The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Specialities
Immune Oncology
[Double endothelin receptor inhibitors]
[A common problem in the hypertension care is the treatment of cases that react difficultly to treatment, including resistant hypertension. The structure of the treatment is particularly challenging. Intensive research is underway in the field of developing new drugs that can be used in the treatment of resistant hypertension, one possibility being dual endothelin receptor inhibitors. In my article, based on the results of the recently published PRECISION study, I present the possible use of the drug group in this area.]
[Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis occurring during treatment with a B-RAF inhibitor in a patient with colorectal adenocarcinoma]
[With the expansion of targeted biological treatments in oncology and the improvement in life expectancies, it is increasingly common to consider the long-term and short-term effects of anti-tumor agents on the kidneys, which significantly influence patient mortality and future oncological treatment options. B-RAF inhibitors are widely used, primarily in cases of malignant melanoma and colorectal cancers. We present the case of a young patient with colorectal adenocarcinoma treated with B-RAF (v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B) and EGFR (epidermal growth factor) inhibitors as second line agents. During treatment, acute renal failure developed, necessitating hemodialysis. Renal biopsy confirmed acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, and we suspected the nephrotoxic effect of the B-RAF inhibitor as the underlying cause. Steroid treatment was initiated, but unfortunately, we lost the patient due to rapid progression of the malignant disease.]
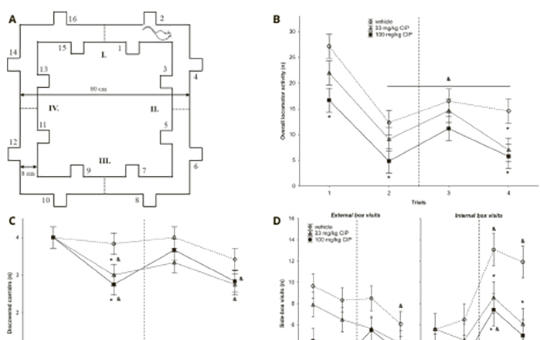
Neurobehavioral impairments in ciprofloxacin- treated osteoarthritic adult rats
Ciprofloxacin (CIP) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic widely used in clinical practice to treat musculoskeletal infections. Fluoroquinolone-induced neurotoxic adverse events have been reported in a few case reports, all the preclinical studies on its neuropsychiatric side effects involved only healthy animals. This study firstly investigated the behavioral effects of CIP in an osteoarthritis rat model with joint destruction and pain.
Prognostic value of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase-1 expression in glial tumors
Gliomas are the most common primary malignant central nervous system tumors in adults, exhibiting a poor prognosis. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase-1 has important functions in cancer immunotherapy due to its role in escaping cancer cells from the immune system. In this study we purposed to evaluate the correlation between IDO-1 expression and clinicopathological parameters in gliomas, and whether IDO-1 can be a prognostic marker.
[Evolution in medical therapy of heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction: clinical importance of the rapid titration strategy]
[Both, mortality and morbidity of chronic heart failure are persistently high, thus its adequate disease management is of pre-eminent importance. For heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) numerous evidence are available to improve its prognosis, including reduction of mortality, sudden cardiac death, and hospitalizations. Large randomized clinical trials have been shown that angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors), angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), B-blockers, mineralocotricoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2 inhibitors) reduce both morbidity and mortality of HFrEF patients. Accordingly, the heart failure recommendation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) issued 2021, proposed the basic therapy for HFrEF in 4 pillars: ACEI/ARNI, BB, MRA and SGLT2 inhibitors.
Instead of the earlier approach of stepwise sequential therapy, the new recommendation advocates for simultaneous initiation of all four drug classes with rapid titration to the target dose. The STRONG-HF clinical trial aimed to compare the rapid titration with its conventional strategy. Concerning the primary composite endpoint of repeated heart failure in 180 days with rehospitalization and all-cause mortality compared with changes in quality of life and rehospitalization by heart failure as separate endpoints, the rapid titration was significantly more efficient solution.
When optimizing therapy, we have also to pay attention to the comorbidities of HFrEF patients, which may compromise the procedure of titration. The consensus document of the ESC Heart Failure Association recommends special patient profiling by comorbidities and specific hemodynamic parameters, followed by therapeutic recommendations on different patient profiles. Overall, SGLT2 inhibitors have the least limiting factors and contraindications, thus they can be used in all profiles without exception – as early as at initiating the therapy.]
[Hematopoietic abnormalities and coagulopathy in community acquired pneumonia associated sepsis]
[In patients with community acquired pneumonia associated sepsis, there are emerging frequently hematopoietic changes and disturbed haemostasis of varying severity as a part of the multiorgan dysfunctions. Between 2012 and 2020, we diagnosed community acquired pneumonia in 1826 patients. Among them, we recognised 218 cases of developing sepsis with typical symptoms and laboratory changes. In these septic patients, we registered the frequency and severity of anaemia, the quantitative and qualitative changes of leucocytes, the numerical abnormalities of platelets, and the pathologic haemostasis. The septic patients’ most frequent hematopoietic disorders were anaemia (n=159) and leucocytosis (n=151). Extremely severe leucocytosis (white blood cell count >50000/microlitre) was diagnosed in six patients. Decreased leucocyte count (leucopenia, agranulocytosis) was detected in 34 cases. There were three cases of leukemoid reaction: in prevalent leucocytosis we observed myelocytes, metamyelocytes and some atypical myeloid cells in the peripheral blood. In one patient crista biopsy was performed with Jamshidi technic, due to severe pancytopenia in the peripheral blood count. The histology of the crista biopsy revealed myelodysplastic bone marrow characteristics. In our patients with sepsis, concerning the number of platelets, the thrombocytopenia dominated (n=82). ]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]1.
2.
3.
4.
5.