The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2013;26(05)
Content
[The effects of caring for children who have suffered trauma on pediatric nurses]
[Aim of the study: In case of children suffering trauma immediate care taking psychological aspests into consideration is very important. However, for the caregivers going through these cases cause secondary traumatization and increased mental burden, and they are not provided with professional help to process these, which ultimately may lead to burn-out. Sample and method: The authors have carried out a questionnaire survey among pediatric nurses at Pediatric Surgery Departments (N=90) and as a control group at Internal Medicine Departments (N=90) of five hospitals. Results: Significant differences were found between the two groups, as the nurses working at pediatric trauma departments consider their work as mentally more burdensome, they think the children’s mental care is important and would like to have a full-time psychologist at the ward. Besides they have encountered significantly higher number of cases in which they were unable to respond properly to the children’s psychological reactions. This have ultimately affected their family relations, and they also need trainings and help to mentally process these cases. Significant difference was found in the Secondary Traumatic Stress Scale scores too. Conclusions: In pediatric traumatology departments it would worth greater emphasis on helping nurses with their emotional processing of traumas, on recognizing symptoms of secondary traumatization and on adequate training.]
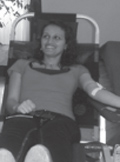
[The state of health of Roma in Nagykálló ]
[Aim of the study: To assess the unique lifestyle characteristics and state of health of the Roma minority living in a closed community. The author assumed that the Roma have a different attitude towards their own health and to the healthcare supply system. Sample and method: At the Sántha Kálmán Mental Health Centre and Specialist Hospital, in May 2012 a unique blood donation day was organised for the Roma population. As a part of the program, besides the medical tests, a questionnaire-based survey was conducted. (N=100) The author processed the data using Microsoft Excel, and presented the results with descriptive statistical methods. Results: Of the more than 100 who volunteered, 38 were able to give blood. Among the respondents the majority of women were aged 41-50 years (39%), and most of the men were in the 31-40 age bracket. More than half of the respondents (57%) consume alcohol regularly or occasionally, while 47% of them smoke. Some 39% of those surveyed consider their own state of health to be bad. Some 56% of the respondents are satisfied with the provision of healthcare, despite the fact that almost half of them have experienced some kind of discrimination during their care. Conclusions: The bad state of health of the Roma is related to the lower quality of life, the low level of education, alcohol consumption and smoking. The Roma are aware of the screening tests and consider them important; indeed, some of them also regularly give blood, but the communication targeting them is not effective. The Roma population experience discrimination more frequently then the other members of society. It is imperative that training in tolerance towards the Roma be incorporated into healthcare education. It is also necessary to improve the supportive relationship with healthcare. One means of achieving this could be the inclusion of Roma in healthcare efforts.]
[Nursing documentation related to attitudes and the management of time spent on administrative activities]
[Aims of the study: The aim of the study was to explore how did the institutes manage to achieve the legal requirements related to nursing documentation since the introduction of the law. The other aim was to determine the conditions of effective application of the nursing documentation. Sample and methods: Qualitative and quantitative methods were applied as well. In a quantitative, cross-sectional study a questionnaire survey was performed involving 150 nurses. By the means of retrospective data analysis 200 closed nursing documentation were examined. The data analysis was carried out with SPSS 17.0 statistical software. The level of significance was set to p<0.05. Results: The nursing documentation is not personalized (p<0.01) and its information content is not sufficient to learn about the patient’s condition at the time of admission and to evaluate the effects of nursing on the state of the patient. The personalization and information content strongly depends on the nurses’ attitude towards the administration process. Conclusions: As the theory and practice of the nursing documentation are not in accordance, it is necessary to define the principles more precisely and to survey and reorganize the existing documentations. ]
[Causes of leg problems in chronic kidney failure, and opportunities for prevention]
[In patients with chronic kidney failure, especially diabetic haemodialysis patients, the risk of lower-limb complications increases. Through the early recognition of changes in the leg, the definition of risk factors and timely intervention, the prevalence of ulcers and amputations can be reduced. The author aims, through a review of the specialist literature, to provide skills for the recognition of lower-limb complications occurring in chronic kidney patients, and to summarise the most common factors leading to amputation, and the opportunities for prevention. It gives guidance for the definition of risk factors, briefly describes the procedure for assessing the condition of the leg, and the basic principles and options relating to patient education. ]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
3.
4.
5.