[Comparison of Past and Present – Case Reports]
HERMANN Zoltánné 1
MARCH 08, 2024
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2024;37(01)
HERMANN Zoltánné 1
MARCH 08, 2024
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2024;37(01)
Szöveg nagyítása:
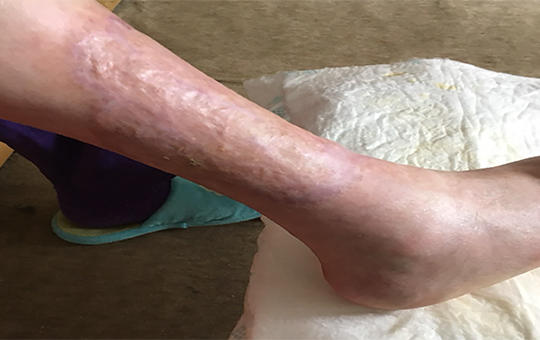
[The treatment of chronic wounds is an important and challenging task in home care. These wounds do not heal for a long time or recur, and are usually painful and easily infected. Proper home care is a determining factor in the healing process of these wounds. The use of smart dressings is absolute necessity in the treatment of chronic wounds. The use of mobile phone applications can also make home care activities more effective. These experiences will be presented by describing 4 cases.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Drug use is still on the rise today, with designer drugs being particularly dangerous. In addition to the general effects on the body, we must also mention the negative effects on the oral cavity. Many people do not realise that oral health can also be at risk, although oral lesions can develop as a result of poor oral hygiene, infections or neurological symptoms caused by the way in which the drug is used, or even by the way in which it is taken. In addition to dental caries, it is important to mention oral infections, tooth wear, or even Kaposi’s sarcoma due to possible HIV infection. Recognition of these oral lesions and of illegal drug use is not only a task for dental professionals, but also for the whole health care system.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The aim of this paper is to provide information on the history and cultural context of the work of Saint John of God, who became the patron saint of nurses and health workers. Sixteenth-century Spain served as a cradle for the innovations of Saint John and his followers, who established hospitals and provided care for the sick and the poor at a time when the Church was immersed in theological debates and thus seemed to forget one of its main missions: humanitarian and charitable aid to those most in need. The development of the Hospitaller Order’s nursing and health care practices, far ahead of its time, including the implementation of rules and regulations for hospitals and the extraordinary training of health professionals, is analysed. The continued work of the Religious of St. John of God, who operate health care and social service institutions in more than 50 countries today, is highlighted. Overall, we wish to provide a historical and cultural overview of the role of nursing and health care in society in the transition from the Middle Ages to the Modern Age. For this purpose, an analysis of the corresponding medieval and contemporary historical literature has been carried out beforehand.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[In Hungary, people’s oral hygiene is very poor and signs of this can be seen from a very young age. The development of good oral hygiene habits should start after birth and be maintained throughout life in order to prevent the development of oral diseases. However, the consequences of poor oral hygiene are not only visible in the oral cavity, but can also have a detrimental effect on the whole organ system, leading to the development of serious diseases. To prevent these, health professionals at all levels of health care need to take preventive action.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The purpose of the study is to investigate the quality of life of young adults in relation to oral health and how smoking affects this. The aim is to explore the differences in oral health-related quality of life between smokers, non-smokers, and quitters in a given age group.
The survey was conducted using a self-designed online questionnaire that included the Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP-14) questionnaire. The survey was conducted from May 01 to June 30, 2023, using a nonrandom sampling method that relied on easily accessible subjects. Data were processed and analysed using IBM SPSS 20.0 statistical software, descriptive statistics, Kruskal-Wallis test, and Spearman’s rank correlation analysis (p<0.05).
Based on the 317 assessable responses, smokers had a higher average OHIP-14 total score than non-smokers and quitters, but there were no significant differences in oral health-related quality of life between the groups (p=0.540). Four self-reported questions were added to the OHIP-14 questionnaire: dissatisfied with the colour of their teeth; afraid of communicating with others without seeing their teeth being seen; afraid of having a serious oral problem; afraid of losing their teeth. These issues are highly correlated with the OHIP-14 questionnaire and fear of oral lesions appears to be present among smokers.
