The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Specialities
Gastroenterology
[Sumatriptan-naproxen sodium fix-dose combination for acute migraine treatment, a review]
[Migraine as a common primary headache disorder has a significant negative effect on quality of life of the patients. Its pharmacotreatment includes acute and preventative therapies. Based on the shared therapeutic guideline of the European Headache Federation and the European Academy of Neurology for acute migraine treatment a combination of triptans and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is recommended for acute migraine treatment in triptan-nonresponders. In this short review we summarized the results of the randomized controlled clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness and safety of sumatriptan (85 mg)/naproxen sodium (500 mg) fix-dose combination. It was revealed that the fix-dose combination was better than placebo for the primary outcomes of exemption of pain and headache relief at 2 hours. Furthermore the combination showed beneficial effect on accompanying symptoms of migraine attack (i.e. nausea, photo- and phonophobia). Adverse events were mild or moderate in severity and rarely led to withdrawal of the drug.
It can be concluded that sumatriptan (85 mg)/naproxen sodium (500 mg) fix-dose combination is effective, safe and well-tolerated in the acute treatment of migraine. ]
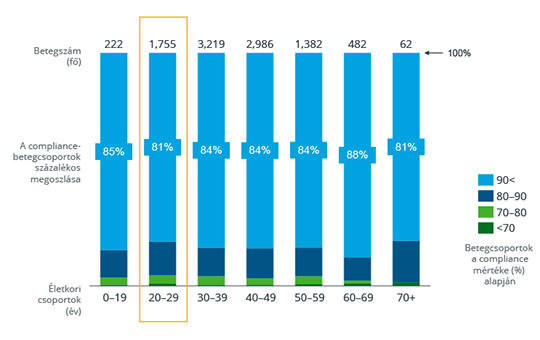
[Assessment of compliance and patient pathway among multiple sclerosis patients on disease modifying treatment]
[Epidemiological data and the number of patients treated suggest that the proportion of Hungarian patients with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) receiving disease-modifying therapy (DMT) is lower than in some neighboring countries. We investigated possible reasons for this.
First we analysed patient compliance based on an anonymised database of the National Health Insurance Fund (NHIF). A total of 5441 patients were included in the analysis from NHIF prescription data from 1 July 2014 to 28 February 2021. In the second part of the study, a quantitative and qualitative assessment of patient journeys of MS patients was conducted.
The compliance of Hungarian MS patients is good compared to international MS treatment data and outstanding compared to other neurological and other diseases, e.g. cardiovascular. This cannot be said about the results of the patient pathway analysis based on patient interviews. Patients indicated that they often have difficulty accessing public health care. Tracing their pathways revealed that they needed to see 3-5 doctors (general practitioner, various specialists) before a diagnosis was made. However, they gave positive feedback about MS Centres. They trusted their doctors, found them empathetic, but they would have liked more time to discuss lifestyle issues.
Compared to some neighbouring countries, Hungary has a lower proportion of patients with treated MS, which, given the good compliance of patients, highlights the problem of patient path in Hungary. Further training of fellow physicians is also a task for neurologists specialising in MS. Just as the most common symptoms of stroke have been successfully introduced into the public consciousness, the same can be the aim for MS.]
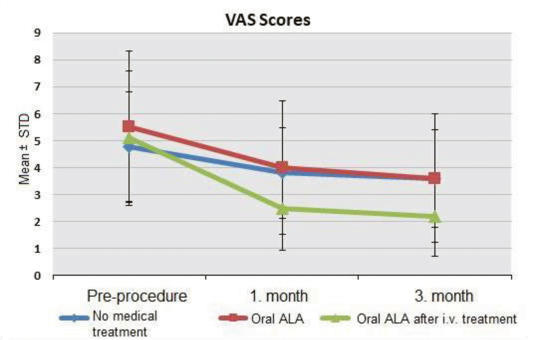
Efficacy of intravenous alpha lipoic acid in the treatment of neuropatic pain due to carpal tunnel syndrome
In this study, we analyzed the effect of oral and oral + intravenous Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) treatment on pain level and physical examination findings in patients diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). A total of 115 patients patricipated in the study. 40 patients were treated with oral ALA after iv. ALA the¬rapy, 35 patients received only oral ALA treatment and 40 patients did not receive any medication.
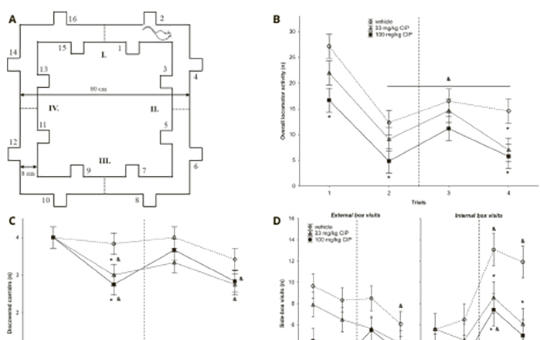
Neurobehavioral impairments in ciprofloxacin- treated osteoarthritic adult rats
Ciprofloxacin (CIP) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic widely used in clinical practice to treat musculoskeletal infections. Fluoroquinolone-induced neurotoxic adverse events have been reported in a few case reports, all the preclinical studies on its neuropsychiatric side effects involved only healthy animals. This study firstly investigated the behavioral effects of CIP in an osteoarthritis rat model with joint destruction and pain.
Prognostic value of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase-1 expression in glial tumors
Gliomas are the most common primary malignant central nervous system tumors in adults, exhibiting a poor prognosis. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase-1 has important functions in cancer immunotherapy due to its role in escaping cancer cells from the immune system. In this study we purposed to evaluate the correlation between IDO-1 expression and clinicopathological parameters in gliomas, and whether IDO-1 can be a prognostic marker.
[The practice of periprocedural anticoagulation – birth of a local consensus]
[The problem of periprocedural anticoagulation is emerging more and more frequently in the day-to-day patient care. There is fundamental the interdisciplinary approach spanning the borders of different specialties by establishing the “anticoagulant team” including specialists as cardiologist, anesthesiologist and surgical experts for hands-on interventions (surgeon, traumatologist, obstetrician, endoscopic specialist etc.) and even the GPs as well. Such a communication can help considerably in the patient management and it would be useful to define local protocols and consensus papers adapted for the concerning hospitals. This review provides an overview of the points of considerations, the proposed practice of interruption and re-administration of oral anticuagulants, and the treatment of bleedings. ]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.