The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2004;14(11)
Content
[CHARACTERISTICS OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES]
[In the article the author reviews some features of autoimmune diseases and defines autoimmunity and autoimmune disease. According to epidemiological data, the number of patients increases and the causes are discussed in this paper. The pathogenetical background, the characteristics of the loss of immunetolerance are detailed. The author deals with the features of the pathomechanism, the course of the diseases and with the problems of the progression and classification. He also presents the expectations of clinicians to molecular medicine.]
[LIPID-LOWERING THERAPY BASED ON RISK ASSESSMENT]
[The authors’ brief review follows the changes made to therapeutic guidelines based on primary and secondary prevention trials. They describe the main characteristics of National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel-I (NCEP ATP-I), ATP-II and ATP-III, and the decisions of the Hungarian Consensus Conference with respect to the lowering of lipids. The authors highlight the clinical importance of the evaluation of cardiovascular risk factors before the commencement of lipid-lowering therapy. They emphasize the significance of achieving the target values for low-density lipoprotein. Current dyslipidemia treatment guidelines focus on determining coronary heart disease risk status and matching the intensity of plasma LDL-C reduction to that perceived risk. Adding plasma C-reactive protein measurement to current risk assessment techniques may improve the identification of patients in the primary prevention population who may require more aggressive lipid-lowering therapy.]
[THE ROLE OF ORAL ANTIDIABETIC AGENTS AND ACE INHIBITORS IN THE PREVENTION OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS]
[Nowadays Type 2 diabetes is considered as a cardiovascular disease,. The cause of death among 80% of people with Type 2 diabetes is of cardiovascular origin, with the most common cause of death of myocardial infarction. Optimal solution would be the prevention of the disease and there are also some possibilities for intervention. The present paper summarises the role of antidiabetic agents and ACE inhibitors in the prevention of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. The incidence rate of Type 2 diabetes decreased by 36% using acarbose in the STOP NIDDM Trial and by 31% using metformin in the Diabetes Prevention Program. The rate of risk reduction regarding the incidence of Type 2 diabetes during the ALLHAT Study compared the subjects treated with thiazid diuretics among those treated with amlodipine was 25% by the end of the second year and 16% by the end of the fourth year, while the corresponding data for patients treated with lisinopril were 40% and 30%, respectively. The action of lisinopril on the better bioavailability of Insulin like growth factor I. (IGF-I) probably contributes to the beneficial effect of lisinopril on insulin sensitivity.]
[DIVERTICULOSIS, DIVERTICULITIS - SYMPTOMS, DIAGNOSTICS AND TREATMENT]
[Diverticulosis of the colon is frequent in developed countries. Decreased intake of dietary fibre have been implicated as an important pathogenetic factor. Most of the affected patients are asymptomatic but 10-20% of them have abdominal problems. Clinical manifestations range from simple, non-complicated form (abdominal pain, distension, constipation, urgency etc.) to severe complications (diverticulitis, abscess, peritonitis, perforation, haemorrhage etc.) The diagnosis and therapy of different forms of diverticular disease can be very simple but in several cases differential diagnostical problems and therapeutical difficulties may arise. The gold standard for establishment of uncomplicated diverticulosis is the barium enema or colonoscopy. In case of complicated forms non-invasive methods (US, CT scan, CT-colonography, MRI) have to be preferred. These examinations have no risk for perforation and extraintestinal pathology (air, fluid, abscess) can be detected. Colonoscopy or angiography are the methods of choice in case of haematochesia. The choice of therapy is based on clinical presentation, symptoms and pathology. Fibre supplementation is recommended for patients with diverticulosis without symptoms. In case of noncomplicated symptomatic diverticular disease fiber supplementation or cyclic administration of broad spectrum, poorly absorbable antibiotic can be effective in the prevention of inflammatory episodes and complications. If some of the severe or recurrent complications can not be treated conservatively, surgery is necessary. Prevention of diverticulosis and diverticular disease has to be emphasized. While fibre supplementation in the diet is recommended, other efficacious preventive strategies remain to be identified.]
