The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Hungarian Radiology - 2002;76(05)
Content
[Examination of pancreatic exocrine function with secretin stimulated magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography]
[INTRODUCTION - The aim of this study was to assess the feasibility and usefulness of SS-MRPD for evaluation of the pancreatic exocrine function. PATIENTS AND METHODS - SS-MRPD was performed in 20 patients with mild (n=8) or severe (n=12) chronic pancreatitis (according to the grade of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency indicated by the Lundh test) and in 10 volunteers without pancreatic disease. MRPD images were evaluated before and 10 min after the iv. administration of 0.5 IU/kg secretin. The changes in pancreatic tissue T2 signal intensity and duodenal filling after the injection of secretin were determined by means of SS-MRPD. The SSMRPD findings were then compared with those of the Lundh test. RESULTS - The basal pancreatic T2 signal intensity was significantly higher in the patients with a mild or a severe exocrine pancreatic insufficiency as compared with the controls (826.5±36.36 and 908±80.51 vs 659.2±41.67). The pancreatic T2 signal intensity exhibited a significant elevation after secretin administration both in the volunteers and in the patients with mild or severe chronic pancreatitis. This elevation was significantly lower in both the mild and the severe chronic pancreatitis patients than in the volunteers (66.85±15.77 and 24.45±5.85, respectively, vs. 200.0± 45.07). After the administration of secretin, the diameter of the duodenum was significantly increased in all three groups. This duodenal filling was significantly reduced in patients with a mild or a severe exocrine pancreatic insufficiency as compared with the volunteers (4.12±1.33 and 1.70±0.77 vs. 15.38± 1.73). There was no significant difference in pancreatic T2 signal intensity changes or in duodenal filling in patients with a mild or a severe exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. There were significant correlations between the pancreatic T2 signal intensity changes and the duodenal filling and the results of the Lundh test (r= -0.616 and -0.78). CONCLUSION - These results demonstrate that the administration of secretin increases the T2 signal intensity of the pancreatic tissue and the diameter of the duodenum to different extents in normal subjects and in patients with chronic pancreatitis. This suggests that SS-MRPD can provide information of value in the assessment of an exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.]
[Intraoperative intracranial ultrasound imaging in neurosurgery]
[Diagnostic ultrasound imaging started in the 1940s. Up to the present it underwent on radical changes. Article briefly reviews the major steps of the development of ultrasound technique in neurosurgery, and possibilities of applications of different ultrasound methods in neurosurgery are described. Authors discuss their experiences with Hawk 2102 ultrasound system used in intraoperative procedures in 113 cases. Data compared with the literature. Conclusions are that use of intraoperative ultrasound in neurosurgery is modern and simple and it has various application fields. Intracranial lesions are well localized with its use, so the risk of operations decreases. Main disadvantages that ultrasound imaging requires bony trepanation and special transducers are needed for different lesions.]
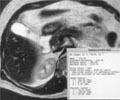
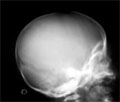
[Osteopetrosis in the infancy]
[INTRODUCTION - The authors present a relatively rare, autosomal recessive osteogenetic disorder, which appearance is typical in the first year of life. The malignant osteopetrosis of infants has characteristic radiologic and haematologic status, which is often an incidental finding. CASE REPORT - A 6-month-old Chinese boy was referred with the suspition of bronchopneumony to perform a chest Xray. On the bases of our findings, additional X-ray studies were done (skull, wrist, dorsal spine, hip, femur). A general increase in the density of the bones with characteristic settlement were demonstrated. CONCLUSION - Reporting such a rare disease may help in the differential diagnosis of the osteopathies with diffusely increased density.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.