The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Specialities
Infectology
[What the doctor caring for elderly hypertensive patients needs to know about frailty]
[ The frailty syndrome – a highly complex pathological condition intertwined with physiological aging, that leads to the old patient’s co-organizational insufficiency in warding off the increasing internal and external stresses – is gaining more and more emphasis in recent professional papers and treatment guidelines for hypertension of aged patients. This geriatric syndrome requires a high degree of caution and restraint in medical decisions and also on several cardiovascular interventions, such as antihypertensive treatment, and its extent, due to the possibility of harmful adverse therapeutical responses. That threat comes to the fore especially in the second stage of old age (aged over 80 years) as a result of the increasing frequency and severity of frailty. The paper defines frailty, its types/severity, and variants, and presents the simplified or more complex – but also time-consuming – diagnostic procedures, as well as the future promises for early detectability of the frailty risk separatable from signals of aging, even in normal conditions. The aim of the paper to draw the attention of caregivers treating high blood pressure or other cardiovascular conditions in old patients to test more carefully the risk of frailty or its already acting condition and consider its potentially harmful influence for adverse therapeutic responses.]
[The path to the heart through the kidney. New perspectives for reducing residual cardiovascular risk – pathways and mediators of mesodermal cross-talk]
[The continued high morbidity of cardiovascular diseases justifies the exploration of “residual” risk factors. During embryonic development, the cardiovascular organs, bones, muscles, kidney, and adipose tissue differentiate from the mesoderm, the remaining humoral and mechanical communication between cell lines partly explains the phenomenon of residual cardiovascular risk, and partly leads to the delineation of new therapeutic targets. Among the common factors in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis and atherosclerosis, inflammation can be highlighted, which makes the beneficial effects of biological therapy treatment understandable. The Klotho system and the AGE-RAGE axis are responsible for age-related systemic changes. Cardiokines, myokines, osteokines, adipokines, and hepatokines are molecular mediators of complex interactions between individual organs. In particular, the cardio-renoprotective effects of the GLP-1RA and SGLT2i drug classes already used in diabetology are part of the systemic beneficial effect. Similarly, blocking mineralocorticoid receptors with finerenone has a generalized anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and anti-fibrotic effects. Regular exercise has always been recommended for cardiovascular patients, but now more and more mechanisms are becoming known that highlight the role of skeletal muscle in regulating the entire metabolism. Simultaneous use with the diet, it can be a simple and effective method to control the progression of cardiovascular disease.]
[Desmopressin may counteract polyuria in lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Review of the literature]
[Lithium is a simple ion that remains the best, safest and least expensive treatment for the prevention of recurrent episodes of bipolar disorder. However, in many patients administration of lithium is associated with renal side effects. The most frequent side effect is a defect in urinary concentration which may lead to permanent lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Patients suffer from a disturbed night therefore it is an eminent goal to secure them some rest. In our previous work administration of excessive doses of desmopressin resulted in clinically relevant antidiuresis in lithium-induced nephrogenic insipidus enhanced by indomethacine The purpose of the present paper is to review the literature concerning the use of desmopressin in lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.]
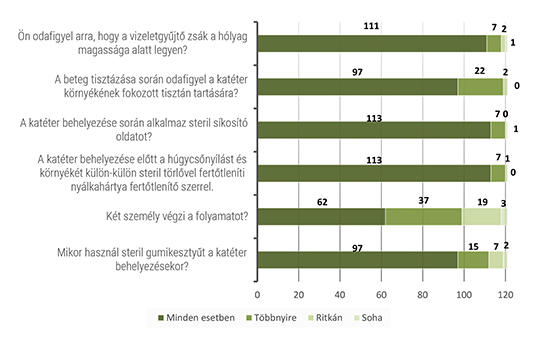
[The Role of Nurses in the Prevention, Early Recognition and Treatment of Nosocomial Sepsis]
[The aim of my research was to assess the knowledge of nurses on the subject of sepsis.
I conducted my research among nurses working in Hungary through an online questionnaire. The respondents were required to answer 31 electronic questions, covering the topics of prevention, recognition, and treatment. A total of 121 respondents participated in the study (N=121). The obtained results were analyzed using statistical methods to describe them.
Based on the answers to the questions on prevention, recognition, and treatment, it was evident that the respondents’ knowledge on the subject was inadequate. Only 12% of the respondents were able to correctly distinguish between the conditions of SIRS, sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. The depth of knowledge was not influenced by work experience or workplace profile.
The results indicated that the nurses who filled out the questionnaire do not always follow professional protocols and, in some cases, have incomplete knowledge on the subject. Based on the research findings, I formulated recommendations, mainly focusing on the necessity of further education for nurses and the utilization of modern technology to promote prevention, recognition, and treatment.]
[Who is the Person called Lector or the Value of Intellectual Work?]
[To dispell the general misconception that professional proofreading is a pretence activity necessarily associated with institutional accreditation only. This clarification is urgently needed as the scientific assessment of professional materials is a reviewer’s competence, but the evaluation process is currently not regulated.
The structured interview method was adopted in the empirical research using a descriptive statistical approach. Data were collected via phone, the proofreading fee were determined using the remuneration nomenclatures compiled by publishers and translation agencies. A written and a project worksheet were adopted as data processing instruments.
The fee for proofreading without editing was HUF 106,658.4 using a multiplier of HUF 0.8/character. This reward raised to HUF 133,323 if a multiplier of HUF 1.0/character was adopted. These fees are in sharp contrast with HUF 10,000 currently offered to the author.
The scientific professional proofreading is seen as the basis of accreditation of all institutions. Therefore the proofreading services should meet stringent professional guidelines and quality standards involving the proper compensation for lectors’ work..]
[Physical activity and exercise in chronic kidney disease. Walk, run, dance, play. Move what you can!]
[The link between regular physical activity and reduced cardiovascular risk in the general population is clear and has been proven by numerous studies. However, the studies available to date on this topic in patients with kidney disease have shown conflicting results, although physical activity in this patient group also has beneficial effects on blood pressure reduction, quality of life, muscle strength, physical fitness and performance. It is important to emphasise that even a minimal increase in physical activity has a positive effect, but international quidelines recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (e.g. cycling or walking) per week for both haemodialysis and non-dialysis kidney patients. For dialysis patients, in addition to exercise on dialysis-free days, intradialytic exercise may also play an important role. Healthcare staff involved in the care of chronic kidney failure patients plays a crucial role in increasing physical activity among kidney patients by appropriate patient education.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.