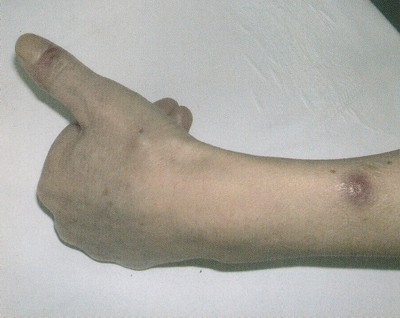
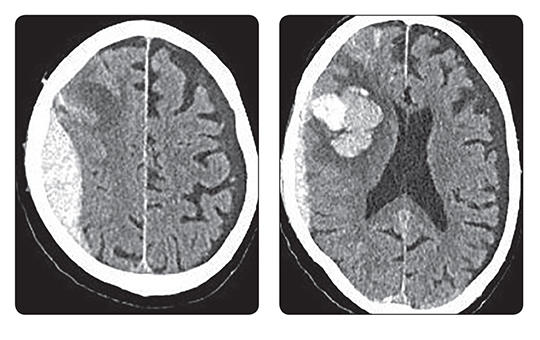
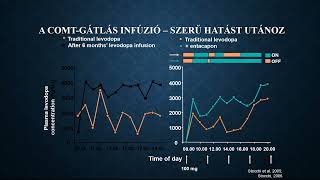
Az egészségügyi dolgozók alig várták az áprilisi fizetésüket, ám minden második munkavállaló csalódott. Pedig sokan ettől tették függővé maradásukat. Folyamatosan érkeznek a panaszok.
Az eLitMed.hu orvostudományi portál a böngészés tökéletesítése érdekében cookie-kat használ.
Ha bővebb információkat szeretne kapni a cookie-k használatáról és arról, hogyan módosíthatja a beállításokat, kattintson ide: Tájékoztató az eLitMed.hu Cookie-használatáról.