The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
LAM Extra for General Practicioners - 2015;7(01)
Content
[Alzheimer’s disease and arrhythmia: cause, effect, complication]
[Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a new endemic of the 21st century which becomes the biggest health and social problem of the ageing societies in the next few decades. Vascular factors, such as cardiac arrhythmias, especially atrial fibrillation, play an important role in the pathogenesis of AD. Arrhythmias might develop as a consequence of AD, too, and they might be caused by the cholinergic medications used in the treatment of AD. In addition, AD has a major influence on the treatment of arrhythmias, especially atrial fibrillation. Because of these, AD and arrhythmias might accompany each other in the practice of several medical specialties; these interactions are reviewed in this paper. ]
[Treatment of hepatits C virus infected patients with cirrhosis in real-life conditions in Hungary with the two pegylated interferons]
[AIMS - In this trial we have analyzed the data of cirrhotic naiv as well as treatment experienced patients with chronic hepatitis C, treated in the East-Hungarian hepatology centers, between 2004 and 2010, because in the era of triple combinations, we mostly treat cirrhotic patients. PATIENTS AND METHODS - We have found 272 patients and in most of them the cirrhosis was proven by biopsy. These patients were treated with pegylated interferon (pegIFN) alpha plus ribavirin in combination, 172 were naiv and 100 patients were treatment experienced. Data were collected retrospectively and the pretreatment parameters like age, sex, body weight, transaminase level, genotype, initial viral load, comorbidities, and proportion of first and repeated treatments have been analyzed. We have investigated the influence of the initial parameters as well as the type of pegIFN on the complete early virologic response (cEVR) and on the sustained virological response (SVR). RESULTS - The cEVR was 27% (74/272) and the SVR was 21% (58/272) in the whole patient population. With pegIFN a-2a, 32% (45/141) cEVR and 28% (39/141) SVR, whereas with pegIFN a-2b 22% (29/131) cEVR and 15% (19/131) SVR were achieved. Among this patient population the largest subgroup was the naiv patients with high viral load (HVL). In this subgroup the SVR was 21% (28/132). However, with pegIFN a-2a SVR was 29% (21/73), whereas with pegIFN a-2b SVR was only 12% (7/59). The above differences found between the two pegIFNs proved to be statistically significant. Age <40 years, low viral load (LVL) and treatment with pegIFN a-2a proved to be independent positive factors influencing cEVR as well as SVR, by multiple logistic regression analysis. CONCLUSION - According to these results, cirrhotic patients with hepatitis C may benefit if pegIFN a-2a is used as backbone therapy in triple combinations. ]
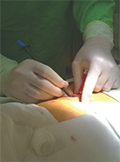
[Insertion of percutaneous peritoneal dialysis catheter using Seldinger technic with assistance of image amplifier ]
[INTRODUCTION - Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) treatment is widespread used over the years as a result of technical progress. As with any renal replacement therapy, in hemodialysis patients in time made vascular access, also the success of the CAPD depends on the in time inserted catheter for peritoneal dialysis. PATIENTS AND METHOD - Inserting a catheter for chronic peritoneal dialysis in Hungary is currently exclusively surgical procedure. The successfully CAPD treatment is so essential to insert the peritoneal dialysis catheter by dedicated surgeon. The intervention is often not a priority in the surgical tender, and in many places queues delaying the surgery. Proposed as an alternative to the percutaneous technique introduction. If nephrologist are familiar with basic surgical procedures by providing appropriate means, the percutaneous catheter insertion technique can be performed. RESULTS - In the spring of 2014, we introduced in Hungary first this procedure, which reported in the international literature as percutaneous PD-catheter insertion method. The technique was modified to the primary entry point determined by the typical abdominal puncture site. Puncture of the abdomen is performed by physicians as a routine intervention, which is widely accepted. After selecting the appropriate patient population and detailed medical information, patients are prepeared, under x-ray fluoroscopy imaging the implants were made. So far 10 catheter were implanted under this technique, all of them successfully. Thanks to the minimal invasive intervention, the patients healing was significantly faster, after the day of catheter-insertion we were able to start drainage. By the traditional surgical implantation the recovery time is six weeks. CONCLUsiONS - In all cases, when a surgeon not willing to insert the peritoneal dialysis catheter, the percutaneous technique can be safe. All of the catheters made by us are working well. Of course, the surgical procedure is still indispensable, however, and this is the percutaneous technique’s advantage, the CAPD treatment can be started after the intervention. ]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.