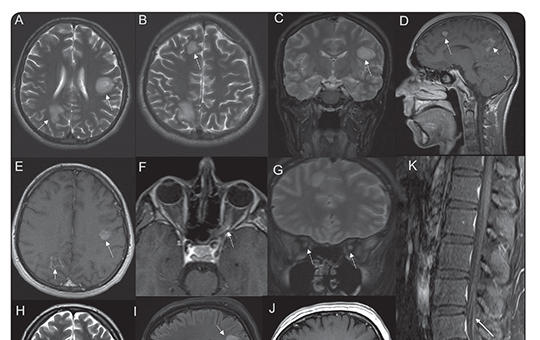
Recurrent simultaneous central nervous system demyelination with possible peripheral demyelination / nodopathy in a seronegative patient
Combined central and peripheral demyelination (CCPD) is a rare disease entity. Onset with the simultaneous central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS) involvement and its recurrence are exceptional. Anti-neurofascin antibodies have been shown to be present in up to 70% of cases, yet seronegative patients also exist. We present a case of seronegative recurrent CCPD. The PNS involvement was compatible with two episodes of recurrent Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS), whereas the CNS involvement pattern was not typical for either multiple sclerosis (MS) or acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. The prognosis was excellent with pulse methylprednisolone, intravenous immunoglobulin, and plasmapheresis. This case highlights the varied clinical presentations of CCPD, extending beyond the realms of MS and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, and underscores the potential for relapse. Importantly, to the best of our knowledge, this represents the inaugural instance of CCPD featuring PNS involvement in the form of recurrent GBS.
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries3.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]4.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Comparison of pain intensity measurements among patients with low-back pain]5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Fear of Falling among Geriatric Patients: a Narrative Review]1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Recurrent simultaneous central nervous system demyelination with possible peripheral demyelination / nodopathy in a seronegative patient2.
3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Predictors of pneumonia in stroke patients with dysphagia: A Turkish study4.
5.
Clinical Neuroscience
Effect of inflammatory response before mechanical thrombectomy on prognosis in stroke patients