[The Role of Nurses in the Prevention, Early Recognition and Treatment of Nosocomial Sepsis]
BAJNÓCZI Judit1
MAY 03, 2023
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2023;36(2)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.55608/nover.36.0007
Journal Article
BAJNÓCZI Judit1
MAY 03, 2023
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2023;36(2)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.55608/nover.36.0007
Journal Article
Szöveg nagyítása:
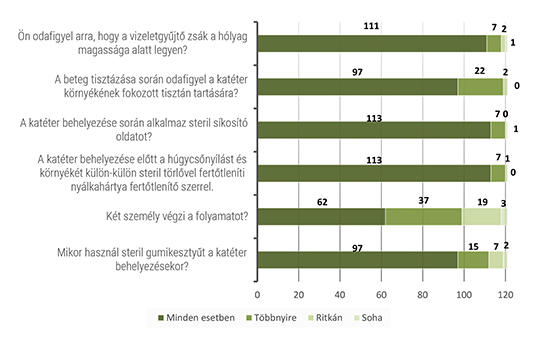
[The aim of my research was to assess the knowledge of nurses on the subject of sepsis.
I conducted my research among nurses working in Hungary through an online questionnaire. The respondents were required to answer 31 electronic questions, covering the topics of prevention, recognition, and treatment. A total of 121 respondents participated in the study (N=121). The obtained results were analyzed using statistical methods to describe them.
Based on the answers to the questions on prevention, recognition, and treatment, it was evident that the respondents’ knowledge on the subject was inadequate. Only 12% of the respondents were able to correctly distinguish between the conditions of SIRS, sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. The depth of knowledge was not influenced by work experience or workplace profile.
The results indicated that the nurses who filled out the questionnaire do not always follow professional protocols and, in some cases, have incomplete knowledge on the subject. Based on the research findings, I formulated recommendations, mainly focusing on the necessity of further education for nurses and the utilization of modern technology to promote prevention, recognition, and treatment.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Last year we celebrated the beginning of the dietary nurse education, which began in 1922 under the leadership of Professor Aladár Soós (1890–1967) at the Faculty of Medicine of Pázmány Péter University. The concept of „dietary” was only known in the United States at that time, so training was the first in Europe.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[To dispell the general misconception that professional proofreading is a pretence activity necessarily associated with institutional accreditation only. This clarification is urgently needed as the scientific assessment of professional materials is a reviewer’s competence, but the evaluation process is currently not regulated.
The structured interview method was adopted in the empirical research using a descriptive statistical approach. Data were collected via phone, the proofreading fee were determined using the remuneration nomenclatures compiled by publishers and translation agencies. A written and a project worksheet were adopted as data processing instruments.
The fee for proofreading without editing was HUF 106,658.4 using a multiplier of HUF 0.8/character. This reward raised to HUF 133,323 if a multiplier of HUF 1.0/character was adopted. These fees are in sharp contrast with HUF 10,000 currently offered to the author.
The scientific professional proofreading is seen as the basis of accreditation of all institutions. Therefore the proofreading services should meet stringent professional guidelines and quality standards involving the proper compensation for lectors’ work..]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[In addition to the joyful nature of pregnancy, this condition uses a great drain to the organization of women, and the oral cavity and teeth are no exceptions. Neglected teething poses several dangers not only to the mother, but to the embryo as well. The mother may develop bleeding gums, inflammation, tooth decay among other problems, and in the foetus may have dental malformations, infection, premature birth or even miscarriage. Researches have shown that pregnant women who are more often attended to dental screening brought a newborn baby into the world with higher weight and the chances of the perinatal complications were on a lower level than those women who were rarely or not tested at all. For this reason, it is an important issue to acutely look after the dental check during pregnancy, not only in dental care but all levels of health care and by almost all professionals with whom the pregnant one meets during that nine months.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[On the occasion of the 75th anniversary of the founding of the World Health Organization, it is time to examine the circumstances of its creation. Based on sources from contemporary articles, the events present the story of the merger of several smaller national health organizations into one, which formed the World Health Organization known and operating today, the WHO.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[On behalf of FOHNEU, 11 occupational health nurses visited CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, in Geneva, Switzerland. The participants were able to see the work of the Occupational Health, Safety and Environment Department, which is the driving force behind CERN’s safety policy. In addition, they were able to learn how CERN’s Medical Service takes care of all aspects of occupational health.]