Young adults do not yet show a significant deterioration in oral quality of life due to smoking, but additional questions are worth considering to assess the quality of life in smokers.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[In the field of wound care, the standard treatment these days is moist wound healing. Numerous advantages of this approach can be found in various studies. In cases of burn injuries, we also prefer this approach in order to provide an optimal wound environment, avoiding scab formation, crust formation, and scar formation. One excellent dressing for moist wound healing is a unique dressing containing PHMB in the world of dressings. It has numerous beneficial properties that can be used in burn injuries, but we have also bravely experimented with the dressing in other areas of wound healing. Currently, I would like to share my experiences related to burn injuries through case studies.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[General surgical routine care nowadays includes stoma placement and stoma therapy, as well as the care of patients living with a stoma. In Hungary, hundreds of stoma formations are performed annually, with the majority of stoma care being provided by stoma therapy nurses during the post-operative period. I would like to share my experiences in patient care through the presentation of case studies. These cases highlight the significant progress in patient healing due to the availability of modern wound treatments, as they effectively manage wound infections and promote wound healing.]
Clinical Neuroscience
In aging societies, the morbidity and mortality of dementia is increasing at a significant rate, thereby imposing burden on healthcare, economy and the society as well. Patients’ and caregivers’ quality of life and life expectancy are greatly determined by the early diagnosis and the initiation of available symptomatic treatments. Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine have been the cornerstones of Alzheimer’s therapy for approximately two decades and over the years, more and more experience has been gained on their use in non-Alzheimer’s dementias too. The aim of our work was to provide a comprehensive summary about the use of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer’s and non-Alzheimers’s dementias.
Clinical Neuroscience
We review the literature on REM parasomnias, and their the underlying mechanisms. Several REM parasomnias are consistent with sleep dissociations, where certain elements of the REM sleep pattern emerge in an inadequate time (sleep paralysis, hypnagogic hallucinations and cataplexy) or are absent/partial in their normal REM sleep time (REM sleep without atonia, underlying REM sleep behavior disorder). The rest of REM parasomnias (sleep related painful erection, catathrenia) may have other still unclear mechanisms. REM parasomnias deserve attention, because in addition to disturbing sleep and causing injuries, they may shed light on REM sleep functions as well as the heterogeneous etiologies of parasomnias. One of them, REM sleep behavior disorder has special importance as a warning sign of evolving neurodegenerative conditions mainly synucleinopathies (some cases synucleinopathies themselves) and it is a model parasomnia revealing that parasomnias may have by autoimmune, iatrogenic and even psychosomatic etiologies.
Clinical Neuroscience
[In this paper we present the Comprehensive Aphasia Test-Hungarian (CAT-H; Zakariás and Lukács, in preparation), an assessment tool newly adapted to Hungarian, currently under standardisation. The test is suitable for the assessment of an acquired language disorder, post-stroke aphasia. The aims of this paper are to present 1) the main characteristics of the test, its areas of application, and the process of the Hungarian adaptation and standardisation, 2) the first results from a sample of Hungarian people with aphasia and healthy controls. Ninety-nine people with aphasia, mostly with unilateral, left hemisphere stroke, and 19 neurologically intact control participants were administered the CAT-H. In addition, we developed a questionnaire assessing demographic and clinical information. The CAT-H consists of two parts, a Cognitive Screening Test and a Language Test. People with aphasia performed significantly worse than the control group in all language and almost all cognitive subtests of the CAT-H. Consistent with our expectations, the control group performed close to ceiling in all subtests, whereas people with aphasia exhibited great individual variability both in the language and the cognitive subtests. In addition, we found that age, time post-onset, and type of stroke were associated with cognitive and linguistic abilities measured by the CAT-H. Our results and our experiences clearly show that the CAT-H provides a comprehensive profile of a person’s impaired and intact language abilities and can be used to monitor language recovery as well as to screen for basic cognitive deficits in aphasia. We hope that the CAT-H will be a unique resource for rehabilitation professionals and aphasia researchers in aphasia assessment and diagnostics in Hungary. ]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.