The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Specialities
Neurology
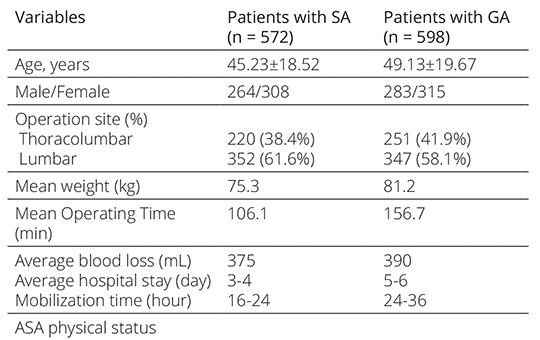
Spinal anesthesia efficiency in thoracolumbar stabilizations
Spinal surgery has an important place in neurosurgery practice. Surgical procedures on the lumbar spine include stabilization, discectomy, foraminotomy and decompression. Lumbar and lower thoracic spinal surgery can be safely performed under spinal anesthesia (SA). However, there are not many studies on the safety and efficacy of spinal anesthesia in patients who have undergone long segment stabilization surgery.
Pembrolizumab-induced peripheral nervous system damage: A combination of myositis/ myasthenia overlap syndrome and motor axonal polyneuropathy
Immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) are effective drugs in cancer treatment that block immune checkpoints and stimulate an attack on cancer cells. However, various side effects were reported with ICIs. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) side effects are three times more frequent than those in the central nervous system. A 63-year-old male patient was admitted to our department with a 10-day history of dyspnea, diplopia, and generalized weakness.
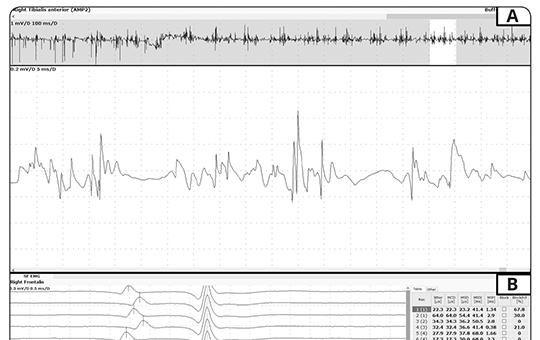
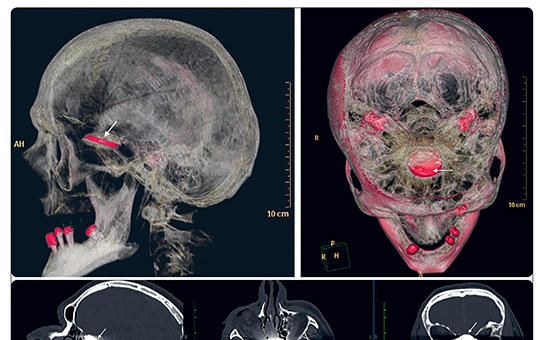
Minimal invasive transnasal endoscopic removal of intracranial foreign body after airbag deployment
Airbag induced injuries such as skull and cervical spine fractures, epidural and subdural hematomas, atlantooccipital dislocations or brainstem lacerations are already documented in published literature, however, no previous case have been published about a penetrating foreign body of the skull base following airbag deployment. Removal of an intracranial foreign body is very dangerous and difficult.
[Sumatriptan-naproxen sodium fix-dose combination for acute migraine treatment, a review]
[Migraine as a common primary headache disorder has a significant negative effect on quality of life of the patients. Its pharmacotreatment includes acute and preventative therapies. Based on the shared therapeutic guideline of the European Headache Federation and the European Academy of Neurology for acute migraine treatment a combination of triptans and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is recommended for acute migraine treatment in triptan-nonresponders. In this short review we summarized the results of the randomized controlled clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness and safety of sumatriptan (85 mg)/naproxen sodium (500 mg) fix-dose combination. It was revealed that the fix-dose combination was better than placebo for the primary outcomes of exemption of pain and headache relief at 2 hours. Furthermore the combination showed beneficial effect on accompanying symptoms of migraine attack (i.e. nausea, photo- and phonophobia). Adverse events were mild or moderate in severity and rarely led to withdrawal of the drug.