Lege Artis Medicinae
[In patients with community acquired pneumonia associated sepsis, there are emerging frequently hematopoietic changes and disturbed haemostasis of varying severity as a part of the multiorgan dysfunctions. Between 2012 and 2020, we diagnosed community acquired pneumonia in 1826 patients. Among them, we recognised 218 cases of developing sepsis with typical symptoms and laboratory changes. In these septic patients, we registered the frequency and severity of anaemia, the quantitative and qualitative changes of leucocytes, the numerical abnormalities of platelets, and the pathologic haemostasis. The septic patients’ most frequent hematopoietic disorders were anaemia (n=159) and leucocytosis (n=151). Extremely severe leucocytosis (white blood cell count >50000/microlitre) was diagnosed in six patients. Decreased leucocyte count (leucopenia, agranulocytosis) was detected in 34 cases. There were three cases of leukemoid reaction: in prevalent leucocytosis we observed myelocytes, metamyelocytes and some atypical myeloid cells in the peripheral blood. In one patient crista biopsy was performed with Jamshidi technic, due to severe pancytopenia in the peripheral blood count. The histology of the crista biopsy revealed myelodysplastic bone marrow characteristics. In our patients with sepsis, concerning the number of platelets, the thrombocytopenia dominated (n=82). ]
Lege Artis Medicinae
[The combination of a beta-lactam and an aminoglycoside antibiotic is widely accepted in the treatment of severe nosocomial infections. In our study we compared two antibiotic regimens: the clinical efficacy of ceftriaxon + netilmicin once-a-day vs ceftazidim + netilmicin twice a-day. Patients: suffering from severe nosocomial infections and characterized by APACHE II, sepsis and injury scores. Dosage: Group | (n=30) – ceftriaxon 2 g iv. + netilmicin (2–7 mg/kg/bw) in one single dose. Group II (n=30) – ceftazidime 2 g bid + netilmicin (2–7 mg/kg/bw) divided in two doses. Laboratory parameters, netilmicin concentrations and cochlear function were checked regularly. 70% of pneumonias were cured or improved, while in the other infections (urinary tract, abdominal, soft tissue) the response rate was 90%. The lowest response rates were observed in Pseudomonas infections in both groups. Response rate in bacteremia was slightly higher in Group I. (5/7 vs 4/8). Four of 7 patients with Staphaureus infections failed to respond in Group II. Both methods of netilmicin administration proved to be safe. Both antibiotic regimens are effective in the treatment of severe nosocomial infections, however once-a-day administration is more convenient for the patients and saves cost.]
Clinical Neuroscience
[Objective - In this prospective observational study we investigated electrophysiological alterations in the early phase of critical illness and correlated electrophysiological findings with the clinical picture and outcome. Methods - We enrolled 21 critically ill surgical patients having ≥12 Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II scores on admission. Routine non-invasive bilateral electroneurography (ENG) examination of median and ulnar nerves was done on five consecutive days starting in two days after admission. Then weekly follow-up was performed. Motor and sensory nerve conduction indices were calculated and correlated with APACHE II and Simplified Acute Physiology Score II severity scores. Results - On the first examination 18/21 patients had >20% reduction in the motor and sensory nerve conduction indices. Severity score systems showed significant negative correlation with the daily change of CMAP and SNAP amplitudes and calculated nerve conduction indices (Spearman’s correlation, p<0,001). Mortality was higher in the patients with worse admission ENG and/or stagnant electrophysiological status or declining tendency in the first week. Conclusions - Electrophysiological alterations appeared soon after the development of critical illness. Early phase alterations showed a strong correlation with patients’ general condition and more severe electrophysiological alterations predisposed to higher mortality. In several cases early alterations proved to be reversible. ]
Lege Artis Medicinae
[Infectious diseases caused by bacteria have been treated successfully by antibiotic the rapy for the past half century, and a diversity of antibacterial agents with widely differing mechanisms of action has been developed by the pharmaceutical industry. However the selective pressure of antibiotic usage has inevitably led to the isolation of resistant bacteria and the rate of emergence of antibiotic resistance appears to be increasing rapidly, reducing the effectiveness of existing agents. Factors responsible for the wide dissemination of antibioticresistant bacteria in both community and hospital practice include the acquisition and spread of resistant genes by plasmids and transposons, inappropriate anti biotic usage and social factors. Mechanisms to controll the emergence of antibiotic resistance require optimal usage of antibiotics by clinicians, control programmes to improve hygiene and to reduce the transmission of resistant bacteria within and between communities, and the continued development of new antibacterial agents.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Aim of the research: The aim of my research is to show detailed analysis of clinical categorizing of sepsis and clarifying its diagnostic difficulties. The study shows the elements of diagnostic and monitoring methodology during attendance including the importance of triage. Research and sampling methods: The research was done in a III progressive level hospital in the capital at the Emergecy Department emphasizing one group of illness: sepsis. 81 patients were analysed according to the 2013 data turnover. The method of the research is based on different document analysis and data gathering. In parallel with it, in the following parts of the study I was examining the competences of nurses with different qualifications at the department who were doing triage activity during attendance.Evaluation of the summarized results was created by SPSS 14.0 programme. Results: It was proved from the summarized data that triage activity done by nurses with septic patients was not influenced neither by professional experience nor by qualification of the nurses. More than half of the patients at the departments was not given the correct classification so they were not given the therapy in time. Conclusions: Nurses at the emergency department do not have the necessary knowledge on classification system of triage , that is why each nurse at the department must have the opportunity to improve their knowledge on triage or those not having it must acquire both theoretical and practical knowledge. ]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.