The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2004;14(06)
Content
[NEW METHODS FOR NON-INVASIVE ASSESSMENT OF AIRWAY DISEASES]
[In chronic obstructive airway diseases there are several unsolved questions regarding the early diagnosis, monitoring treatment, simple detection of exacerbations and the questions of differential diagnosis. These problems indicate the need for the development of new diagnostic methods and their application in clinical practice. This need is further emphasized by the fact that in most chronic airway diseases, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease inflammation has a central role in the pathomechanism and its suppression is the main aim of treatment, but so far, we do not have adequate method for the assessment of inflammation intensity in clinical practice. In recent decades non-invasive sampling techniques directly from the airways have made a progress in respiratory research and at present some of them are available for clinical use. Among these techniques sputum induction, measurement of exhaled biomarkers including exhaled nitric oxide and mediators in exhaled breath condensate samples are used increasingly. The present review summarises our current knowledge on these methods and the most important findings obtained by their applications.]
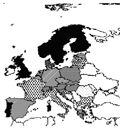
[INCIDENCE RATES OF CHILDHOOD TYPE 1 DIABETES WITHIN EUROPE AND HUNGARY BASED ON EURODIAB DATA]
[Type 1 diabetes is generally believed to be be the result of an immune destruction of pancreatic ßcells in genetically susceptible individuals exposed to environmental risk factors. To study the epidemiology of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus in Europe, the EURODIAB collaborative group established in 1988 prospective geographicallydefined registers of new cases diagnosed under 15 years of age. The 10-year-old study shows a greater than 10-fold range in incidence rate of childhood diabetes in Europe. The standardised average annual incidence rate during the period 1989-1998 ranged from 3,6 cases per 100 000 per year in Macedonia to 43,9 cases per 100 000 per year in Finland. Combined data from all centres indicates that the annual rate of increase in incidence was 3,2% but in some central and eastern European countries it was higher. The age-group-specific rates of increase were 5% for children aged 0-4 years, 3,7% for 5-9 years, and 2,1% for 10-14 years, which shows that the highest rates of increase occurred in the youngest age group. The Hungarian Childhood Diabetes Registry has collected the data of all newly diagnosed children with type 1 diabetes aged 0-14 years since 1st January 1978. The standardised incidence rate during the period 1978-2002 was 8,6 cases per 100000 per year, the lowest in the youngest (0-4 yr), highest in the10-14-year-old-children. There was a linear increasing trend in incidence with the average rate of annual increase of 5,1%. Comparing our incidence rate with other European countries Hungary belongs to the medium-risk countries with similar age- and sex-specific incidence rates. The results of the EURODIAB study confirm a very wide range of incidence rates of childhood type 1 diabetes within Europe and show that the increase in incidence varies from country to country. Such variation seems to be unlikely to be explained by genetic differences, since Europeans (except some small populations) are more homogeneous compared with other populations of other continents. The rapid increase in incidence may be explained by changes in environmental factors.]
[ONCOHEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES WITH SKIN SYMPTOMS]
[INTRODUCTION - Haematologic malignancies can originate from the skin (cutaneous lymphomas, rarely acute myelomonocytic leukemia) or can infiltrate the skin secondarily during the progression of the disease (nodal and systemic non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, Hodgkin'’s disease, chronic lymphocytic leukemia). PATIENTS AND METHODS - The clinical history of seven patients treated by the authors between 1997-2003, is reviewed. CONCLUSIONS - The clinical and histopathologic features of each entity are discussed, emphasizing differences in the clinical course between cutaneous and nodal lymphomas, considering diagnostic difficulties, conventional and recent therapeutic approaches.]
[A CASE OF PRIMARY HEPATIC AMYLOIDOSIS PRESENTING WITH GASTRIC BLEEDING]
[INTRODUCTION - Amyloidosis - at an early stage - has no typical clinical findings, but severe weight loss, hepatomegaly and elevated serum alkaline phosphatase level can be clues to the diagnosis. CASE REPORT - We report a 66-year-old woman presenting at our unit with massive gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroscopy was performed and a haemorragic ulcer was found. Before admission she had lost 20 kg-s in 6 months. The patient had hepatomegaly and markedly elevated serum alkaline phosphatase level. These findings suggested the presence of malignancy, but ultrasound, CT and MR examinations did not support this hypothesis. After liver biopsy the diagnosis of amyloidosis was proven. She had rapid downhill clinical course of gastric bleeding from an ulcer resulting in death. CONCLUSIONS - So far, no specific treatment exists for amyloidosis, but there have been promising results reported about liver transplantation and autologous stem-cell transplantation.]
[REFRACTIVE SURGERY IN THE XXIST CENTURY - SURGICAL CORRECTION OF REFRACTIVE ERRORS]
[Refractive surgical procedures have become more and more popular worldwide. The ultimate aim of these procedures is to change the refractive power of the cornea in order to achieve good uncorrected visual acuity and to get rid of the optical correction need. In this article, the history of refractive surgery, the most important characteristcs and types of the excimer lasers, the most up-to-date refractive surgical techniques and alternative refractive procedures are presented. The lower and upper limits of surgical correction, the newest diagnostic and technical development, i.e. the possibilities of wavefront technology are also discussed.]
[MEDICAL ANTHROPOLOGICAL APPROACH TO CHILDREN'S SURMISES ON SMOKING]
[INTRODUCTION - The aim of our study was to explore school children'’s surmises on smoking. The following questions were in the focus of our analysis: what concepts children have about smoking and smoking-related diseases before adolescence? Have they already tried smoking? METHODS - The study was conducted among 3rd, 4th and 5th year school children (N=128) in two towns of Békés County, namely in Békés and Köröstarcsa. The sample consisted of 57% males and 43% females. Regarding sampling we followed international studies with similar aims where samples of 9-11-year-old average children were thought to be ideal for such study purpose using the draw-and-write technique. RESULTS - Most respondents from the study have not tried smoking yet. On the other hand, there are great number of adults who smoke in children’s environments, in many times, both parents do. Despite these facts, children’s attitudes toward smoking is rather negative. Children'’ s opinions reflect many negative aspects of smoking: the health-damaging effect, the financial aspects, the negative effects for social and physical environment. CONCLUSIONS - Similar to previous international studies, children of our sample possess correct and comprehensive knowledge of the smoking-related health problems. Findings of our study provides a support to the need of a smoking prevention program for children in the age of their negative opinions of smoking and well before the peer group effect is getting significant.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.