The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2013;26(04)
Content
[Infection control, the application of hygiene protocols in acute patient care]
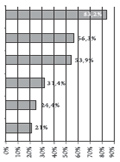
[Aim of the study: A key aspect of patient safety is the reduction, recognition and early treatment of nosocomial infections in order to improve the outcome indicators. The research aimed to assess and draw comparisons relating to whether workers in emergency and intensive-care departments have the appropriate attitude and skills in relation to the prevention of nosocomial hazards. The author also investigated the nature of any correlation between the results and the formal qualifications, employment relationship and motivation of the target group. Sample and method: The sample consisted of paramedical professionals working at the intensive-care and emergency departments of five hospitals in the capital. For the purpose of comparing the results of the study in a practical setting, three nursing activities were observed and evaluated with a questionnaire-based survey. (N=163) Results: Based on the results it can be concluded that the skills of paramedical professionals at emergency and intensive-care departments are satisfactory, but there are some shortcomings. It is clear that the paramedical professionals are aware of the role of the hands in transmitting infection. Of those surveyed, 90 nurses knew that a peripheral cannula needs to be replaced every 72 hours. The majority of the nurses (78%) are aware that the optimal interval for replacing breathing circuits is 24 hours. Conclusions: Non-compliance with the rules is often due to deficient policies, which is why management has an essential role in ensuring successful nosocomial surveillance. ]
[The role of nurses in the early recognition and treatment of sepsis]
[Aim of the study: The aim of the research was to gain a complex assessment of nurses’ skills related to sepsis. Sample and method: The survey was conducted at the University of Szeged, among nurses at four departments of the Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Institute, and at the Cardiac Surgery Post-operative Unit. The survey sample consisted of the specialist nurses at the aforementioned intensive-care departments. The nurses had to complete a questionnaire consisting of 37 questions, concerning the topics of sepsis, hand disinfection and continuous training. The answers were evaluated through a statistic analysis using the SPSS 21 program (Kruskal-Wallis test, binomial test, one-sample T-test and regression analysis), with a significance level of p =0.05. Results: Based on the results, 28.6% of the surveyed sample is capable of differentiating sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock on the basis of the listed symptoms (p <0.001). The answers given to questions relating to the treatment and nursing of septic patients revealed that the level of knowledge is not satisfactory (p <0.001). No correlation could be demonstrated between the number of years spent working in the intensive-care department and the level of sepsis related knowledge (p =0.138). Conclusions: Based on the research results it can be concluded that there is a real need and demand for continuous training in relation to sepsis. ]
[“I can’t, and won’t, do anything else.” Survey of the career orientation and career perception of BSc nursing students]
[Aim of the study: To map out the motivation that drove BSc nursing students to choose a profession in the health sector and begin their college studies. The authors considered it important to include, in the scope of the study, an assessment of the perception and prestige of the chosen vocation, as well as the level of work satisfaction. Sample and methods: The self-completion questionnaire was filled out by BSc nursing students at the Faculty of Health Sciences and Social Studies of the University of Szeged (N=208). The sample consisted of correspondence (n=136) and full-time (n=72) students, who took part in the data gathering on a voluntary basis. Results: A helpful attitude and humanistic values are what most influenced the respondents in relation to their choice of career, and their enrolment in college studies was mainly motivated by their internal drive. These attitudes, however, do not fully offset the low prestige and the negative aspects of the profession. Conclusions: The results show that there is a need for comprehensive reform in the sector, in the interest of improving the prestige of the profession and preventing career abandonment.]
[Factors influencing job satisfaction by health care workers]
[The healthcare workers spend most of their lifetime at the workplace. Job satisfaction is influenced by many factors some of which are connected to the working environment, physical safety at workplace, salary, social relations at workplace and the position in the workplace hierarchy. The diversity of the job, the level of control at workplace, the amount of skills required for the position, the quantity and quality of social relations all contribute to the level of job satisfaction. When the job does not satisfy the most important needs of the workers, job dissatisfaction develops. Dissatisfaction may have many different consequences. It impacts the work performance, extends the length of sick leaves and increases the intent to leave the career. When the health care worker experiences general bad mood, spleen and low self esteem at the workplace, it has a negative influence not only on job satisfaction, but even emotional exhaustion, prolonged anxiety and depression might develop in consequence.]
[Report about the lecturing experiences of five years - the results of excellent team-work]
[Aim of the study: The goal of the study was to assess the satisfaction with in-service trainings of the Educational Board of the Chamber of Health Care Providers’ Regional Organisation in Csongrád County among health care workers; furthermore the presentation of topics and the numbers of participants. Methodology and sample: Between September and December in 2012 four measurements were made using a self-developed questionnaire. The data were analyzed with descriptive statics and chi-square test including 558 people. Results: The majority of responders attended the trainings because these are compulsory. The preparedness of lecturers and the topics were scored on average with 4.5. The participants were satisfied with the organisation of the trainings, but some objected to the number of seats. Conclusions: The negative remarks has to be remedied (enough seats). The quality of the lectures and the diversity of the topics have to be increased so that the participants could utilize their knowledge and their workplaces. ]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.