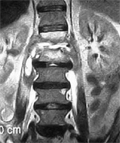
[MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN MUSCULOSKELETAL DIAGNOSTICS]
[The aim of the author is present a practical MRI guideline for partners clinicians working in general or specialist patient care related to musculoskeletal diseases. The evidence based diagnostic decision-making process requires specific and realistic expectations related to MRI in daily practice. The focus message of the article is that the more exact and specific clinical question arrives, the more accurate and precise answer of the radiologist is achieved. The importance of detailed clinical information based optimal planning is emphasized versus “general” studies based on poor clinical information. It is not less important for the referring physician to prepare and inform the patient prior to the MRI study, with the exclusion criteria and contrast agent application all explained. Very few technical details are presented, only as little as possible to understand the clinically relevant properties of the imaging process.]
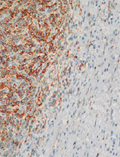
[BENIGN SOLITER FIBROTIC TUMOR OF THE PLEURA - A CASE REPORT]
[INTRODUCTION - Rare asymptomatic pleuropulmonary neoplasms can represent serious differencial diagnostic difficulties both for clinicans and pathologists. Immunohistochemical tests are essential tools for the diagnosis of soliter fibrotic tumor of the pleura. These tests are also of diagnostic and prognostic importance. CASE REPORT - The report summarizes the case of an asymptomatic 63 years old man. The patient was admitted to hospital with a parahilar infiltrate of the right lung. Based on this chest X-ray abnormality pulmonary malignancy was suspected. The patient was referred to surgical intervention and the diagnosis of was based on post-surgical histology. These fibrotic tumors have typical immunohistochemical features. Although the histomorphology of the tumor suggested the presence of a benign tumor the p53 positivity and focal CD34 positivity indicated the possibility of malignant transformation as well. The patient is alive 17 months after surgery and there is no relapse of the disease. CONCLUSION - Although histologically benign, soliter fibrotic tumors of the pleura may occasionally transform into malignant variants. Therefore complete surgical resection and longterm clinical and close radiological follow-up is recommended for these patients. Clinician can plan well ahead the frequency and time of the follow-up with the help of the prognostic factors of hystology.]
[PHYSICAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL CONDITION OF HEALTH CARE WORKERS DEALING WITH THE SERIOUSLY ILL]
[INTRODUCTION - Health care professionals undertaking treatment/nursing of the seriously ill are equally overburdened emotionally, intellectually and physically. This condition might have several, sometimes irreversible negative consequences: avowed difficulties within the communication with patients, families and colleagues, various harms of accumulating, unprocessed stress, severe physical and psychological symptoms of mental burn-out which is very frequent and failures and difficulties of the private life. In our survey we aimed to gain a realistic image of the physical and psychological condition and quality of life of professionals working in Hungarian clinical care in order to provide with indelayable help. METHODS - The basis of the survey was a version of the Hungarostudy 2002 questionnaire, modified for health care professionals. In our sample there were 200 health care professionals dealing with seriously ill and in the control groups 1356 non health care professionals, and 227 health care professionals, choosen from the Hungarostudy survey. In all three groups the proportion of gender, age and education were the same. The results were analysed by the SPSS 10.0 statistical program and the relationship analysis was completed by ANOVA test. RESULTS - The analysis of the answers of those attending in our questionnaire survey - compared to those working in other health care field and to the control group of non health care workers - proves that the ratio of exhaustion and stress-dependent physical and psychological symptoms are prominently, in many cases significantly higher among health care workers dealing with the seriously ill, addiction is more frequent and social net is more unfavourable. These data are even worse for nurses than for doctors and other graduates. CONCLUSION - In treating difficult cases we can start to help with special education that should be general both in gradual and postgradual training.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.