It can be concluded that sumatriptan (85 mg)/naproxen sodium (500 mg) fix-dose combination is effective, safe and well-tolerated in the acute treatment of migraine. ]
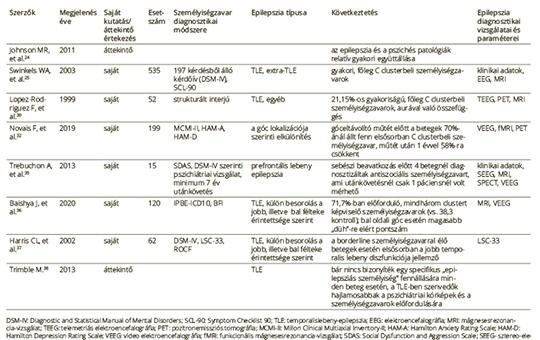
[Importance of personality disorders in epilepsy]
[Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders. Therapeutic success shows high variability between patients, at least 20-30% of the cases are drug-resistant. It can highly affect the social status, interpersonal relationships, mental health and the overall quality of life of those affected.
Although several studies can be found on the psychiatric diseases associated with epilepsy, only a few researches focus on the occurrence of personality disorders accompanying the latter. The aim of this review is to help clinicians to recognize the signs of personality disorders and to investigate their connection and interaction with epilepsy in the light of current experiences.
The researches reviewed in this study confirm that personality disorders and pathological personality traits are common in certain types of epilepsy and they affect many areas of patients’ lives. These studies draw attention to the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to this neurological disorder and to provide suggestions about the available help options. Considering the high frequency of epilepsy-related pathological personality traits that can have a great impact on the therapeutic cooperation and on the patients’ quality of life, it important that the neurologist recognizes early the signs of the patient’s psychological impairment. Thus they can get involved in organizing the support of both the patient and their environment by including psychiatrists, psychologists, social and self-help associations.
As interdisciplinary studies show, epilepsy is a complex disease and besides trying to treat the seizures, it is also important to manage the patient’s psychological and social situation. Cooperation, treatment response and quality of life altogether can be significantly improved if our focus is on guiding the patient through the possibilities of assistance by seeing the complexity and the difficulties of their situation.]
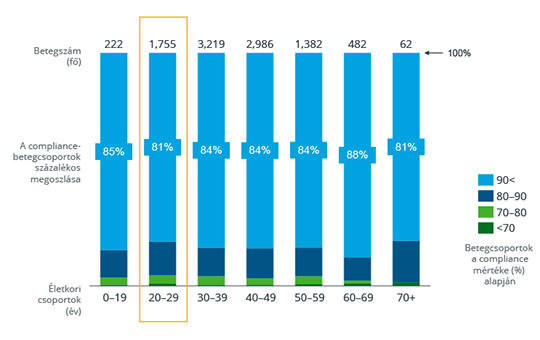
[Assessment of compliance and patient pathway among multiple sclerosis patients on disease modifying treatment]
[Epidemiological data and the number of patients treated suggest that the proportion of Hungarian patients with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) receiving disease-modifying therapy (DMT) is lower than in some neighboring countries. We investigated possible reasons for this.
First we analysed patient compliance based on an anonymised database of the National Health Insurance Fund (NHIF). A total of 5441 patients were included in the analysis from NHIF prescription data from 1 July 2014 to 28 February 2021. In the second part of the study, a quantitative and qualitative assessment of patient journeys of MS patients was conducted.
The compliance of Hungarian MS patients is good compared to international MS treatment data and outstanding compared to other neurological and other diseases, e.g. cardiovascular. This cannot be said about the results of the patient pathway analysis based on patient interviews. Patients indicated that they often have difficulty accessing public health care. Tracing their pathways revealed that they needed to see 3-5 doctors (general practitioner, various specialists) before a diagnosis was made. However, they gave positive feedback about MS Centres. They trusted their doctors, found them empathetic, but they would have liked more time to discuss lifestyle issues.
Compared to some neighbouring countries, Hungary has a lower proportion of patients with treated MS, which, given the good compliance of patients, highlights the problem of patient path in Hungary. Further training of fellow physicians is also a task for neurologists specialising in MS. Just as the most common symptoms of stroke have been successfully introduced into the public consciousness, the same can be the aim for MS.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.